Related to Selection
Last updated:2025-12-10 14:49:03
How do I select an appropriate TencentDB for MySQL instance?
Before purchasing a MySQL instance, it is crucial to understand the features of different instances. This can help you select one that best suits your operations. This section provides guidance on how to select a MySQL instance that is suitable for your business needs.
Instance Information
Before purchasing a MySQL instance, it is essential to consider factors such as price, performance, workload, and business usage scenarios so that you can buy an instance with high cost-effectiveness. As elements such as database storage engine, instance architecture, storage type, and resource isolation policy are closely intertwined and can impact one another, you might feel confused during the selection process. Therefore, this section provides a concise overview of these aspects to help you in selecting a suitable instance.
1. Database Storage Engine
A storage engine refers to the type of tables. The storage engine of database determines the manner in which tables are stored in a computer.
InnoDB: The most frequently used OLTP storage engine, uses multi-version concurrency control (MVCC) and row-level locking technologies, offering high performance and reliable processing capabilities. In comparison to other MySQL storage engines, InnoDB offers functions including data foreign key and rollback, ensuring better data integrity. It also provides higher-level query functionalities. InnoDB kernel has been optimized a lot by Tencent Cloud and therefore has great performance advantages and is extensively applied in scenarios that involve high concurrency and require high performance.
RocksDB: A widely popular high-performance persistent key-value (KV) store, TXRocks is a transactional storage engine developed by Tencent's TXSQL team based on RocksDB. Thanks to the RocksDB LSM Tree storage structure, TXRocks reduces the waste caused by the half-full page and fragmentation mechanism of InnoDB, while also supporting the compact storage formats. Therefore, while providing similar performance as InnoDB, TXRocks can save up to half or even more storage space compared to InnoDB. This makes it more suitable for business scenarios that require high read-write performance and involve large data volumes.
LibraDB: A self-developed OLAP storage engine. With capabilities such as columnar storage, large-scale concurrency execution, and the vectorized execution engine, LibraDB accelerates various complex and time-consuming SQL queries such as complex queries, slow SQL queries, and fuzzy matching in the business, effectively improving the overall SQL execution efficiency. LibraDB is suitable for use cases such as real-time reporting, online analysis, and HTAP. Currently, only read-only instances support the LibraDB engine.
2. Instance Architecture
TencentDB for MySQL supports four instance architectures: single-node, two-node, three-node, and Cluster Edition.
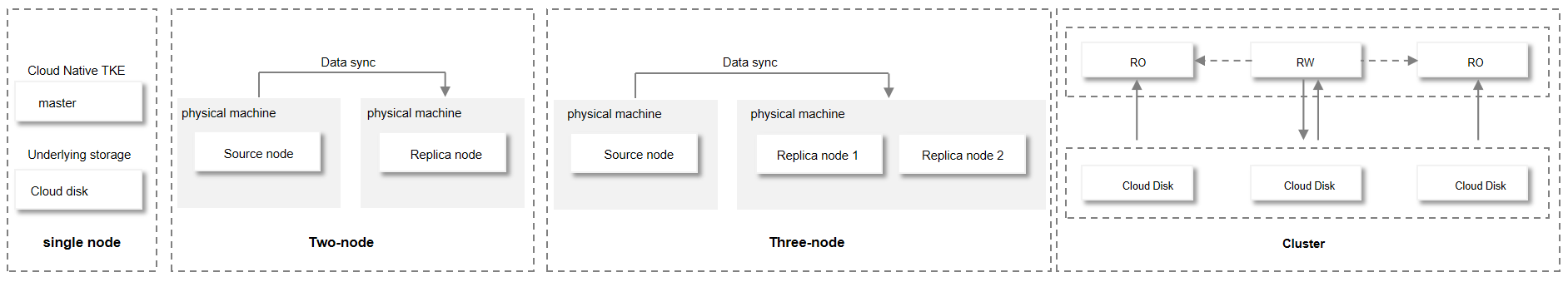
Architecture | Description | Applicable Scenarios |
Single-Node | Supported versions: MySQL 5.7 and 8.0. Node: Single Node. | Personal learning, micro-websites, non-core small-scale enterprise systems, and the development and testing environments of large and medium-sized corporations. |
Two-Node | Supported versions: MySQL 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0. Nodes: One Primary and One Standby. Primary-Standby Replication Mode: Asynchronous or semi-synchronous (default). | Gaming, internet, IoT, retailing e-commerce, logistics, insurance, and securities, etc. |
Three-Node | Supported versions: MySQL 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0. Nodes: One Primary and Two Standbys. Primary-Standby Replication Mode: Asynchronous, strongly synchronous, or semi-synchronous (default). | Gaming, internet, IoT, retailing e-commerce, logistics, insurance, and securities, etc. |
Cluster Edition | Supported versions: MySQL 5.7 and 8.0 Node: one read-write node and up to 5 read-only nodes Primary-secondary replication mode: asynchronous and semi-synchronous (default) | Gaming, Internet, IoT, retail e-commerce, logistics, insurance, and security industry applications. |
III. Storage Classification
The underlying storage of TencentDB for MySQL supports local SSD, Cloud SSD, Premium Disk, and Enhanced SSD.
Performance Metrics | Tremendous SSD | Enhanced SSD CBS | Premium Disk | SSD CBS | Local SSD |
Maximum Capacity per Disk (GB) | 32000 | 32000 | 32000 | 30000 | 12000 |
Maximum IOPS per Disk | Up to 1,000,000 after adding additional performance | Reaches 100,000 with additional performance included | 6000 | 26000 | 150000 |
Calculation Formula of Random IOPS | Benchmark performance: Random IOPS = min{4000 + Capacity (GiB) x 100, 50000} Additional performance: Maximum IOPS = min{additional performance value x 128, 950000} | Baseline Performance: Random IOPS = min{1800 + Capacity (GiB) 50, 50000} Extra Performance: Maximum IOPS = min{Extra Performance Value 128, 50000} For more details, please refer to Enhanced SSD CBS Performance Description | Random IOPS = min{1800 + Capacity (GiB) x 8, 6000} | Random IOPS = min{1800 + Capacity (GiB) * 30, 26,000} | |
Maximum Throughput per Disk (MB/s) | Up to 4,000 MB/s after adding additional performance | Reaches 1,000 with additional performance | 150MB/s | 260 | - |
Throughput Calculation Formula (MB/s) | Benchmark performance: Throughput = min{120 + Capacity (GiB) x 0.5, 350} Additional performance: Throughput = min{additional performance value x 1, 3650} | Baseline Performance: Throughput = min{120 + Capacity (GiB) 0.5, 350} Additional Performance: Throughput = min{Additional Performance Value 1, 650} | Throughput = min{100 + Capacity (GiB) x 0.15, 150} | Throughput = min{120 + Capacity (GiB) * 0.2, 260} | - |
One-Way Random Read/Write Latency (ms) | 0.1ms - 0.5ms | 0.2 - 1 | 0.8ms - 5ms | 0.5 - 3 | Microsecond-level |
IV. Resource Isolation Policy
The isolation policies of TencentDB for MySQL include basic, economical, general, exclusive, standard, enhanced, and flagship types.
Resource Isolation Policy | Description |
Basic Type | Only single-node instances support the basic isolation policy (formerly basic edition), where there is a separation between computing and storage, with the underlying layer using cloud disk storage. |
Economical | Exclusive memory and disk allocation for instances. CPU resources are shared among general specification instances located on the same physical server.* Fixed instance specifications and disk capacity. Suitable for lightweight and low-load use cases such as small websites, Web applications, blogs, forums, and cloud development/test/learning environments, offering excellent cost performance. |
General Type | An instance exclusively utilizes allocated memory and disk resources while sharing CPU resources with other general instances on the same physical machine. * Benefit from resource sharing, bringing higher cost-effectiveness and minor CPU resource reutilization. The disk capacity is not tied to the CPU and memory, allowing for flexible matching. |
Dedicated Type | An instance has dedicated CPU (with core binding), memory, and disk resources. It promises long-term performance stability and remains unaffected by the behavior of other instances on the physical machine. The peak configuration of the dedicated type is to occupy a physical machine alone, taking full control over all its resources. |
Standard | Exclusive CPU and memory allocation for instances, with long-term stable performance. Storage-computing separation architecture with flexible configurations. |
Enhanced | Exclusive CPU and memory allocation for instances, with long-term stable performance. Storage-computing separation architecture with flexible configurations. Tremendous SSD is supported, providing stable and reliable performance. |
Flagship | CPU core with a higher frequency, offering outstanding performance. Exclusive CPU and memory allocation for instances, with long-term stable performance. Storage-computing separation architecture with flexible configurations. Tremendous SSD is supported, providing stable and reliable performance. |
*In extreme cases, resource contention may occur (extremely low probability) for the general isolation policies.
Product Selection
You can follow the following steps to select an instance:
1. Selecting Database Storage Engine
If you require full transaction support and robust read-write concurrency capabilities, InnoDB is recommended.
If you want to reduce storage costs, RocksDB is recommended. It uses about half or even less storage space compared to InnoDB, while still providing similar performance.
If you have business needs for use cases such as real-time reporting, online analysis, and HTAP, it is recommended to add the read-only analysis engine LibraDB to your instances.
2. Selecting Instance Architecture
Single-Node: Applies to scenarios such as personal learning, sparse websites, non-core small business systems, and the development and testing environments for medium to large-sized enterprises.
Two-Node: Adopts the classic master-slave high-availability architecture, ideal for internet, IoT, retailing e-commerce, logistics, gaming industries, or medium to large-sized enterprises.
Three-Node: Necessary for finance-grade reliability, high security, high availability, high disaster recovery capabilities, resembling business of financial, securities, insurance industries, or core database of large enterprises.
Cluster Edition: suitable for complex businesses with frequent changes, large data volumes, high read performance requirements, and frequent scaling needs, or needs for addition/deletion of read-only instances. The enterprises also need to feature high reliability, security, availability, and disaster recovery capabilities.
3. Selecting Storage Type
In terms of storage types, the instances with two-node or three-node architecture support local SSD; the single-node architecture instances support Cloud SSD, Premium Disk, and Enhanced SSD; the Cluster Edition architecture instances support Tremendous SSD, Enhanced SSD, Premium Disk, and Cloud SSD.
Instances with single-node cloud disk architecture are based on cloud-native design, fulfilling requirements in scenarios such as testing, development, and personal learning. They offer a maximum of 30 TB storage space. The size of storage space has an impact on IOPS.
For the performance metrics of different storage types, see Storage Types.
4. Selecting Resource Isolation Policy and Instance Specifications
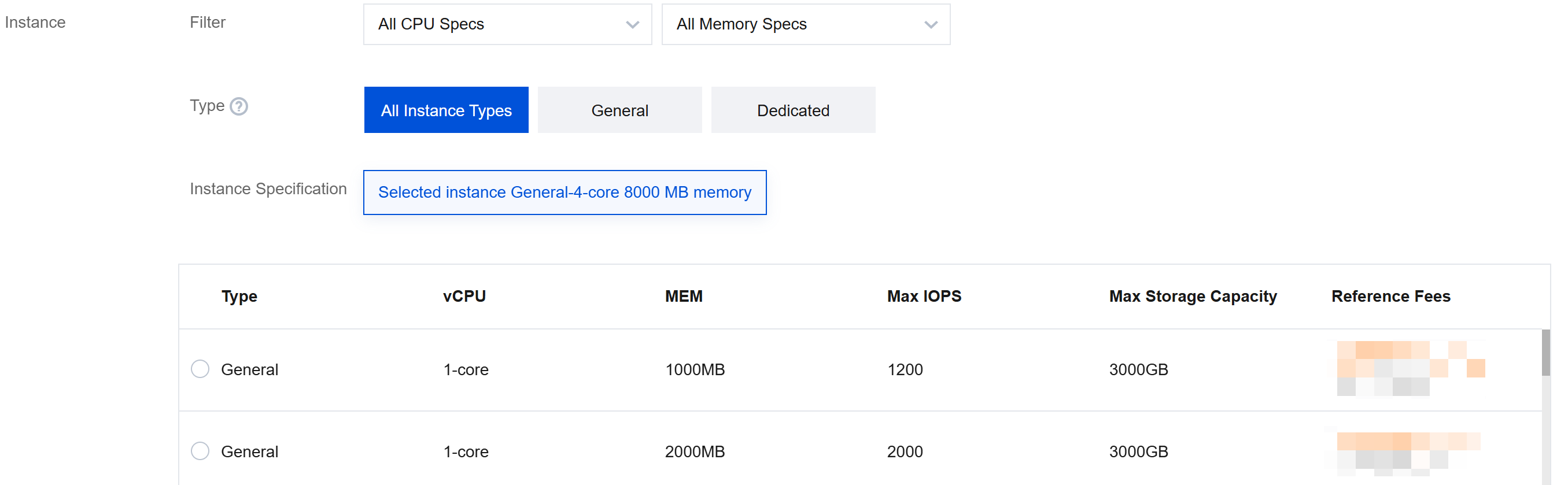
The single-node architecture supports the basic isolation policy; the two-node architecture supports economical, general, and exclusive isolation policies; the three-node architecture supports general and exclusive isolation policies; the Cluster Edition architecture supports standard, enhanced, and flagship isolation policies. Parameters of instance specifications include vCPU, memory, maximum IOPS, and maximum storage capacity, allowing you to choose suitable isolation policies and instance specifications based on your business needs.
Note:
Related Documents
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

