How to Implement Cloud-Native Recording
Last updated:2025-08-01 15:15:57
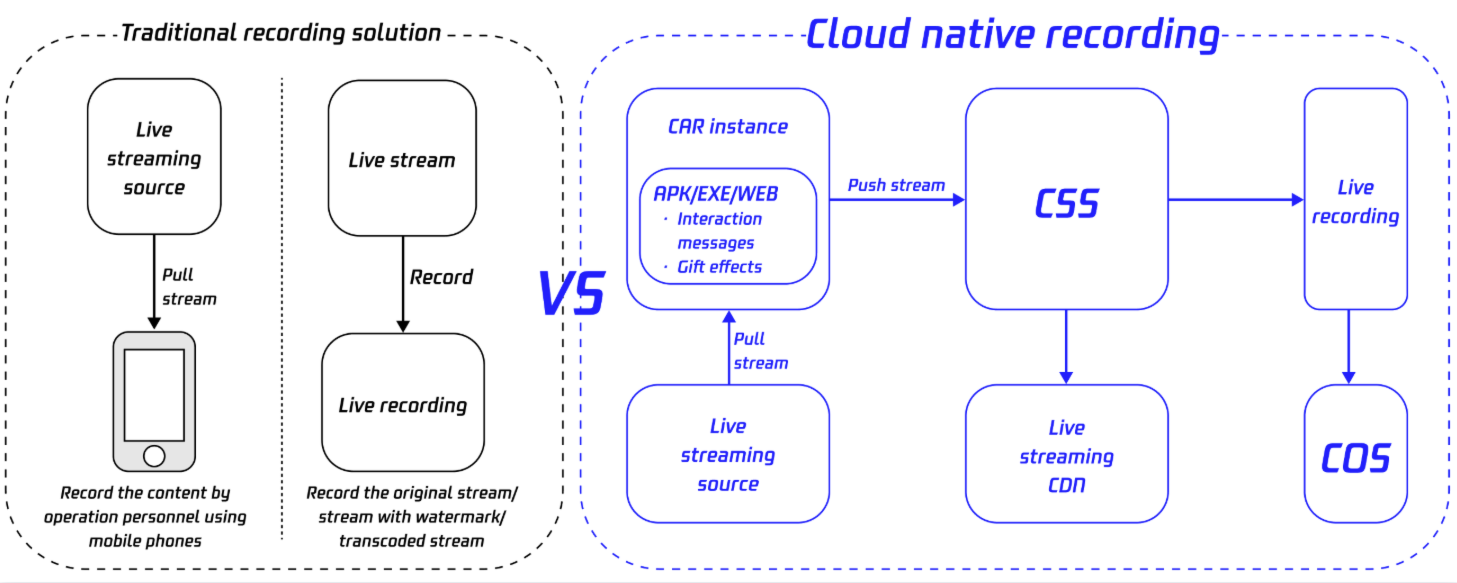
The cloud-native recording scheme powered by Cloud Application Rendering (CAR) is built on Cloud Streaming Services (CSS) and CAR. It migrates the local screen recording feature from the terminal to Windows CAR instances or Android containers, leveraging a virtualized terminal environment with integrated virtual GPU drivers and audio/video capture modules to achieve lossless screen content capture. Streaming and transcoding are completed using Tencent Real-Time Communication (TRTC) and CSS, with the final video files stored in either Video on Demand (VOD) or Cloud Object Storage (COS). This scheme breaks through the limitations of traditional stream recording by enabling complete, user-perspective capture, truly achieving "what you see is what gets recorded". It significantly reduces client-side development costs and simplifies maintenance. Additionally, it supports custom APK, EXE, and WEB clients, allowing advanced features to be implemented in the cloud. This effectively addresses the high development threshold and operational complexity of custom terminals, providing a highly available, low-latency cloud-native recording solution for scenarios such as Cloud App and Cloud Phone.
Applicable Scenario
Interactive Live Streaming/Voice Chat Room Scenarios
In response to the limitations of traditional recording in interactive live streaming and voice chat room scenarios, where only the clean stream is captured and audience interactions are not retained, the cloud-native recording scheme of CAR enables real-time, full-element capture through a virtualized terminal environment. It supports the synchronized recording of interactive elements such as live video, co-hosted audio, dynamic comments, and gift effects. By generating complete and immersive video files, the scheme delivers low-latency, millisecond-level on-cloud recording capabilities, making it ideal for scenarios such as sports event playback, UGC content repurposing, and compliance review. It redefines the standard for interactive live recording by truly achieving "what you see is what gets recorded".
Online Class Recording
In online education scenarios, traditional recording methods often struggle to fully replicate the interactive experience of an in-person classroom. The cloud-native recording scheme of CAR addresses this challenge by virtualizing the teaching terminal, enabling the synchronized recording of the entire instructional process, including the teacher's lecture, animated courseware, PPT presentations, as well as interactive activities such as online quizzes, polls, and whiteboard collaboration. The recorded teaching videos support knowledge sharing, secondary distribution, and learning outcome analysis, providing online education institutions with a full-linkage recording solution that spans content creation to performance assessment.
Application Page Recognition and Recording
In response to the limitations of traditional recording schemes for web and client-side applications, where audience interactions are not retained, the cloud-native recording scheme of CAR leverages a virtualized terminal environment to enable lossless audio and video capture. It supports complete recording of dynamic elements such as live comments, gift effects, and co-hosted audio. Integrated with the intelligent identification capabilities of Tencent Cloud Media Processing Service (MPS), the scheme can automatically extract on-screen text, voice content, and behavioral data from the audience's perspective to generate a structured content library. This scheme not only meets the needs of compliance review and secondary distribution but also supports scenario-based data analysis and user behavior prediction through integration with large language model (LLM) training APIs. The accumulation of recorded content under this scheme helps improve scenario conversion rates, making it a vital tool for content assetization in digital operations.
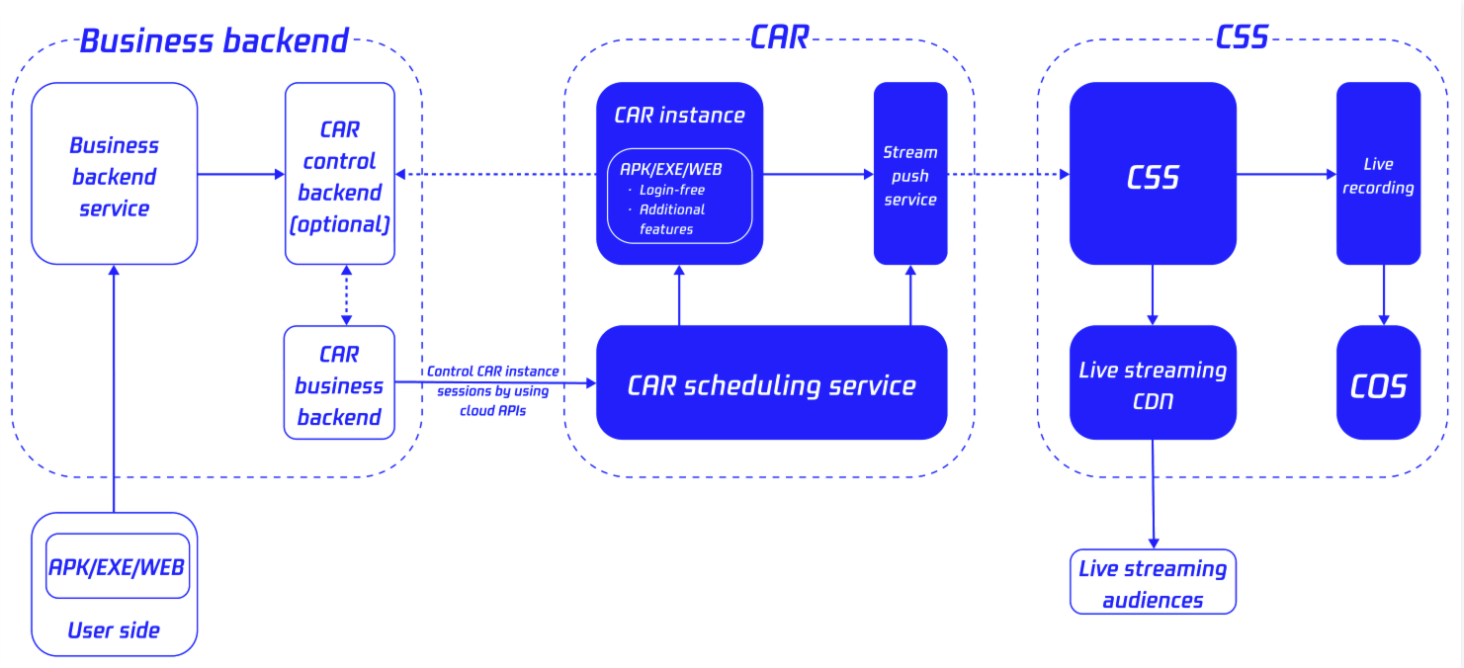
Architecture and Process
Cloud native recording uses APK/EXE/WEB content as the recorded content source to achieve a recording effect of "what you see is what you get". Users only need to start a cloud phone concurrency instance or a CAR instance, push the stream to CSS, and use the recording module to generate recording files. They can directly upload the files to VOD or COS or use them as the live streaming source to distribute the content to audiences.
Feature Strengths
Strengths | Description |
Wide range of applicable scenarios | It applies to scenarios such as interactive live streaming and voice chat rooms, online classrooms, and application screen identification. |
Excellent reproduction effect | In scenarios such as sports event playback, UGC content creation, and compliance review, all visual effects and external interactive elements can be captured, ensuring a fully accurate reproduction of the original experience. |
Low integration cost | Users do not need to integrate an SDK on the client side. Instead, APIs can be called directly from the business backend. |
Low transformation cost | APK, EXE, and WEB applications running in the cloud require minimal adaptation, as the original versions can be directly deployed. |
Powerful extended features | Cloud-based APK, EXE, and WEB applications can be customized to implement complex features that are not suitable for deployment on local terminals. |
Customer Cases
Requirement Background | A country-wide popular live streaming App needs to accumulate video content of interaction features such as "anchor PK" and "voice chat room" as UGC materials for secondary distribution. |
Original Solution | Operation personnel use mobile phones to manually record the screen content during live streaming. |
Pain Points | Only the anchor's perspective can be captured, without the ability to synchronously record audience-side elements such as cross-room co-hosting or animated comments. Rely on manual operations, resulting in low efficiency in content capture. In voice chat room scenarios, screen recording should be performed on mobile devices, making it impossible to accumulate content automatically and at scale. |
Current Solution | Use the cloud-native recording architecture of CAR to run customized, login-free Android containers in the cloud. Leverage a multi-stream composition engine to synchronously capture the main stream (anchor video), auxiliary stream (co-hosted audio), and overlay stream (animated comments). When the anchor starts streaming, the customer's backend automatically sends a message to the Cloud App, which then joins the specified room and starts playing the video upon receiving the signal. Leverage CSS recording capabilities to capture and store video content. |
Prerequisites
You have activated CSS and added a stream push domain name.
The CAR service has been enabled, along with the cloud-based streaming service, supporting both streaming to CSS and streaming to a specified address.
Directions
1. If the client is in EXE format, upload the EXE file in the CAR console. If it is a WEB browser-based client, there is no need to upload the browser; simply create and claim a WEB application in the CAR console. For APK-format clients, contact a Tencent business representative to be added to the allowlist so that the backend can enable the APK application creation feature.
2. See User Guide of CAR to create a project, purchase a CAR concurrency package, and test and release the project.
3. In CSS, go to record template, and choose to store in VOD or store in COS based on your needs. You can also push the stream to a designated address and record as needed according to your business scenario.
4. Call the StartPublishStream API to push the complete stream of the client in the CAR instance to CSS.
5. Start recording in the CSS console and save the complete stream of the client as a recording file. The live stream can be used for playback and distribution. Users can also use the intelligent identification feature of MPS to recognize content such as text and audio.
Fee Description
The client runs in a cloud instance, which will incur CAR concurrency fees.
Stream push to CSS will incur CSS upstream push fees. By default, only downstream playback fees are charged. For scenarios with imbalanced upstream and downstream traffic (downstream playback:upstream push < 10:1), additional stream push fees will be charged according to the actual stream push traffic if the daily peak stream push bandwidth is greater than 100 Mbps.
Using the live recording feature of CSS will incur live recording fees.
Recording and Storing to COS
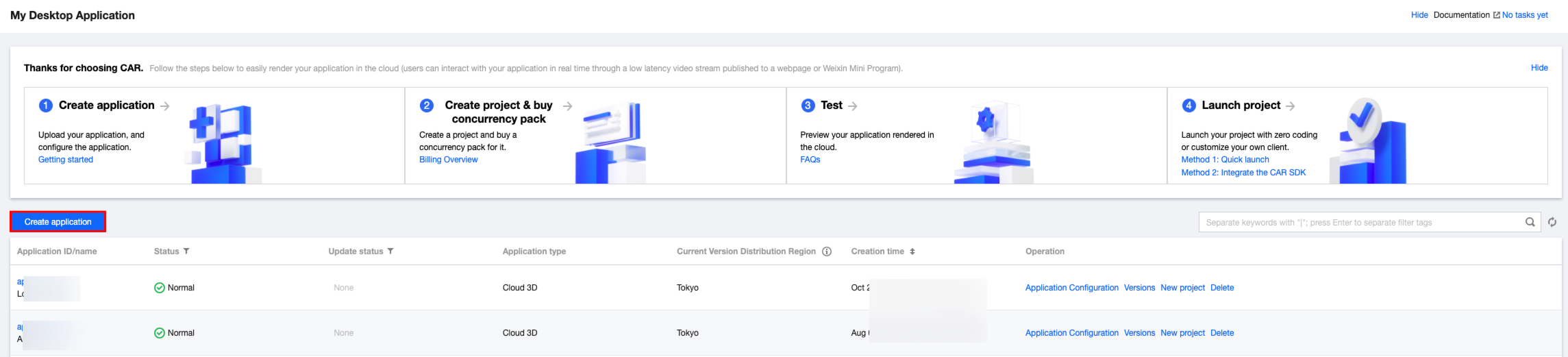
1. See CAR Quick Start to prepare your CAR APK, EXE, or WEB application. Create a project and purchase a CAR concurrency package. Taking the creation of a cloud WEB application as an example:
1.1 Go to the CAR console, click My Desktop Applications, and click Create Application.
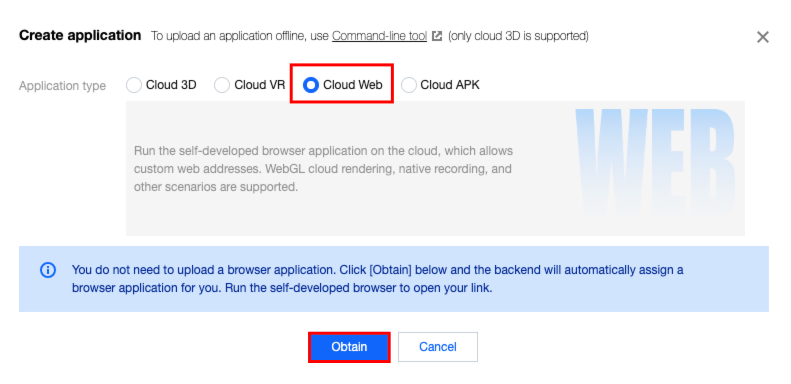
1.2 On the Create Application page, select Cloud Web, and click Obtain.
1.3 Go to the CAR console, choose Management Center > Project Management, and click Create a Project. On the New Application Project page, select the Associated Application and the desired Concurrency Specification, and then click Create Now.
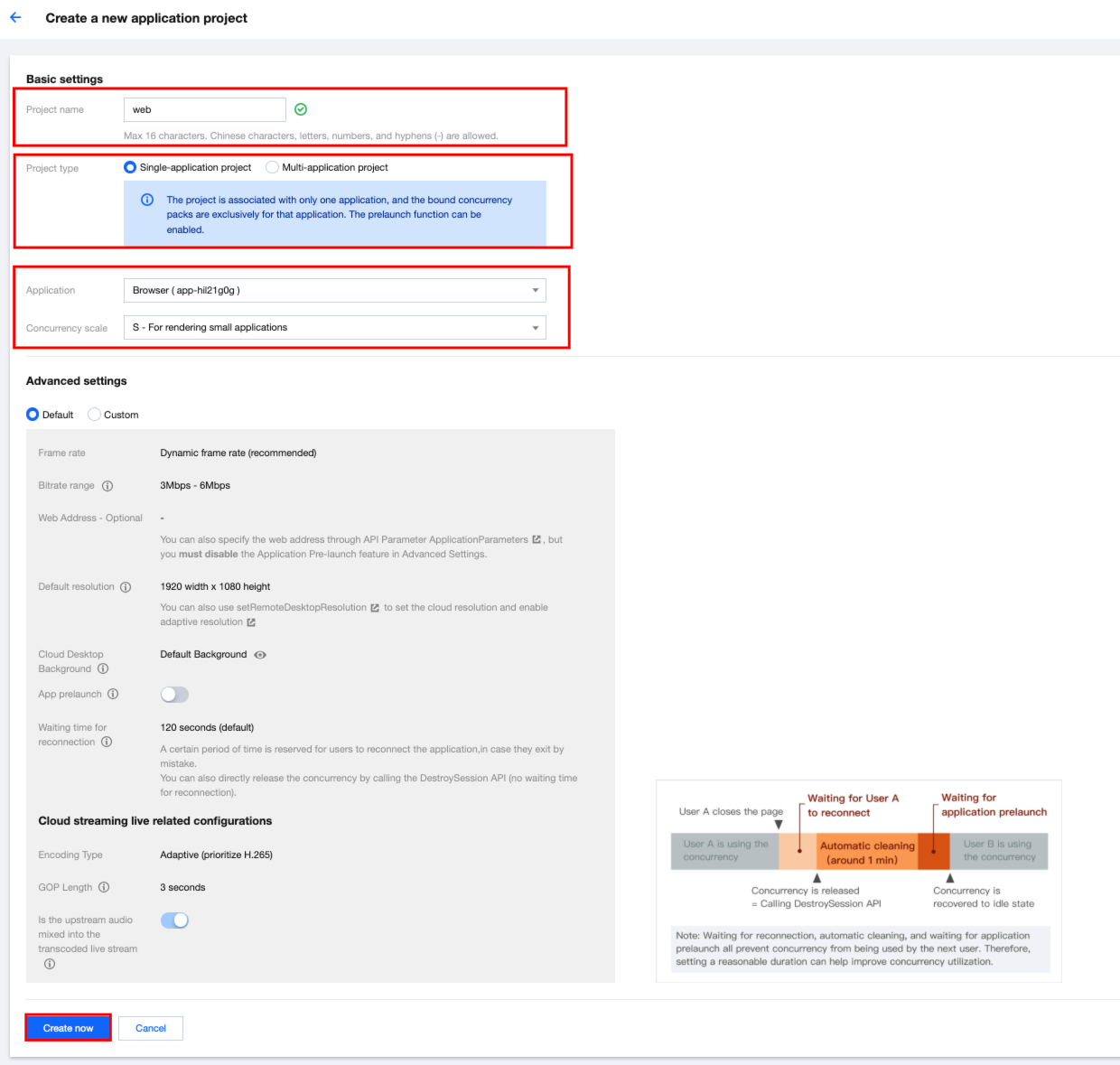
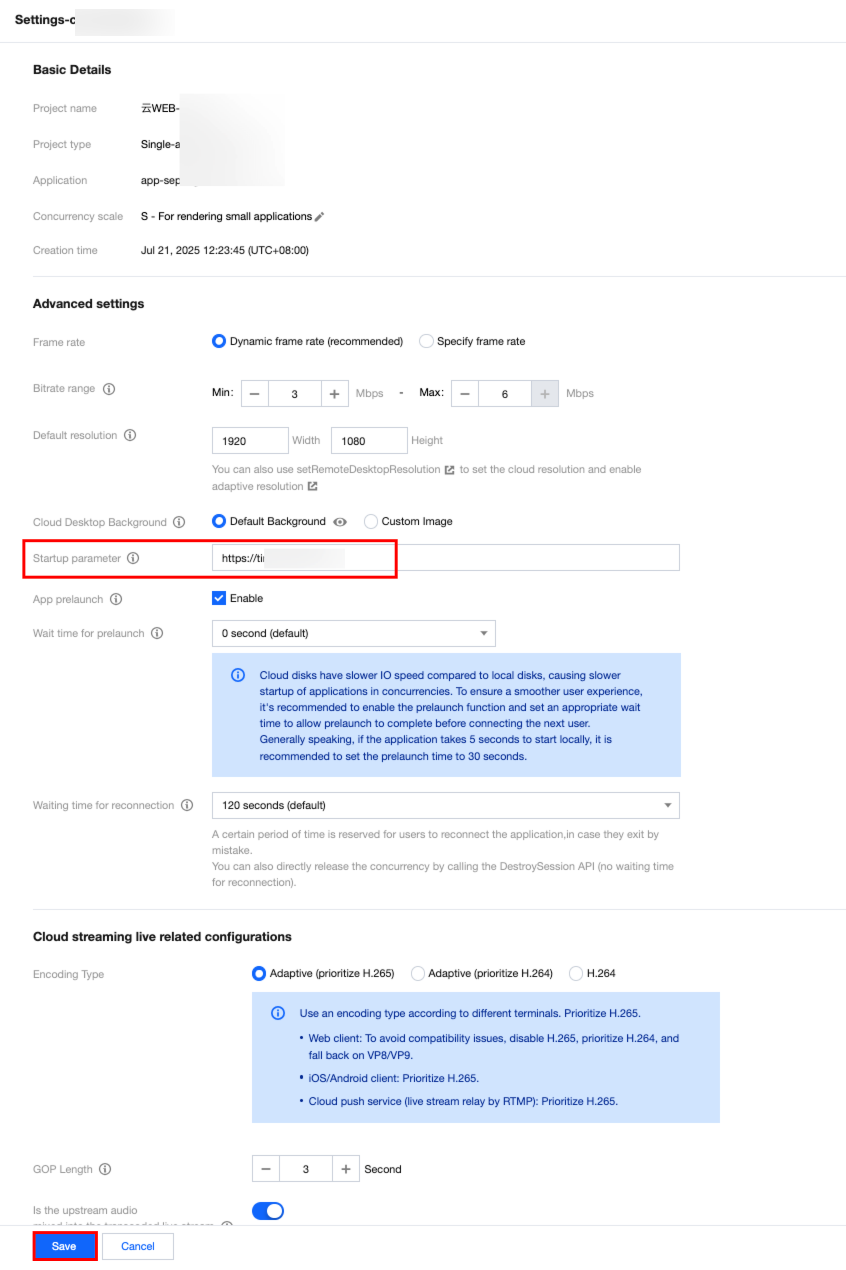
1.4 See Concurrency Pack to bind a concurrency package to the project, and then click Project Settings (for demonstration only; choose actual parameters based on your use case). Enter the web address and click Save.
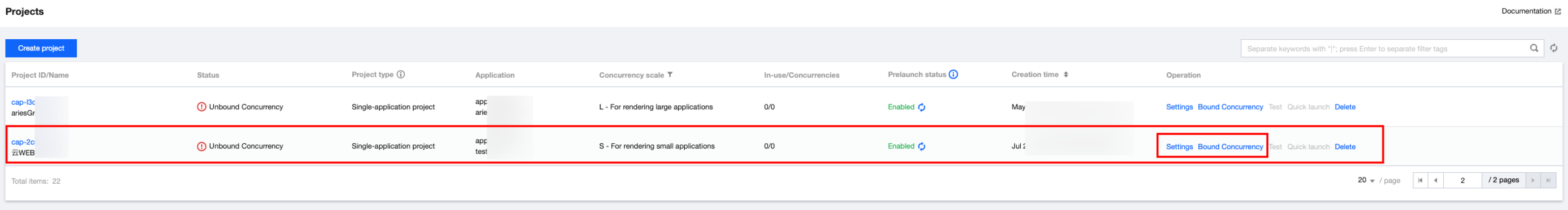
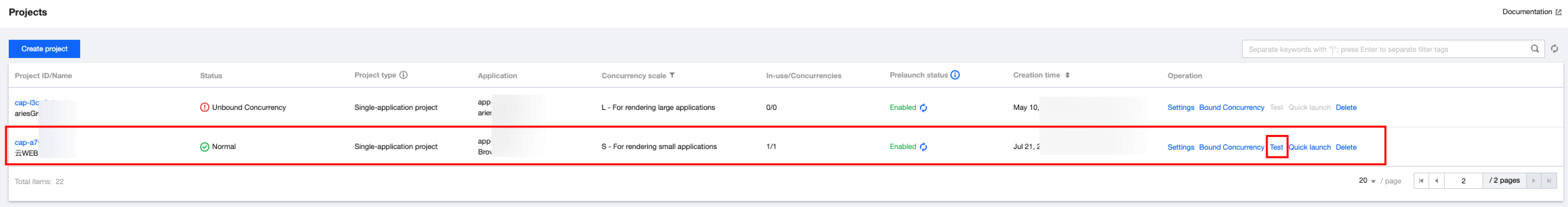
1.5 Click Effect test to ensure the content intended for streaming is displayed correctly.
2. Select store in COS to configure the template. You can create the recording template via the CSS console or through the API.
2.1 Go to the CSS console, choose feature configuration > live recording feature > store to COS, configure the relevant parameters as needed, and save the settings.
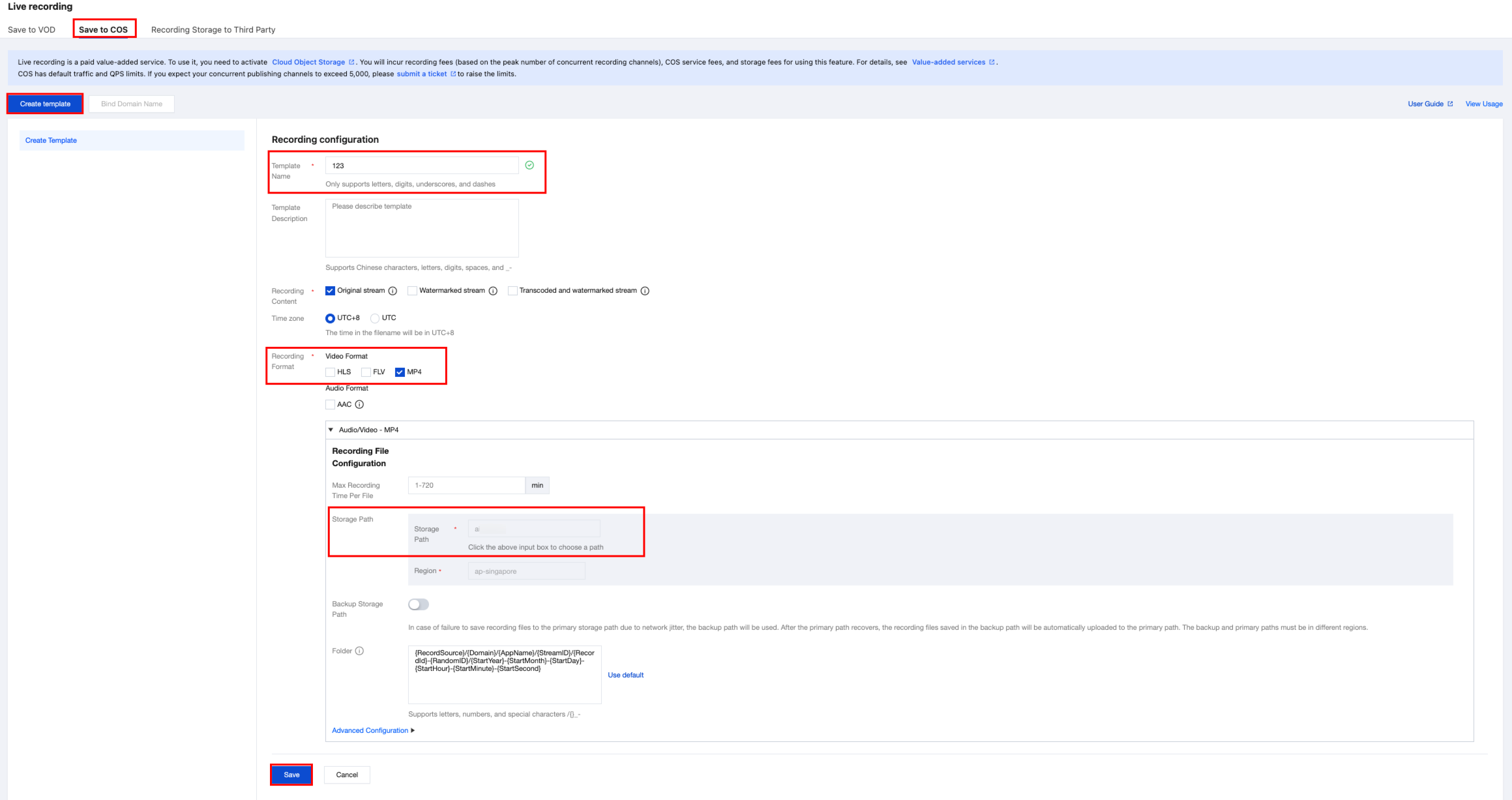
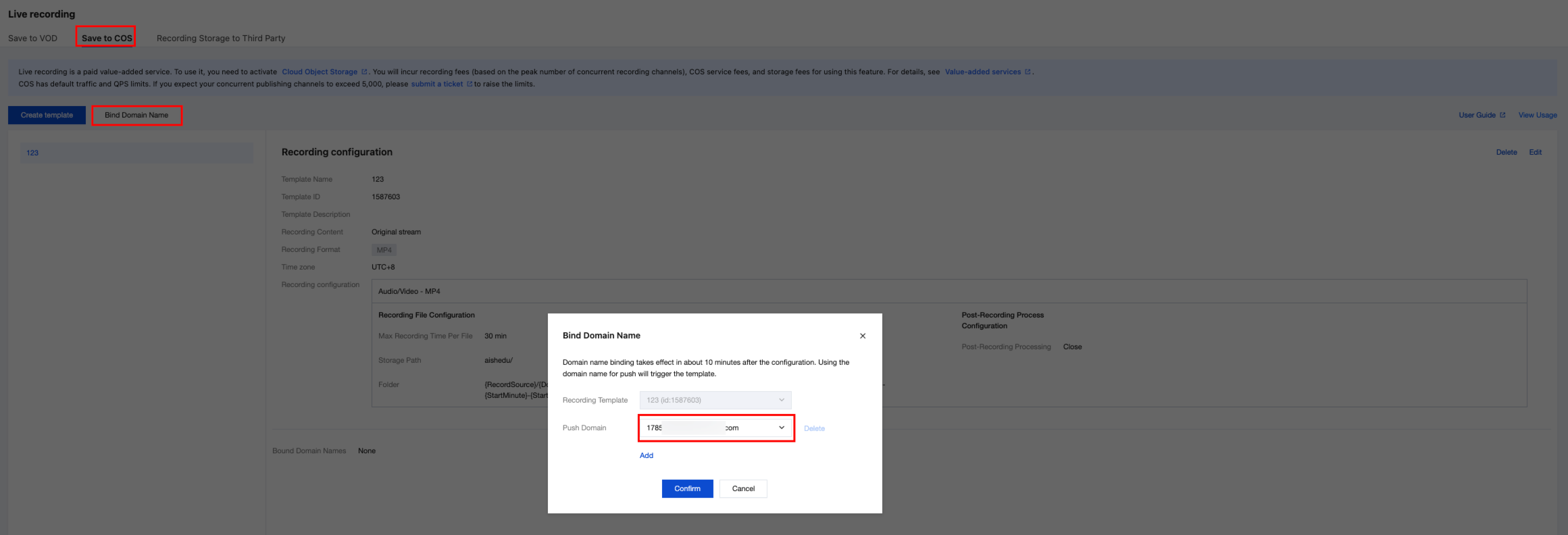
2.2 Bind a domain name to the template via Bind Domain Name. You can add your own domain name under the CSS console > domain name management. In this case, a test domain name is used.
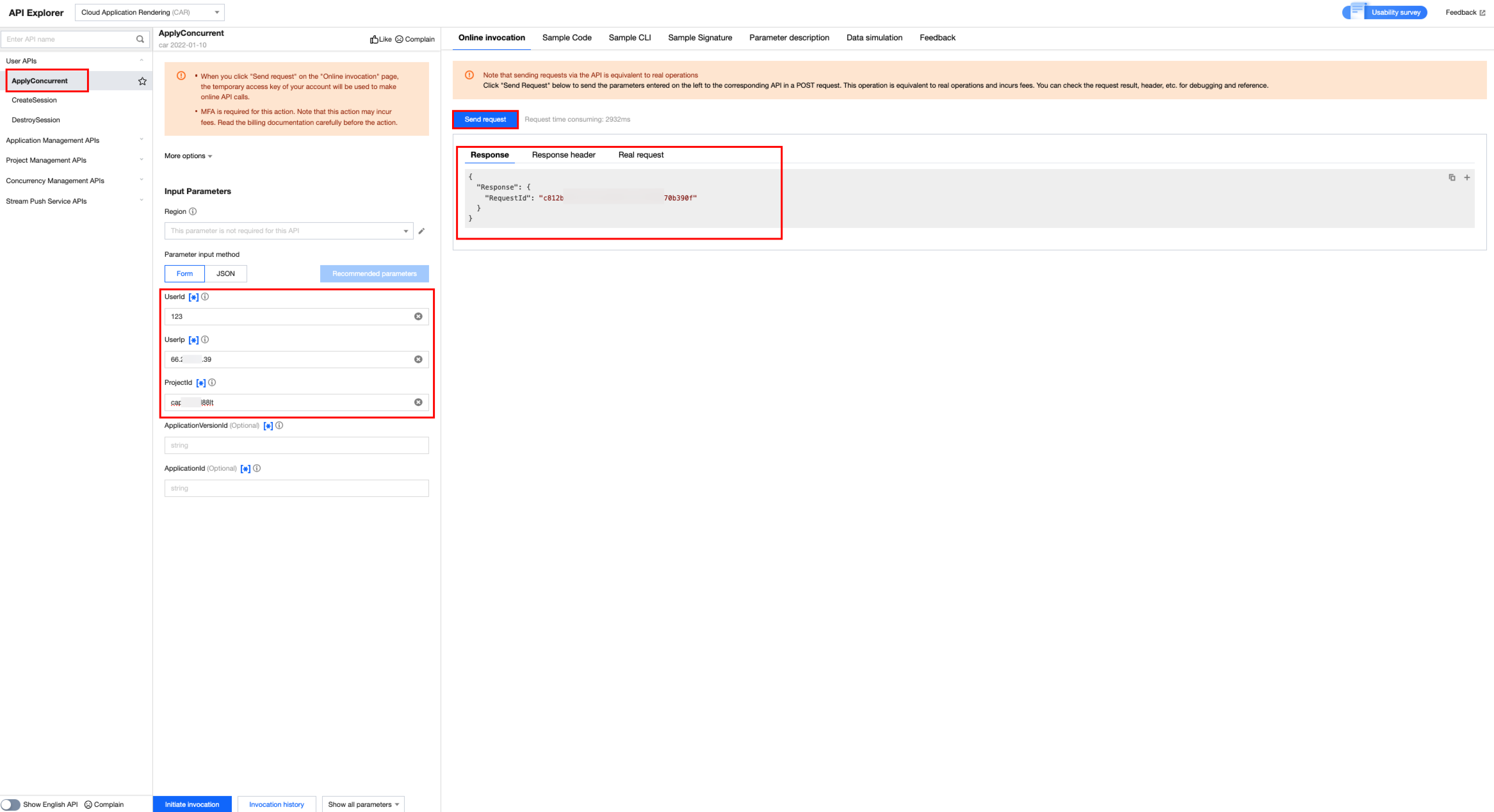
3. Use the API to request concurrency and create session to initiate cloud-based streaming.
Request concurrency (UserId: Ensure consistent naming throughout the process).
Create session.
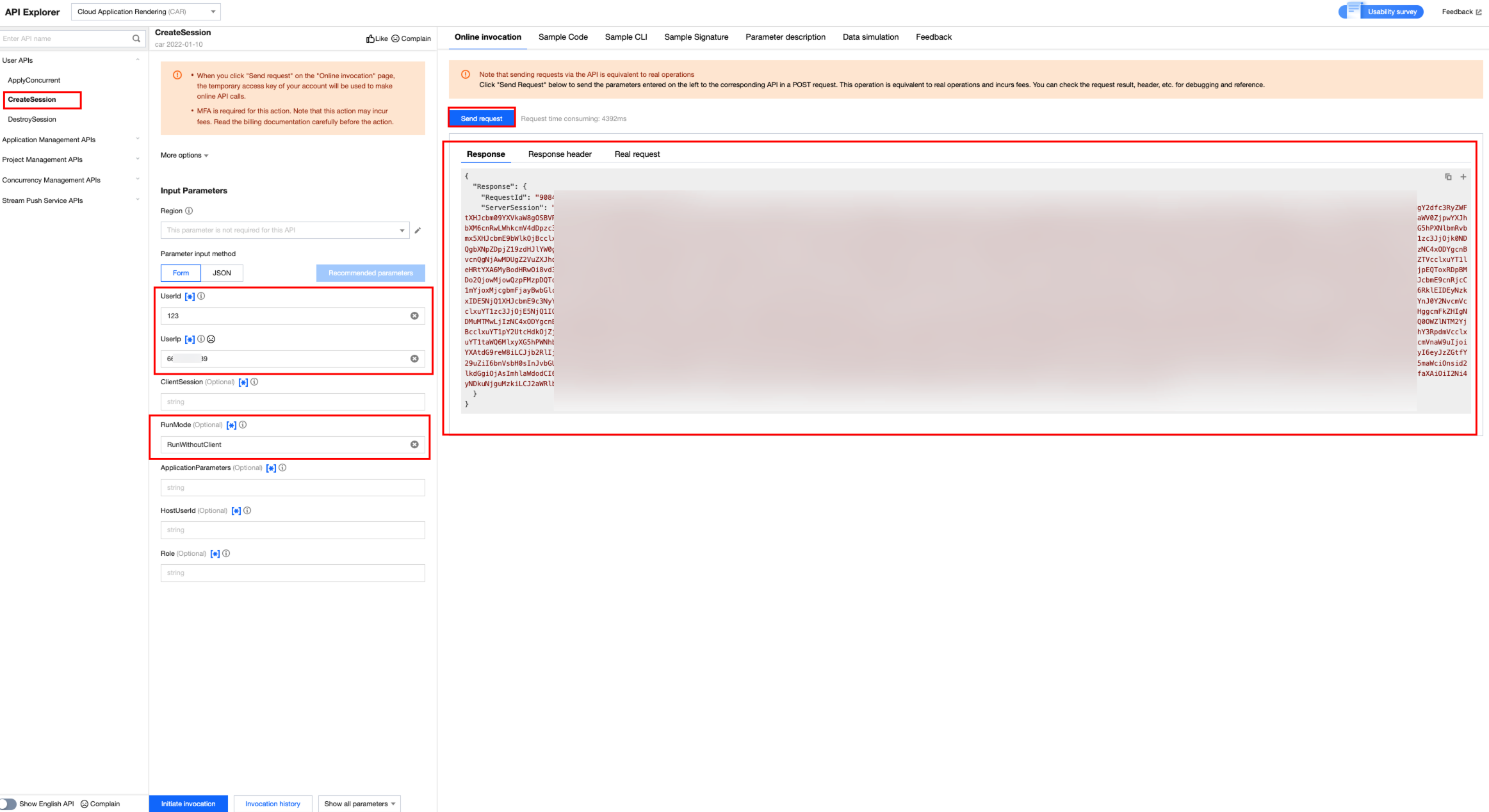
Start cloud-based streaming.
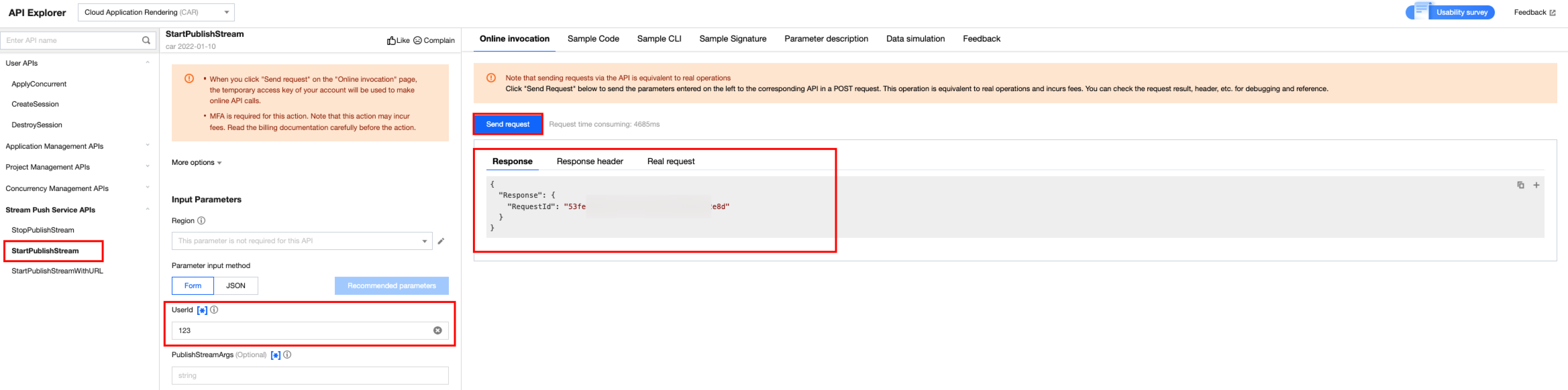
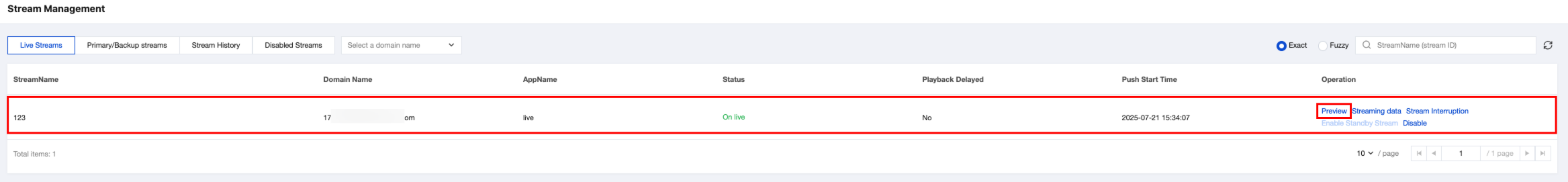
4. You can view the stream in real time and perform related operations under Stream Management in CSS.
In the CSS console, click Stream Management, and click Preview under the online stream to watch the real-time preview.
5. Use the API to stop cloud-based streaming and terminate the session.
Stop cloud-based streaming.
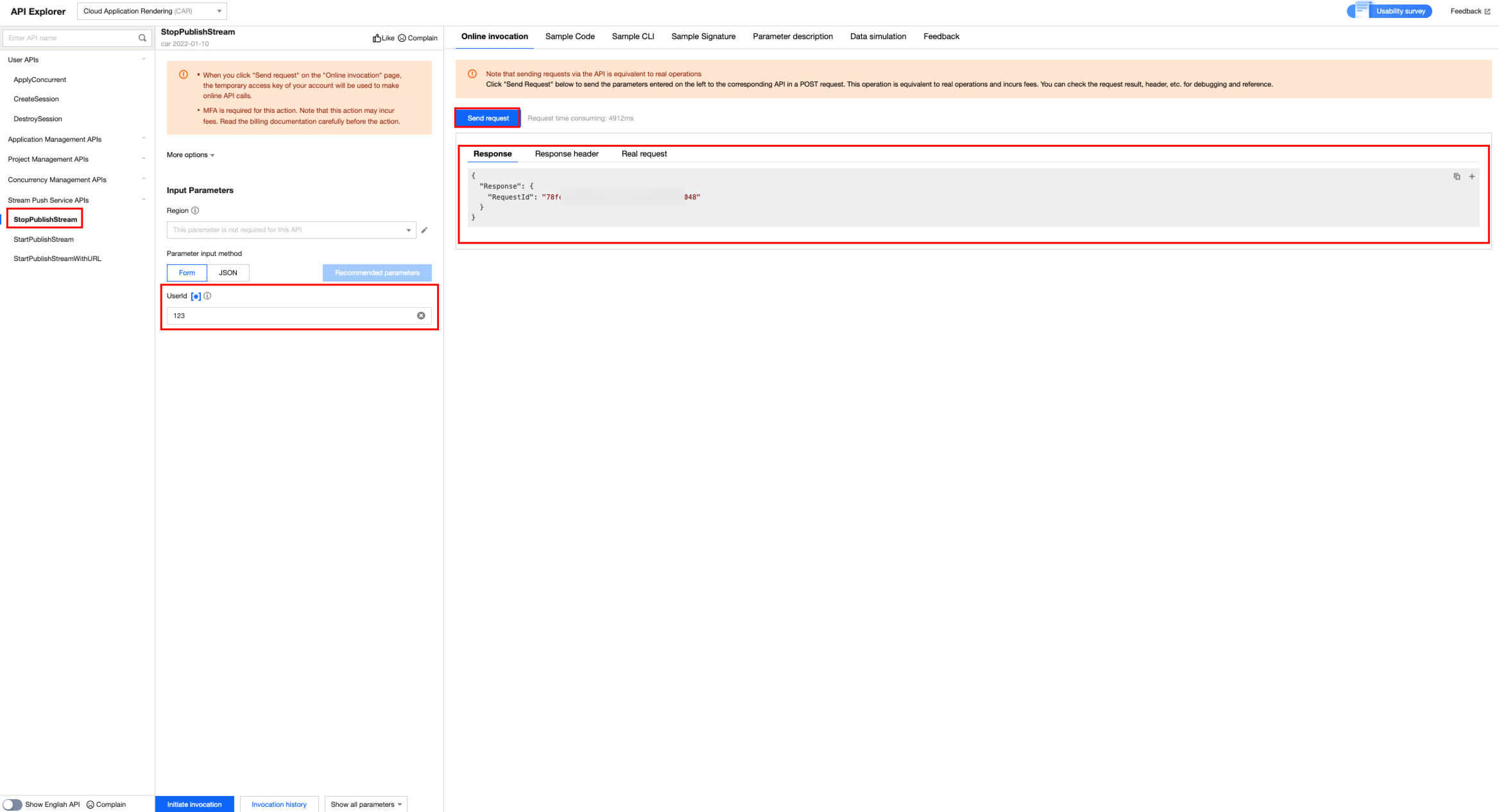
Terminate the session.
In Tencent Cloud Object Storage > bucket list, locate the storage path defined in the template settings and preview the recorded files.

Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

