Using TencentDB for MySQL to Upgrade MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0
Last updated:2025-10-27 17:59:55
Using TencentDB for MySQL to Upgrade MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0
Last updated: 2025-10-27 17:59:55
In 2018, MySQL officially released the new MySQL 8.0 Community Edition, which has significant improvements in performance, features, security, and maintainability, compared with the MySQL 5.7 Community Edition. Although MySQL 5.7 Community Edition has a wide user base and is a trusted service version, MySQL officially stopped issue fixing and feature updating for it from October 2023. Therefore, MySQL encourages and recommends users to upgrade MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0 for better database services. However, upgrading from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0 is not easy. It requires substantial preparations before upgrading, and upgrade failures with difficult-to-parse causes may occur during the upgrade process, making users cautious about upgrading the database version. Given this background, TencentDB for MySQL provides users with an easy and convenient solution to stably upgrade MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0. This document describes the lifecycle support status of the official MySQL database versions, issues with upgrading from MySQL 5.7 Community Edition to MySQL 8.0 Community Edition, and the solution provided by TencentDB for MySQL.
Lifecycle Support Status for Official MySQL Database Version
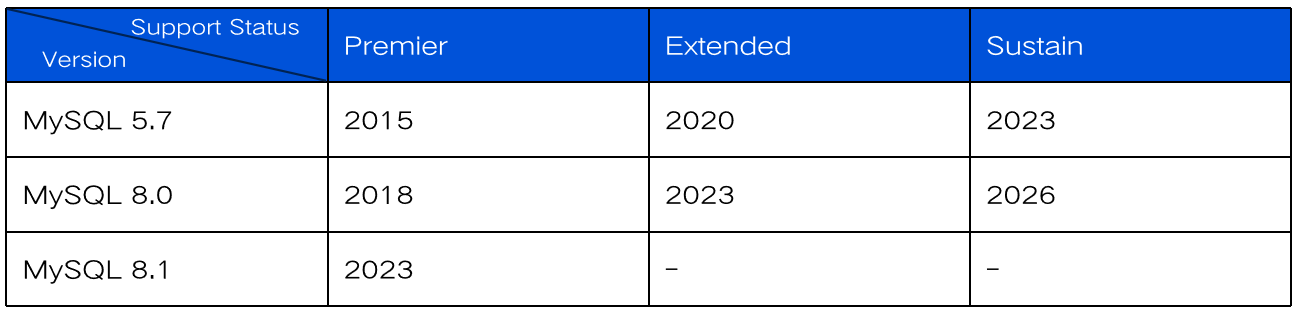
MySQL 5.7 was officially released by Oracle in October 2015 as a major upgrade from MySQL 5.6. It achieved significant breakthroughs in performance optimization, feature expansion, and security enhancement, quickly becoming the mainstream choice for enterprise-level database deployment. In 2018, the introduction of MySQL 8.0 further pushed the boundaries of database technology. On October 25, 2023, the MySQL community released the final version of the 5.7 series, 5.7.44, marking the official entry into the end-of-life phase of this version. After this date, issue fixing and feature updating will no longer be provided. Based on long-term considerations for technology evolution and security maintenance, the official strongly recommends that users migrate to the continuously maintained MySQL 8.0 to obtain more comprehensive technical support and more advanced database features.
Core Features of MySQL 8.0 Community Edition
Feature | Description |
The issue of file residue caused by DDL interruption in MySQL 5.7 has been resolved, ensuring atomicity in file operations and resolving data inconsistency between the server layer and engine layer. | |
DDL execution duration is significantly reduced, achieving quick completion of table structure changes and eliminating Binlog replication latency. Note: You can start to use this feature from the MySQL 8.0 20241001 version. To upgrade the database kernel minor version, see Upgrading Kernel Minor Version. | |
Compared with traditional replication methods, it is more efficient to directly authorize and clone plugins on the source instance, greatly improving MySQL scalability. | |
Indexes can be set as invisible to the optimizer, thereby avoiding potential repeated deletion and indexing. | |
Multiple JSON functions are added and JSON memory usage is optimized. |
Core Features of TencentDB for MySQL 8.0
Note:
The TXSQL team of TencentDB for MySQL has optimized and developed based on MySQL 8.0 Community Edition. For more self-developed kernel features, see TXSQL Engine Kernel Version Release Notes.
Feature | Description |
Tencent Cloud TXSQL kernel team has optimized the parallel replication feature, which supports parallel processing by table. This feature effectively splits the granularity to the table level, increases parallelism, and thus reduces primary-secondary latency. | |
The dynamic switching of the thread pool has been optimized, allowing the thread pool to be dynamically enabled or disabled without restarting the database service. | |
Secondary partitioning | Support secondary partitions of range or list type, improving data management and query efficiency. |
Recycle bin | Support placing tables dropped or truncated by user operations into a recycle bin, allowing data recovery when needed. |
The flashback query feature is designed and implemented on the InnoDB engine, allowing historical data before misoperations to be queried by simple SQL statements. | |
Kill idle transactions that exceed a certain duration, promptly releasing resources. |
Issues with Upgrading from MySQL 5.7 Community Edition to MySQL 8.0 Community Edition
Issue 1: Substantial Preparations Required Before Upgrading
MySQL 8.0 has many significant changes in data dictionary architecture refactoring, storage engine optimization, and SQL syntax expansion, resulting in notable version differences and functional evolution compared to the MySQL 5.7 version. To ensure a smooth upgrade process, it is recommended to conduct a comprehensive compatibility assessment before version migration and develop complete pre-check plans and contingency plans to avoid potential technical risks. The main differences between MySQL 8.0 and MySQL 5.7 are shown in the figure below. For detailed differences, see MySQL Official Documentation.
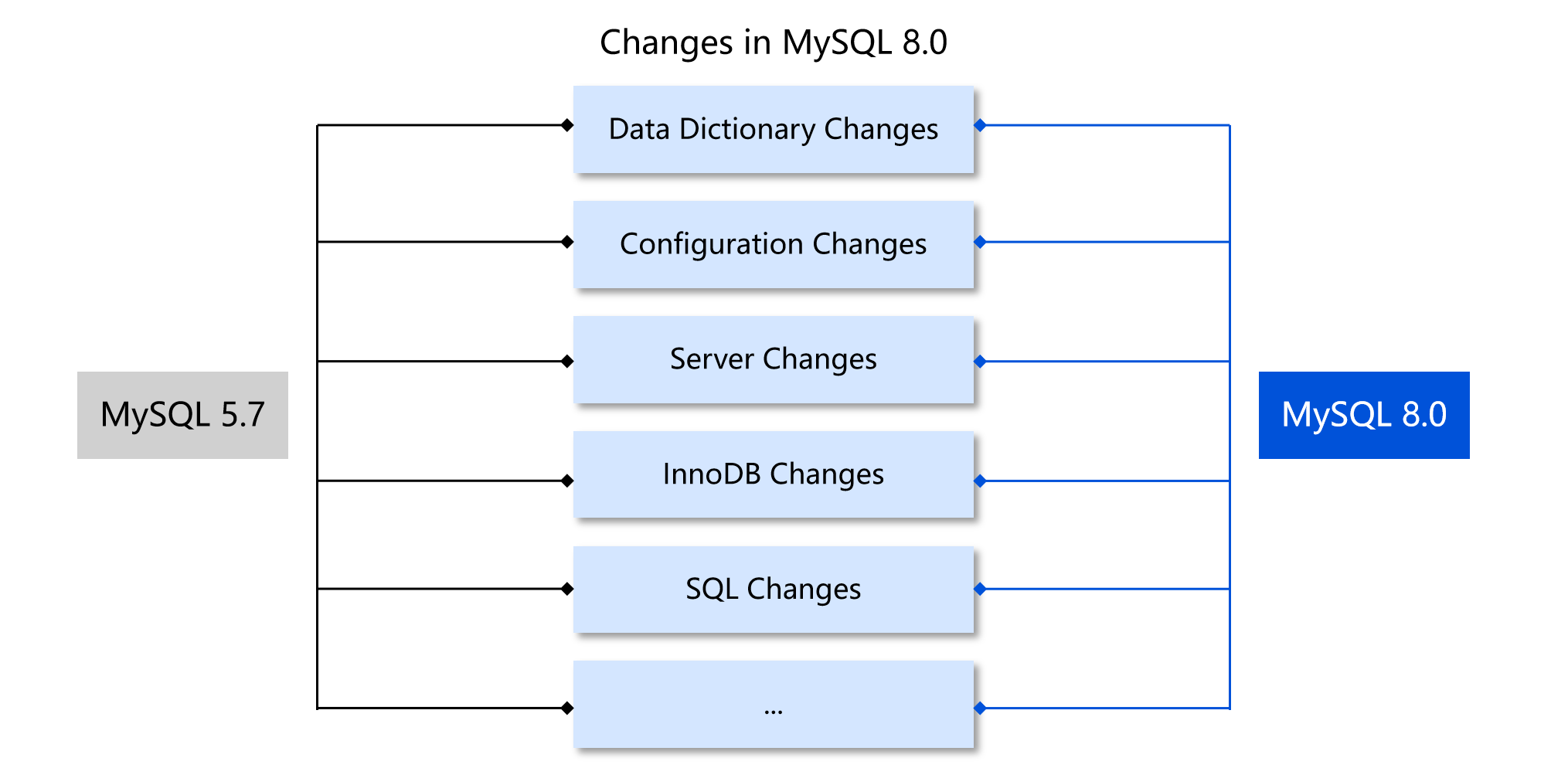
The upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0 is performed via an inplace upgrade, which starts the MySQL 5.7 instance by directly using the MySQL 8.0 binary file. The upgrade program will automatically perform related checks and upgrades.
The preparations before upgrading are intended to eliminate incompatible changes that the upgrade program is unable to process automatically. The main work is as follows.
MySQL 8.0 introduces a new data dictionary to store metadata in the database, with the Server layer and InnoDB layer sharing the same metadata. All views in MySQL 8.0's information_schema are derived from data dictionary tables, and InnoDB-related views have been renamed (INNODB_SYS_XXX renamed to INNODB_XXX). If a user's application depends on these views, it is necessary to ensure the application has made corresponding modifications. Before upgrading, confirm whether the business depends on system tables removed in MySQL 8.0 (such as mysql.proc and mysql.event). If so, use new access methods to obtain the required data. In addition, for user tables with the same name as MySQL 8.0 system tables (such as catalogs and routines), manual
RENAME/DROP TABLE operations are required.TencentDB for MySQL 8.0 no longer supports some legacy data types. If a table contains fields with data types not supported by MySQL 8.0, they need to be repaired before upgrading by
REPAIR TABLE or logical export and import. For more information, see Preparing Your Installation for Upgrade.In MySQL 8.0, partition table processing has been moved from the server layer to the engine layer, and MySQL server no longer supports generic partitioning. Non-native partition tables are deprecated in MySQL 8.0. Therefore, such partition tables need to be converted to native type (such as InnoDB) or need to be deleted.
Triggers in early MySQL 5.7 versions (earlier than 5.0.17) do not support the DEFINER attribute, so there might be triggers missing the DEFINER attribute in a MySQL 5.7 instance. These triggers will cause the upgrade to MySQL 8.0 to fail. Before upgrading, you need to recreate these triggers that are missing the DEFINER attribute.
In MySQL 8.0, there is a length limit for foreign key constraints. If a foreign key constraint is too long, it may result in errors and failures during the upgrade. Therefore, before performing the upgrade, you need to modify the length of foreign key constraints to less than 64 characters.
In MySQL versions earlier than 8.0, the maximum length for view column names is 255 characters, while in MySQL 8.0, it is shortened to 64 characters. Therefore, before upgrading, you need to modify view column names that are too long to less than 64 characters.
In MySQL 8.0, the length of a single ENUM or SET column element should not exceed 255 characters or 1,020 bytes. Therefore, you need to modify the ENUM and SET values that exceed this limit before upgrading.
If the .frm file and InnoDB data dictionary table metadata are inconsistent, upgrade errors may occur. Therefore, before upgrading, logical export and import of data are required. If there are orphaned .frm files (.frm files without corresponding .ibd files), cleanup needs to be performed.
MySQL 8.0 has deprecated some spatial functions. If a generated column contains deleted functions (new spatial functions start with ST and MBR), you need to modify the corresponding columns before upgrading.
Before upgrading, ensure that the MySQL 5.7 instance has been shut down correctly, meaning there should be no pending REDO logs to apply and no transactions waiting to roll back before upgrading.
MySQL 8.0 introduced some new reserved words. Most of them are prohibited from being used as table names or column names. Therefore, you need to process any new reserved words introduced in MySQL 8.0 that exist in MySQL 5.7.
Before upgrading, you need to modify the deprecated sql_mode variable content (such as NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER) to a mode supported by MySQL 8.0 to avoid instance startup failure.
For instances of versions later than MySQL 8.0 (8.0.13 and later), InnoDB partition tables are not allowed in shared tablespaces (system tablespaces and common tablespaces). Therefore, before upgrading, you need to move shared tablespaces to standalone tablespaces.
In MySQL 8.0 instances, the GROUP BY clause does not support ASC or DESC collations. Therefore, before upgrading, you need to modify or delete stored procedures containing such syntax.
In MySQL 5.7, lower_case_table_names is a modifiable value. In MySQL 8.0, it is an initialization parameter, and once instance initialization is completed, it cannot be modified. When upgrading, if you need to change this parameter value to 1, ensure table names are in lowercase before upgrading to avoid upgrade errors.
The configuration of character sets and collations may differ between MySQL 5.7 and MySQL 8.0, possibly causing index invalidation, query errors, and other issues, for example:
The default character set for MySQL 8.0 is utf8mb4, which uses 1 to 4 bytes to store a character, while the default character set for MySQL 5.7 is utf8mb3, which uses 1 to 3 bytes to store a character. Therefore, field and index lengths are affected. Under REDUNDANT or COMPACT row formats, the maximum index length allowed by the InnoDB engine is 767 bytes. Correspondingly, the maximum number of characters allowed for an index in MySQL 5.7 is 255, whereas in 8.0, an index exceeding 191 characters cannot be created.
If a table was created using the utf8mb3 character set in MySQL 5.7, and after upgrading to MySQL 8.0, the default character set used is utf8mb4, then new tables created without specifying a character set will default to utf8mb4. When a JOIN operation involving fields of the new table (utf8mb4) and the migrated table (utf8mb3) occurs, the index may become invalid due to inconsistent character set types on both sides of the JOIN.
If a table was created using the utf8mb4_general_ci collation in MySQL 5.7 and the default collation after upgrading to MySQL 8.0 is utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci, then tables created without specifying a collation will default to utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci. Since utf8mb4_general_ci and utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci have the same priority (the collation cannot be chosen), when a JOIN operation involving fields between a new table and a migrated table occurs, an error will be reported due to incompatible collations on both sides of the JOIN.
To avoid issues caused by character sets, check the usage of character sets and collations in MySQL before upgrading. You can also use the following SQL to modify the character sets and collations of databases, tables, and fields.
# Modify the character set and collation of a database.ALTER DATABASE database_name CHARACTER SET = charset COLLATE = collation;# Modify the character set and collation of a table.ALTER TABLE table_name CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET charset COLLATE collation;# Modify the character set and collation of a field.ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE column_name column_name type CHARACTER SET charset COLLATE collation;
In addition to the above preparations, business-wise adaptation is also required for differences in drivers, error codes, parameters, and optimizers between versions. For self-built instances, before performing a major version upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0, you can use MySQL Shell, the mysqlcheck tool, and the community upgrade check documentation to review preparations. For changes and detailed checkpoints when upgrading from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0, see MySQL Official Documentation.
Issue 2: Upgrade Failures That Are Difficult to Analyze
Although the community provides comprehensive upgrade check tools and detailed help documentation to assist users in compatibility assessment and troubleshooting before version upgrading, upgrade failures still occur frequently during actual upgrade operations, and it is difficult to analyze the causes for the failures one by one from the log information. The reasons for the difficulty in analyzing upgrade failures include, but are not limited to, the following points:
Error messages are unclear. Errors caused by different reasons may be recorded as the same or similar errors in the logs. Users need to invest a large amount of time and effort to troubleshoot the root cause, increasing upgrade difficulty.
Error messages are incomplete. After an issue occurs and is specifically resolved, it is found that repeated issues cause failures again. This is because the upgrade program stops prematurely upon first detection of a certain type of error, preventing all identical issues from being detected in one go. Users need to perform multiple attempts and troubleshooting, increasing the complexity and time cost of the upgrade.
Some errors only provide an error prompt without a corresponding solution. Users need to find solutions on their own or seek help from the community, increasing confusion and uncertainty during the upgrade process.
Some issues in MySQL 5.7 or earlier versions have been fixed, but handling for existing instances is still insufficient.
Using TencentDB for MySQL for Easy Upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0
The TencentDB for MySQL team has accumulated extensive experience, established comprehensive pre-upgrade check logic, and analyzed and fixed issues arising during upgrades to ensure a smooth upgrade process. TencentDB for MySQL will also extend support for different MySQL versions, providing users with a more ample buffer time. The lifecycles of MySQL Community Edition and TencentDB for MySQL are as follows:
Version | Start Date of Tencent Cloud Support | End Date of Tencent Cloud Support | End Date of Community Support |
MySQL 5.7 | June 2017 | September 2028 | October 2023 |
MySQL 8.0 | August 2020 | - | April 2026 |
Compared to users who self-upgrade their self-built MySQL, when TencentDB for MySQL users perform a major version upgrade, they do not need to perform tedious checks, repeatedly review error logs, or troubleshoot issues one by one. They only need to click the upgrade button in the console, and all upgrade actions will be automatically completed in the background.
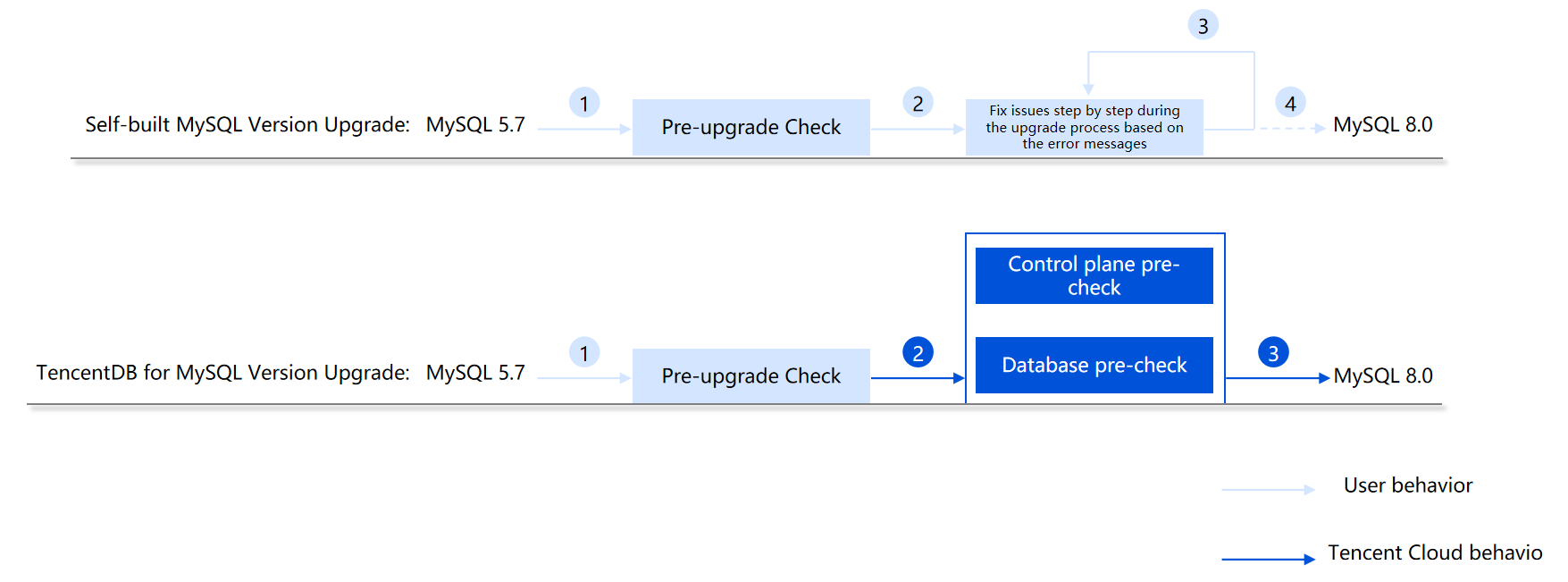
Upgrade Method
Summary
During a database major version upgrade, detailed pre-upgrade checks should be performed, issues during the upgrade should be resolved step by step, and post-upgrade verification and testing work should be completed. While TencentDB for MySQL may not have completely resolved all issues in the upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0, the TencentDB for MySQL team has been continuously working on fixing and building solutions and has provided users with a simple and efficient mechanism for major database version upgrades. As the MySQL 8.0 version stabilizes and advances, the issues associated with major database version upgrades will be gradually resolved.
Documentation
For methods on migrating self-built MySQL or third-party cloud database for MySQL to TencentDB for MySQL, see Migrating with DTS.
To learn about database versions and the functional differences between MySQL 8.0 and MySQL 5.7, see Database Versions.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

