Differences in Redis Major Version Command Usage
Last updated:2026-01-28 10:07:37
Command/Feature | Cloud Redis 5.0 | Cloud Redis 6.2 | Cloud Redis 7.0 | Description |
RESP3 | - | - | - | Currently not supported. Assess whether your business framework uses HELLO 3 auth username password for authentication, and whether the RESP3 protocol is used. If so, downgrade to RESP2. |
ACL | - | - | - | The access control list (ACL) feature is not supported at present; confirm whether your business relies on this feature. This limitation affects all command APIs related to ACL users, including acl, auth, migrate auth, and client kill user. |
Module | - | - | - | Modules are not supported in the current version. Confirm whether your business enables this feature. |
client-side-caching | - | - | - | Currently not supported. Confirm whether your business relies on client-side caching optimization. |
pub/sub | - | - | - | TencentDB for Redis® Cluster Edition has enhanced the pubsub command. For details, see Differences Between the Proxy Architecture and Direct Connection Mode. |
Cluster multi-DB | Multi-DB is supported in cluster mode. | | | However, it is not recommended to use or rely on this feature. Commands such as select and swapdb are enabled. Some clients may determine cluster mode based on the success of select, which can cause misjudgments. |
lua readonly table | Defining non-local functions is not allowed. | | | To address CVE security vulnerabilities, the community has enabled read-only table protection in the Lua sandbox, which prohibits redefining global (non-local) functions. Otherwise, execution will fail with the error: ERR Attempt to modify a readonly table ... Perform a full scan of all Lua calls, such as eval, script, and function, and explicitly change all custom functions to use local definitions: eval "local function xxx() return 'hello' end" 0.Note: This change is a breaking change, but it has been released by the community as a minor version security patch. Differences may exist across cloud providers and major/minor versions (such as rollback or lack of backporting). Do not rely on legacy usage. Businesses should comply with specifications to avoid production failures. For more information, see Lua readonly tables (CVE-2022-24736, CVE-2022-24735). |
lua print | lua print is allowed. | | lua print is not allowed. | To fix CVE security vulnerabilities, the print function in the Lua sandbox has been removed (breaking change). Continuing to use it will cause an error: ERR ... nonexistent global variable 'print' ...Troubleshoot all eval and script Lua scripts, and delete or replace all print(...) calls. For logging, use the official API: redis.log(redis.LOG_NOTICE, 'hello'). |
script load | Scripts loaded with script load are compiled and cached, and the command (including the script content) is disseminated as a write command to all secondary nodes to ensure identical script caches. If AOF persistence is enabled, script load is written to AOF in the same format as received. | | | Starting from Redis 7.0 (community edition), Lua scripts are no longer persisted. Cloud Redis 7.0 retains Lua persistence. |
script flush | The script flush command is disseminated to both primary and secondary nodes and written to the AOF file. When the primary node clears its local script cache, it synchronizes the flush command to the secondary nodes, ensuring that their caches are cleared as well and preventing inconsistencies between the primary and secondary script caches. If AOF persistence is enabled, script flush is also written to AOF. | | | |
Lua script persistence | In primary-secondary replication, RDB snapshots also store Lua scripts. | | | |
Lua EVAL script eviction | All the latest minor versions support Lua script eviction. Note: To prevent abuse of EVAL by embedding parameters directly into the script body, Redis introduced an LRU eviction mechanism with a limit of 500 entries. This eviction applies only to scripts generated by EVAL. When the limit is exceeded, the least recently used scripts are automatically evicted. Scripts loaded with SCRIPT LOAD are not affected. | | | No changes are required for your business. This update only backports the behavior from higher community versions to ensure consistency with the latest official release. Note: In typical scenarios, scripts are fully delivered through EVAL each time. Even if they are evicted by the LRU mechanism, it does not affect your business. However, if users adopt a nonstandard approach—first loading the script onto the server using EVAL and manually computing the SHA, then calling EVALSHA—when a single transaction involves more than 500 scripts, the least recently used script may be evicted. This can cause subsequent EVALSHA calls to return a NOSCRIPT error and lead to transaction failure. |
Lua memory abuse limit | All latest minor versions across all cloud major versions support Lua memory limits. Note: In the community edition, Lua does not verify maxmemory when executing write commands. This allows malicious scripts (such as infinite loops with SET, EVAL "for i=1,10000000000 do redis.call('SET', 'key-:' .. i, 'value-:' .. i) end" 0) to bypass the memory upper limit. To prevent machine OOM in cloud environments, memory usage is monitored in real time during Lua execution. Once the limit is exceeded, an OOM error is returned immediately. | | | Normal business workloads are not affected as long as the instance has sufficient maxmemory. The cloud-side also provides the extra-maxmemory parameter, which can reserve additional memory space for an instance when necessary. Note: If an OOM is triggered, the Lua script will fail midway, and atomicity cannot be guaranteed. |
Dictionary rehash optimization | All latest minor versions across all cloud major versions support dictionary rehash optimization. Note: In the community edition, dictionary implementation uses an incremental rehash mechanism consisting of both active and passive rehash. Passive rehash occurs during the processing of each user request, which triggers additional rehash operations. This results in extra memory accesses, increasing request latency and reducing node throughput. To improve performance, the cloud edition disables passive rehash, retaining only active rehash. | | | Note: Disabling passive rehash slows down the rehash process and may slightly increase the probability of hash collisions. Temporary memory used during rehash may also remain longer in monitoring metrics compared with the community edition. However, user requests generally avoid additional performance jitters from passive rehash, which benefits most use cases. Only in certain rare extreme cases, such as very high-frequency write workloads, will performance regress to levels close to the community edition. To address this, the cloud edition provides the passive-rehash-enabled configuration option for flexible control over enabling or disabling passive rehash. |
Replica primary-secondary disconnection redirection | All the latest minor versions across all cloud major versions support replica primary-secondary disconnection redirection. Note: When a replica disconnects from the primary node, before failover completes, read requests sent to the replica are redirected to the primary node. This prevents serving stale data while the replica is in read-only mode due to the disconnection. | | | No special processing is required from your business. |
info/client info/client list | Field support across different versions may not be fully compatible with the community edition. The proxy layer will block sensitive fields as needed. For details, see Differences Between the Proxy Architecture and Direct Connection Mode. | | | Check whether your business relies on the client command. If not required, avoid executing client list to prevent slow queries and excessive node memory usage. |
cluster slots | Cluster Edition hides or converts certain sensitive information in cluster slots and other commands. | | | |
Commands such as auth/migrate auth/client kill user/acl setuser and others | No ACL component. | ACL-related APIs are not supported. | | - |
command/ command info | The command command provides metadata about commands to client libraries for routing decisions, redirection, and other operations. | | | No special processing is required from your business. |
geo* store | The following issues were fixed in Redis 6.2 and 7.0: For geo commands (such as georadius, georadiusbymember, and geosearchstore) that support the store option, when the source key is empty, the behavior was changed from "return an empty array without deleting the target key" to "delete the target key and return 0." | | | 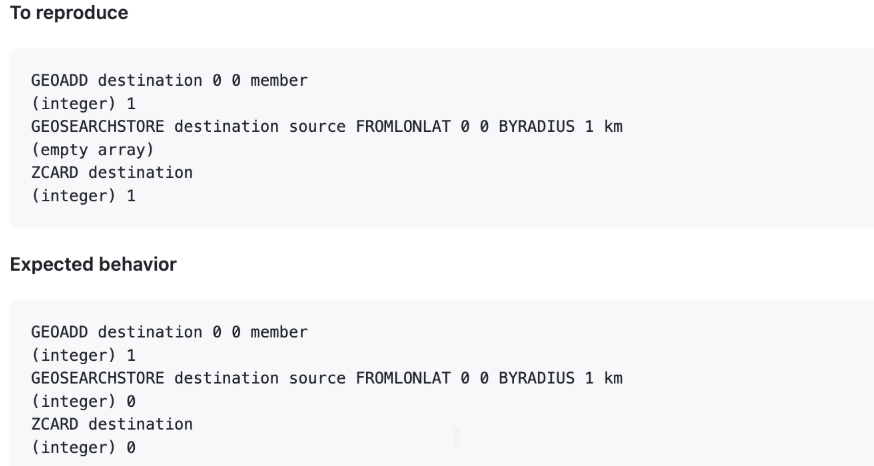 |
zrangestore | Fixed an issue where the ZRANGESTORE command could crash Redis when the configuration item zset-max-ziplist-entries was set to 0. | | | - |
lpop/rpop coun | The return behavior of LPOP/RPOP was unified in versions 6.2.7 and 7.0.0: 1. When the key exists and count = 0, an empty array [] is returned (previously returned nil). 2. When the key does not exist and the count parameter is specified, an empty array [] with length -1 is returned (previously returned nil). | | 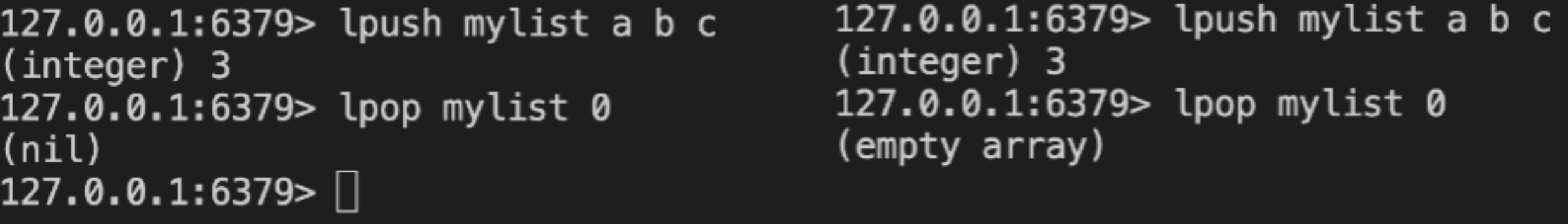 | 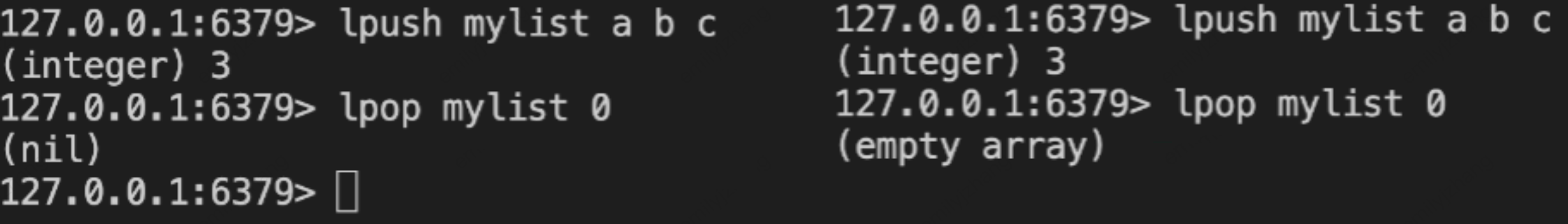 |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

