- Tutorial
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Public Image Release Notes
- Announcements
- Updating Some Image Pip Package Management Tools for CentOS 7
- CentOS 8 End of Maintenance
- Discontinuation of Support for SUSE Commercial Images
- Price Reduction in Selected Availability Zones
- OrcaTerm Proxy IP Addresses Updates
- Pay-as-you-go Price Adjustments for Standard S3 CVMs in the Silicon Valley Region
- Vulnerability repairing for Linux images
- Stopping supporting for Ubuntu 10.04 images
- Solution to Tomcat Start Failure on Ubuntu14.04
- Upgrading Virtio network card drive for Windows CVMs
- About Configuration of Security Group Port 53
- Windows Server 2003 System Images End of Support Announcement
- End of Support for Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition SP1 64-bit System Images
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Operation Guide Overview
- Use Limits
- Convenience Features
- Instances
- Creating Instances
- Managing Instance Launch Template
- Batch Sequential Naming or Pattern String-Based Naming
- Logging In to Linux Instances
- Logging in to Windows instance
- Adjusting Configuration
- View Instance Details
- Renaming Instances
- Resetting Instance Password
- Managing Instance IPs
- Changing Instance Subnet
- Changing Security Group
- Conversion from Pay-As-You-Go to Monthly Subscription
- Searching for Instances
- Exporting Instance List
- Renewing Instances
- Starting Up Instances
- Shutting Down Instances
- Restarting Instances
- Reinstalling System
- Using Tencent Cloud Automation Tools to execute commands
- Terminating/Returning Instances
- Enabling Instance Termination Protection
- Instance Repossession or Recovering
- Spot Instances
- Querying the Repossession Status of a Spot Instance
- No Charges When Shut Down for Pay-as-You-Go Instances
- Managing Roles
- Enabling and Disabling Hyper-Threading
- Reserved Instances
- Images
- Migrating Servers
- Maintenance Tasks
- Cloud Disks
- Networking
- Security
- Security Groups
- Protection of Sensitive Operations
- Managing Login Password
- Managing SSH Keys
- Spread Placement Group
- Unblocking Port 25
- Tags
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Sample Console Configuration
- Best Practice
- Best Practices
- Choosing the CVM Model
- Setting up a Website
- Building an Environment
- Building a Website
- Building an Application
- Building a Visual GUI
- Data Backup
- Uploading Local Files to CVM
- Copying Local Files to CVMs
- Uploading Files from Windows to a Windows CVM via MSTSC
- Uploading Files from MacOS to Windows CVM Using MRD
- Uploading Files from Linux to Windows CVM using RDP
- Uploading files via WinSCP to a Linux CVM from Windows
- Uploading Files from Linux or MacOS to Linux CVM via SCP
- Uploading Files from Linux to a CVM Using FTP
- Uploading Files from Windows to a CVM Using FTP
- Other CVM Operations
- CVM Access to COS via a Private Network
- Best Practices for Boot Mode Legacy BIOS and UEFI
- Recovering Data on Linux CVMs
- Managing Disk Space on Windows CVMs
- Changing Kernel of a Linux Instance Manually
- Setting Up Windows-based AD Domain on a CVM
- Network Performance Test
- High-throughput Network Performance Test
- Using USB/IP to Share USB Devices in Linux
- Using RemoteFx to Redirect USB Devices in Windows
- Using AVX-512 Instructions to Accelerate AI Applications on CVM
- Building Tencent SGX Confidential Computing Environment
- Configuring Persistent Memory in M6p Instances
- Calling Cloud APIs via Python to Share Custom Images in Batches
- Operations Guide
- Initializing Data Disks
- Environment Configurations
- Installing Software
- User Data
- Work with Operating Systems
- System Activation
- System Updates
- System Shutdown
- Configuring High-performance Power Management
- Windows Recovery Mode
- Updating the Virtio ENI Driver
- Modifying SID
- Modifying VNC Resolution
- Ensuring Unique SIDs for CVMs Using Sysprep
- Use of the atop Monitoring Tools by Linux Instances
- Introduction to Linux Kernel Parameters
- Others
- Troubleshooting
- Instance-Related Failures
- CVM Login Failures
- Windows Instance Login Failures
- Windows Instance Login Failures
- An authentication error occurred when you tried to log in to a Windows instance remotely
- Failed to Reset the CVM Password or the CVM Password Is Invalid
- Connection to a Windows CVM through Remote Desktop was denied
- Requires network-level identity verification
- Problems occurred when you tried to log in to a Windows CVM remotely on Mac
- Failed to log in to a Windows CVM due to high CPU and memory usage
- Failed to connect to a remote computer through Remote Desktop
- Credentials Not Work
- Windows instance: no remote Desktop license server can provide license
- Remote Login Failure Due To Port Issues
- Linux Instance Login Failures
- Linux Instance Login Failures
- Unable to Log in to a Linux Instance via SSH Key
- Failing to log in to a Linux CVM due to high CPU and memory usage
- Remote Login Failure due to Port Issues
- VNC Login Error (Module is Unknown)
- VNC Login Error (Account Locked due to XXX Failed Logins)
- VNC Login Error (Login Failed with Correct Password)
- VNC or SSH Login Error (Permission Denied)
- Login Failure Due to /etc/fstab Configuration Errors
- sshd Configuration File Permissions
- Infinite Loop Call in /etc/profile
- Login Failure Due to Server Isolation
- Login Failure Due to High Bandwidth Occupation
- Remote Connect Failure Due to Security Group Settings
- Troubleshooting Linux Instance Issues via VNC and Rescue Mode
- Failed to shut down or restart a CVM
- Network Namespace Creation Failure
- Kernel and IO Issues
- Missing System bin or lib Soft Link
- Suspected Infection with Virus
- "no space left on device" Error During File Creation
- Linux CVM Memory Issues
- Network Related Failures
- Instance-Related Failures
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Region APIs
- Instance APIs
- DescribeInstances
- DescribeInstanceFamilyConfigs
- DescribeZoneInstanceConfigInfos
- DescribeInstanceTypeConfigs
- DescribeInstancesOperationLimit
- DescribeInstanceVncUrl
- InquiryPriceRunInstances
- InquiryPriceResetInstance
- InquiryPriceResetInstancesType
- InquiryPriceResizeInstanceDisks
- RunInstances
- StartInstances
- RebootInstances
- StopInstances
- ResetInstance
- TerminateInstances
- ResetInstancesType
- ResizeInstanceDisks
- ResetInstancesPassword
- ModifyInstancesAttribute
- ModifyInstancesProject
- InquirePricePurchaseReservedInstancesOffering
- DescribeReservedInstancesConfigInfos
- DescribeInstancesStatus
- PurchaseReservedInstancesOffering
- Cloud Hosting Cluster APIs
- Placement Group APIs
- Image APIs
- Key APIs
- Security Group APIs
- Network APIs
- Instance Launch Template APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Related Agreement
- Glossary
- Tutorial
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Public Image Release Notes
- Announcements
- Updating Some Image Pip Package Management Tools for CentOS 7
- CentOS 8 End of Maintenance
- Discontinuation of Support for SUSE Commercial Images
- Price Reduction in Selected Availability Zones
- OrcaTerm Proxy IP Addresses Updates
- Pay-as-you-go Price Adjustments for Standard S3 CVMs in the Silicon Valley Region
- Vulnerability repairing for Linux images
- Stopping supporting for Ubuntu 10.04 images
- Solution to Tomcat Start Failure on Ubuntu14.04
- Upgrading Virtio network card drive for Windows CVMs
- About Configuration of Security Group Port 53
- Windows Server 2003 System Images End of Support Announcement
- End of Support for Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition SP1 64-bit System Images
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Operation Guide Overview
- Use Limits
- Convenience Features
- Instances
- Creating Instances
- Managing Instance Launch Template
- Batch Sequential Naming or Pattern String-Based Naming
- Logging In to Linux Instances
- Logging in to Windows instance
- Adjusting Configuration
- View Instance Details
- Renaming Instances
- Resetting Instance Password
- Managing Instance IPs
- Changing Instance Subnet
- Changing Security Group
- Conversion from Pay-As-You-Go to Monthly Subscription
- Searching for Instances
- Exporting Instance List
- Renewing Instances
- Starting Up Instances
- Shutting Down Instances
- Restarting Instances
- Reinstalling System
- Using Tencent Cloud Automation Tools to execute commands
- Terminating/Returning Instances
- Enabling Instance Termination Protection
- Instance Repossession or Recovering
- Spot Instances
- Querying the Repossession Status of a Spot Instance
- No Charges When Shut Down for Pay-as-You-Go Instances
- Managing Roles
- Enabling and Disabling Hyper-Threading
- Reserved Instances
- Images
- Migrating Servers
- Maintenance Tasks
- Cloud Disks
- Networking
- Security
- Security Groups
- Protection of Sensitive Operations
- Managing Login Password
- Managing SSH Keys
- Spread Placement Group
- Unblocking Port 25
- Tags
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Sample Console Configuration
- Best Practice
- Best Practices
- Choosing the CVM Model
- Setting up a Website
- Building an Environment
- Building a Website
- Building an Application
- Building a Visual GUI
- Data Backup
- Uploading Local Files to CVM
- Copying Local Files to CVMs
- Uploading Files from Windows to a Windows CVM via MSTSC
- Uploading Files from MacOS to Windows CVM Using MRD
- Uploading Files from Linux to Windows CVM using RDP
- Uploading files via WinSCP to a Linux CVM from Windows
- Uploading Files from Linux or MacOS to Linux CVM via SCP
- Uploading Files from Linux to a CVM Using FTP
- Uploading Files from Windows to a CVM Using FTP
- Other CVM Operations
- CVM Access to COS via a Private Network
- Best Practices for Boot Mode Legacy BIOS and UEFI
- Recovering Data on Linux CVMs
- Managing Disk Space on Windows CVMs
- Changing Kernel of a Linux Instance Manually
- Setting Up Windows-based AD Domain on a CVM
- Network Performance Test
- High-throughput Network Performance Test
- Using USB/IP to Share USB Devices in Linux
- Using RemoteFx to Redirect USB Devices in Windows
- Using AVX-512 Instructions to Accelerate AI Applications on CVM
- Building Tencent SGX Confidential Computing Environment
- Configuring Persistent Memory in M6p Instances
- Calling Cloud APIs via Python to Share Custom Images in Batches
- Operations Guide
- Initializing Data Disks
- Environment Configurations
- Installing Software
- User Data
- Work with Operating Systems
- System Activation
- System Updates
- System Shutdown
- Configuring High-performance Power Management
- Windows Recovery Mode
- Updating the Virtio ENI Driver
- Modifying SID
- Modifying VNC Resolution
- Ensuring Unique SIDs for CVMs Using Sysprep
- Use of the atop Monitoring Tools by Linux Instances
- Introduction to Linux Kernel Parameters
- Others
- Troubleshooting
- Instance-Related Failures
- CVM Login Failures
- Windows Instance Login Failures
- Windows Instance Login Failures
- An authentication error occurred when you tried to log in to a Windows instance remotely
- Failed to Reset the CVM Password or the CVM Password Is Invalid
- Connection to a Windows CVM through Remote Desktop was denied
- Requires network-level identity verification
- Problems occurred when you tried to log in to a Windows CVM remotely on Mac
- Failed to log in to a Windows CVM due to high CPU and memory usage
- Failed to connect to a remote computer through Remote Desktop
- Credentials Not Work
- Windows instance: no remote Desktop license server can provide license
- Remote Login Failure Due To Port Issues
- Linux Instance Login Failures
- Linux Instance Login Failures
- Unable to Log in to a Linux Instance via SSH Key
- Failing to log in to a Linux CVM due to high CPU and memory usage
- Remote Login Failure due to Port Issues
- VNC Login Error (Module is Unknown)
- VNC Login Error (Account Locked due to XXX Failed Logins)
- VNC Login Error (Login Failed with Correct Password)
- VNC or SSH Login Error (Permission Denied)
- Login Failure Due to /etc/fstab Configuration Errors
- sshd Configuration File Permissions
- Infinite Loop Call in /etc/profile
- Login Failure Due to Server Isolation
- Login Failure Due to High Bandwidth Occupation
- Remote Connect Failure Due to Security Group Settings
- Troubleshooting Linux Instance Issues via VNC and Rescue Mode
- Failed to shut down or restart a CVM
- Network Namespace Creation Failure
- Kernel and IO Issues
- Missing System bin or lib Soft Link
- Suspected Infection with Virus
- "no space left on device" Error During File Creation
- Linux CVM Memory Issues
- Network Related Failures
- Instance-Related Failures
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Region APIs
- Instance APIs
- DescribeInstances
- DescribeInstanceFamilyConfigs
- DescribeZoneInstanceConfigInfos
- DescribeInstanceTypeConfigs
- DescribeInstancesOperationLimit
- DescribeInstanceVncUrl
- InquiryPriceRunInstances
- InquiryPriceResetInstance
- InquiryPriceResetInstancesType
- InquiryPriceResizeInstanceDisks
- RunInstances
- StartInstances
- RebootInstances
- StopInstances
- ResetInstance
- TerminateInstances
- ResetInstancesType
- ResizeInstanceDisks
- ResetInstancesPassword
- ModifyInstancesAttribute
- ModifyInstancesProject
- InquirePricePurchaseReservedInstancesOffering
- DescribeReservedInstancesConfigInfos
- DescribeInstancesStatus
- PurchaseReservedInstancesOffering
- Cloud Hosting Cluster APIs
- Placement Group APIs
- Image APIs
- Key APIs
- Security Group APIs
- Network APIs
- Instance Launch Template APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Related Agreement
- Glossary
Overview
The LNMP environment is a website server architecture consisting of Nginx, MySQL or MariaDB, and PHP running on Linux. This document describes how to manually set up the LNMP environment on a Tencent Cloud CVM.
To manually set up the LNMP environment, you should familiarize yourself with common Linux commands such as installing software via YUM in CentOS, and understand the usage and version compatibility of the software to be installed.
Note:
It’s recommended that you can configure the LNMP environment through the image environment of Tencent Cloud marketplace, and it may take a long time to set up the LNMP environment manually.
Software
The following software is used to build the LNMP environment.
Linux: Linux operating system. This document uses CentOS 7.6 as an example.
Nginx: web server. This document uses Nginx 1.17.7 as an example.
MariaDB: database. This document uses MariaDB 10.4.8 as an example.
PHP: scripting language. This document uses PHP 7.2.22 as an example.
Prerequisite
Setting up a LNMP environment requires a Linux CVM. If you have not purchased one yet, see Getting Started with Linux CVMs.
Directions
Step 1: log in to a Linux instance
Log in to the Linux instance using standard login method. You can also use any of the following login methods you are comfortable with:
Step 2: install Nginx
1. Run the following command to create a file named
nginx.repo under /etc/yum.repos.d/.vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
2. Press i to switch to the editing mode and enter the following.
[nginx]name = nginx repobaseurl = https://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/7/$basearch/gpgcheck = 0enabled = 1
3. Click Esc and enter :wq to save and close the file.
4. Run the following command to install Nginx.
yum install -y nginx
5. Run the following command to open the
default.conf file.vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
6. Press i to switch to the edit mode to modify the
default.conf file.7. Find
server{...} and replace the content inside the curly brackets with the following. This is to cancel the listening of the IPv6 address and configure Nginx to realize linkage with PHP.server {listen 80;root /usr/share/nginx/html;server_name localhost;#charset koi8-r;#access_log /var/log/nginx/log/host.access.log main;#location / {index index.php index.html index.htm;}#error_page 404 /404.html;#redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html#error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;location = /50x.html {root /usr/share/nginx/html;}#pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000#location ~ .php$ {fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;fastcgi_index index.php;fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;include fastcgi_params;}}
8. Press Esc and enter :wq to save and close the file.
9. Run the following command to start Nginx.
systemctl start nginx
10. Run the following command to enable Nginx autostart.
systemctl enable nginx
11. Enter the following URL in your local browser and verify whether the Nginx service is working properly.
http://[Public IP address of the CVM instance]
If the following appears, Nginx has been successfully installed and configured.
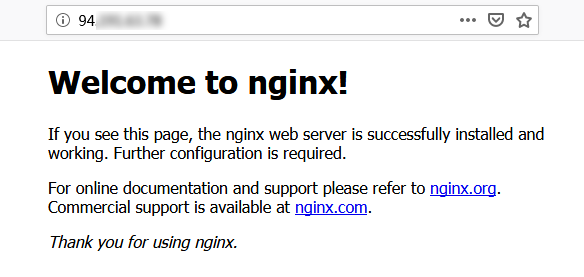

Step 3: install a database
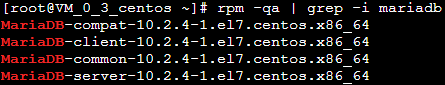
1. Run the following command to check if MariaDB is already installed.
rpm -qa | grep -i mariadb
If the following appears, MariaDB is already installed.

yum -y remove [Package name]
If nothing is returned, MySQL has not been installed. In this case, proceed to the next step.
2. Execute the following command to create the
MariaDB.repo file under /etc/yum.repos.d/.vi /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
3. Press i to switch to edit mode and enter the following content to add MariaDB.
Note:
Different operating systems require different versions of MariaDB. Download MariaDB that is compatible with your operating system.
If your CVM has private network access, change
mirrors.cloud.tencent.com to the private network address mirrors.tencentyun.com. In this way, your public network traffic will not be affected and the access is faster.# MariaDB 10.4 CentOS repository list - created 2019-11-05 11:56 UTC# http://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/[mariadb]name = MariaDBbaseurl = https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/mariadb/yum/10.4/centos7-amd64gpgkey=https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/mariadb/yum/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDBgpgcheck=1
4. Press Esc, enter :wq, save the file and return.
5. Run the following command to install MariaDB. Please pay attention to the installation progress and wait for the installation to complete.
yum -y install MariaDB-client MariaDB-server
6. Run the following command to start the MariaDB service.
systemctl start mariadb
7. Run the following command to enable MariaDB autostart.
systemctl enable mariadb
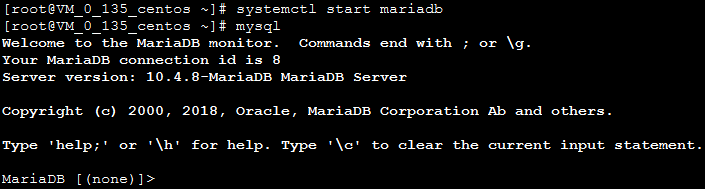
8. Run the following command to verify that MariaDB is successfully installed.
mysql
If the following appears, MariaDB has been successfully installed.

9. Run the following command to exit MariaDB.
\\q
Step 4: install and configure PHP
1. Run the following commands to update the software source of PHP in Yum.
rpm -Uvh https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
2. Run the following command to install the packages required for PHP 7.2.
yum -y install mod_php72w.x86_64 php72w-cli.x86_64 php72w-common.x86_64 php72w-mysqlnd php72w-fpm.x86_64
3. Run the following command to start the PHP-FPM service.
systemctl start php-fpm
4. Run the following command to enable PHP-FPM autostart.
systemctl enable php-fpm
Verifying the Environment Configuration
Follow these steps to verify that the LNMP environment has been built successfully.
1. Run the following command to create a test file.
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" >> /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
2. Run the following command to restart the Nginx service.
systemctl restart nginx
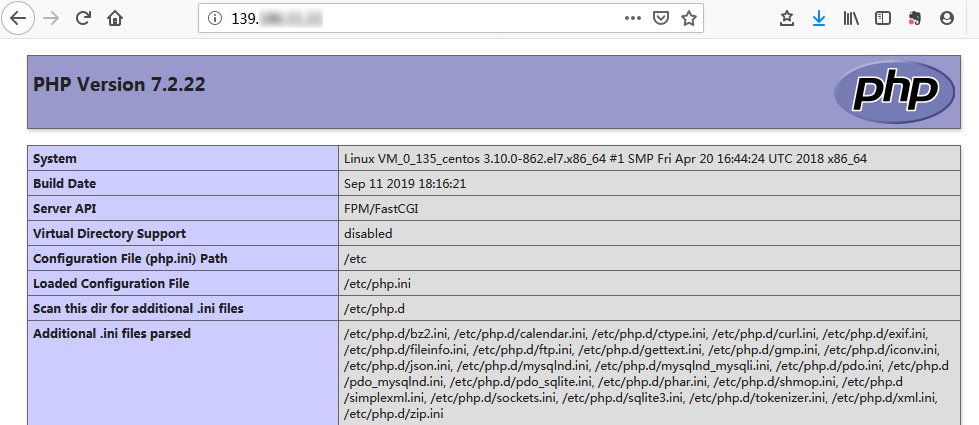
3. Enter the following URL in a local browser to check whether the environment configuration is successful.
http://[Public IP address of the CVM instance]
If the following appears, the environment has been successfully configured.

Related Operations
After the LNMP environment is built, you can manually build a WordPress website to familiarize yourself with CVM and its features.
FAQs
If you encounter a problem when using CVM, refer to the following documents for troubleshooting:
CVM login: Password Login and SSH Key Login and Login and Remote Access.
CVM network: IP Address and Port.
CVM disks: System and Data Disks.

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?