Managing Existing Resource
Last updated:2024-12-02 16:01:33
Scenario
This document describes how to use Terraform to manage resources created in the Tencent Cloud console.
Directions
To take over an existing resource (for example, TencentDB for PostgreSQL alarm policy in this document) on Terraform, you only need to reflect its state in both the source and state files of Terraform.
Getting the resource ID
1. Log in to the Cloud Monitor console and select Alarm Configuration > Alarm Policy on the left sidebar.
2. Find and record the target policy ID as shown below: 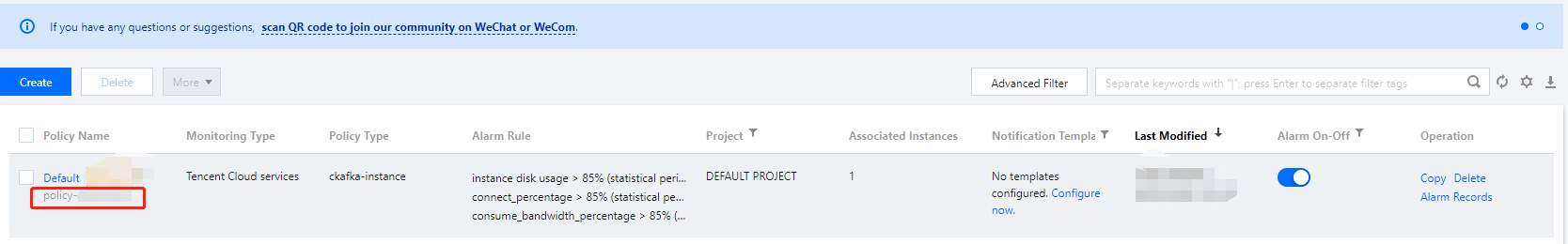

Importing the resource file
1. Go to the Terraform working directory and run the following command to view the
main.tf content.tencent-cloud cat main.tf
The following information will appear:
resource "tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy" "policy" {}
2. Run the following command in the directory where the file is located to complete the initialization.
terraform init --upgrade
The following information will appear:
Initializing the backend...Initializing provider plugins...- Finding latest version of tencentcloudstack/tencentcloud...- Installing tencentcloudstack/tencentcloud v1.60.22...- Installed tencentcloudstack/tencentcloud v1.60.22 (signed by a HashiCorp partner, key ID 84F69E1C1BECF459)Partner and community providers are signed by their developers.If you'd like to know more about provider signing, you can read about it here:https://www.terraform.io/docs/cli/plugins/signing.htmlTerraform has made some changes to the provider dependency selections recordedin the .terraform.lock.hcl file. Review those changes and commit them to yourversion control system if they represent changes you intended to make.Terraform has been successfully initialized!You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to seeany changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commandsshould now work.If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, othercommands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
3. After the initialization is completed, run the following command to import resources into the state file.
terraform import tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy policy-vor9w72r
The response is as follows:
➜ terraform import tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy policy-vor9w72rtencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy: Importing from ID "policy-vor9w72r"...tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy: Import prepared!Prepared tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy for importtencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy: Refreshing state... [id=policy-vor9w72r]Import successful!The resources that were imported are shown above. These resources are now inyour Terraform state and will henceforth be managed by Terraform.
4. Run the following command to view the state file.
cat terraform.tfstate
You can view the following resource information:
{"version": 4,"terraform_version": "1.1.0","serial": 1,"lineage": "35791a73-d371-db51-5871-bfee13426217","outputs": {},"resources": [{"mode": "managed","type": "tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy","name": "policy","provider": "provider[\\"registry.terraform.io/tencentcloudstack/tencentcloud\\"]","instances": [{"schema_version": 0,"attributes": {"conditions": [{"is_union_rule": 0,"rules": [{"continue_period": 5,"description": "cpu","filter": [],"is_power_notice": 0,"metric_name": "Cpu","notice_frequency": 86400,"operator": "gt","period": 60,"rule_type": "STATIC","unit": "%","value": "90"}]}],"conditon_template_id": null,"create_time": null,"enable": 1,"event_conditions": [{"continue_period": 0,"description": "HASwitch","filter": [],"is_power_notice": 0,"metric_name": "ha_switch","notice_frequency": 0,"operator": "","period": 0,"rule_type": "","unit": "","value": ""}],"id": "policy-vor9w72r","monitor_type": "MT_QCE","namespace": "POSTGRESQL","notice_ids": ["notice-l9ziyxw6"],"policy_name": "PgSql","project_id": 0,"remark": "","trigger_tasks": [],"update_time": null},"sensitive_attributes": [],"private": "eyJzY2hlbWFfdmVyc2lvbiI6IjAifQ=="}]}]}
Updating the source file
1. Run the following command to print the resource information.
terraform show
The response is as follows:
# tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy:resource "tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy" "policy" {enable = 1id = "policy-vor9w72r"monitor_type = "MT_QCE"namespace = "POSTGRESQL"notice_ids = ["notice-l9ziyxw6",]policy_name = "PgSql"project_id = 0conditions {is_union_rule = 0rules {continue_period = 5description = "cpu"is_power_notice = 0metric_name = "Cpu"notice_frequency = 86400operator = "gt"period = 60rule_type = "STATIC"unit = "%"value = "90"}}event_conditions {continue_period = 0description = "HASwitch"is_power_notice = 0metric_name = "ha_switch"notice_frequency = 0period = 0}}
2. Copy the resource code to the Terraform source file
tencentcloud.tf. You need to delete any options that cannot be set, such as ID. Below is the content of the edited tencentcloud.tf file:provider tencentcloud {}resource "tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy" "policy" {enable = 1# id = "policy-vor9w72r"monitor_type = "MT_QCE"namespace = "POSTGRESQL"notice_ids = ["notice-l9ziyxw6",]policy_name = "PgSql"project_id = 0conditions {is_union_rule = 0rules {continue_period = 5description = "cpu"is_power_notice = 0metric_name = "Cpu"notice_frequency = 86400operator = "gt"period = 60rule_type = "STATIC"unit = "%"value = "90"}}event_conditions {continue_period = 0description = "HASwitch"is_power_notice = 0metric_name = "ha_switch"notice_frequency = 0period = 0}}
Verification
Run the following command for a refresh using the code and state file in the current working directory.
terraform plan
The following information is returned, showing that the resource has been successfully taken over by Terraform.
tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy: Refreshing state... [id=policy-vor9w72r]No changes. Your infrastructure matches the configuration.Terraform has compared your real infrastructure against your configuration and found no differences, so no changes are needed.
At this point, Terraform has taken over the resource. You can delete it with the
destroy command or modify it just like the code. After modifying, for example, the alarm threshold, run the following command for an update.terraform plan
The following information is returned, showing that Terraform indicates that the alarm policy will be updated after value modification.
tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy: Refreshing state... [id=policy-vor9w72r]Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:~ update in-placeTerraform will perform the following actions:# tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy.policy will be updated in-place~ resource "tencentcloud_monitor_alarm_policy" "policy" {id = "policy-vor9w72r"# (6 unchanged attributes hidden)~ conditions {# (1 unchanged attribute hidden)~ rules {~ value = "90" -> "99"# (9 unchanged attributes hidden)}}# (1 unchanged block hidden)}Plan: 0 to add, 1 to change, 0 to destroy.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

