Basic Concepts
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:40:38
MQTT
An industry standard protocol in the fields of Internet of Things and mobile Internet, suitable for data transmission between mobile devices.
MQTT Server
Implement the MQTT protocol server, responsible for maintaining persistent connections with MQTT Clients, routing messages to corresponding clients, or forwarding messages to other MQTT service nodes, while also handling the storage of MQTT offline messages.
MQTT Client
Device or application that uses the MQTT protocol to connect to the MQTT server.
Topic
Used to identify message categories and structure. The Publisher publishes messages to specific topics, and the Subscriber subscribes to specific topics to receive related messages.
Topic Prefix
Topic prefix is a core concept in TDMQ for MQTT that enables aggregated management and monitoring of topics sharing the same hierarchical prefix. It allows you to view monitoring data by treating multiple subtopics with a common prefix as a single logical entity.
Wildcard Characters
Subscribers can use wildcards in subscribed topics to achieve the purpose of subscribing to multiple topics at once. MQTT supports two types of topic wildcards: single-layer wildcard (+) and multi-layer wildcard (#), to satisfy different subscription requirements.
Single-level wildcard "+" can be used at any level of a topic filter. It can be used in multiple levels of a topic filter and can be combined with multi-level wildcards. For example, "sport/tennis/+" matches "sport/tennis/player1" and "sport/tennis/player2", but does not match "sport/tennis/player1/ranking". In addition, since the single-level wildcard only matches a single level, "sport/+" does not match "sport", but matches "sport/".
"#" can match any number of levels within a topic. The multi-layer wildcard represents the parent level and any number of child levels. For example, if a client subscribes to "sport/tennis/player1/#", it will receive messages published under these topic names: "sport/tennis/player1", "sport/tennis/player1/ranking", "sport/tennis/player1/score/wimbledon". "sport/#" also matches messages with the topic "sport", because "#" includes the parent level.
Session Management
A session is the sum of stateful interactions between a client and a server. The session duration may be consistent with the underlying transport layer network connection, or may span multiple transport layer network connection cycles.
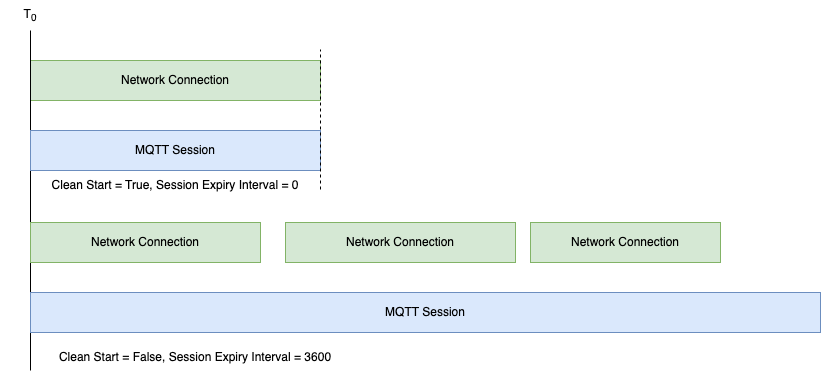
The MQTT v5 protocol defines the lifecycle of sessions through two fields: Clean Start and Session Expiry Interval.
Note:
MQTT v3.1 and MQTT v3.1.1 only include the Clean Session attribute, which defines the following mapping:
- | Clean Start | Session Expiry Interval |
CleanSession=True | True | 0 |
CleanSession=False | False | 259,200 |
Client Identifier (Client Identifier)
Client ID is the unique identifier for each client. Users must ensure its global uniqueness based on their business scenarios. Using the same ClientID to connect to the MQTT server will be rejected.
QoS
QoS (Quality of Service) refers to the service quality of message transmission. Each message can have its QoS set individually during sending. It includes the following levels:
QoS = 0 means at most once delivery, and messages may be lost.
QoS = 1 means at least once delivery, messages can be ensured to arrive but may duplicate.
QoS = 2 means exactly once delivery, messages are guaranteed to arrive and will not duplicate.
Message Retention
Message Retention is used to ensure that devices newly subscribed to a Topic can promptly receive the latest status messages, even if the messages were published before the device subscribed. When a client publishes a message with the "Retain" flag, the proxy server retains this message. Therefore, any client subscribed to the corresponding Topic will receive the last retained message, even if the recent publisher is not in an active state.
Legacy Message
A will message is used to notify other subscribers of a client's offline status or perform some predefined operations when the client is disconnected due to an exception. When the client is disconnected due to an exception (for example, a network failure or client crash), the MQTT broker will automatically publish this will message to other subscribers, enabling them to be aware of the client's offline status or perform some predefined operations, such as updating the online status.
Shared Subscription
Shared Subscription allows multiple clients to share a subscription to a topic, with only one client receiving messages published to that topic. When the primary client goes offline, it can seamlessly switch to another client to continue receiving messages, ensuring high availability.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

