Database Parameter Adjustment
Last updated:2025-08-22 18:02:19
TencentDB for MongoDB (MongoDB) supports the adjustment of certain database parameters, allowing database features to better align with workload needs.
Background
During daily Ops, quickly adjusting certain database parameters enables targeted optimization of query and management performance to meet evolving business needs. Additionally, the system supports real-time access to parameter change history, providing a reliable basis for diagnosing issues.
Version Description
Currently, MongoDB 3.2 and later versions support database parameter modification. However, the modifiable parameters may vary by version. See the parameters displayed in the console for accurate information.
Use Instructions
Currently, the parameter modification feature only supports changes that take effect without requiring a restart. Parameters that require a restart to take effect will be supported in future versions. You may also configure such parameters manually through the MongoDB shell. Restarting may cause connection interruptions, so plan your workloads accordingly and proceed with caution.
When updating the cluster architecture or configuration, such as adjusting the configuration specifications, modifying nodes, adjusting shards, upgrading nodes, or migrating nodes, you do not need to reconfigure parameters. The system will automatically synchronize the parameter configuration data.
Prerequisites
You have created a TencentDB for MongoDB instance.
The instance is running properly.
Adjusting Parameters
1. Log in to the TencentDB for MongoDB console.
2. In the left sidebar, choose Replica Set Instance or Shard Instance. The operations for both are similar.
3. In the instance list on the right, locate the target instance.
4. Click the target instance ID to go to the Instance Details page.
5. Switch to the Parameter Settings tab, go to the Modifiable Parameter page, and click Modify Current Value.
6. In the input box under the Current Value column, re-enter the values of the parameters you want to modify, as shown in the figure below.
Note:
You can modify multiple parameters at the same time.
When modifying parameters, be sure to set them according to the Acceptable Values.
In the Restart upon Modification column, check whether the instance will be restarted. Restarting may cause connection interruptions, so plan your workloads accordingly and proceed with caution.
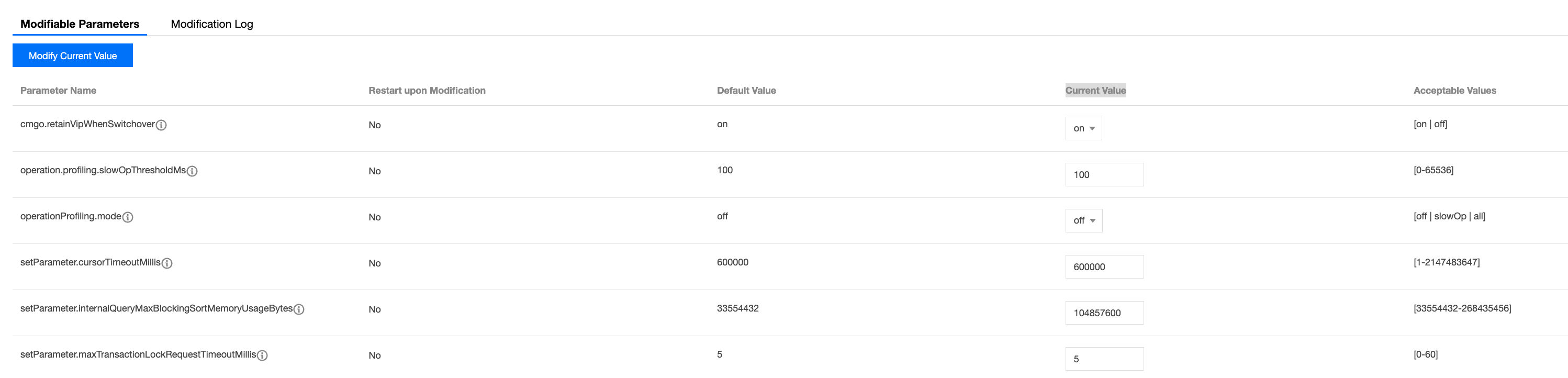
The scope of parameter effectiveness varies depending on the instance version and architecture. The parameters that can be modified in the current version are listed in the table below.
Parameter Name | Restart Required After Modification | Default Value | Reference Value | Supported Version | Supported Instance Type | Applicable Scope | Parameter Description |
operation.profiling.slowOpThresholdMs | No | 100 | [0-65536] | 4.0, 4.2, 4.4, 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0 | Replica and shard | mongod and mongos | Sets the threshold for identifying slow queries, in milliseconds. |
operationProfiling.mode | No | off | [off | slowOp | all] | | Replica and shard | mongod | This parameter is used to set the operation profiling mode of the database. By selecting different modes, you can record performance data of database operations to facilitate performance tuning and troubleshooting. The available options for this parameter are: off: Disable operation profiling. slowOp: Record operations considered slow, defined as those whose execution time exceeds the specified threshold. The default threshold is 100 milliseconds. all: Record performance data for all operations. |
setParameter.cursorTimeoutMillis | No | 600000 | [1-2147483647] | | Replica and shard | mongod and mongos | This parameter is used to set the maximum idle time for a cursor. If a cursor is not accessed within the specified period, it will be automatically disabled to release associated resources. By default, the value is set to 10 minutes. You can adjust the timeout duration by modifying this parameter. Note that setting the value to 0 disables the cursor timeout mechanism, meaning the cursor will remain enabled until explicitly disabled by the client. |
setParameter.intenalQueryExecMaxBlockingSortBytes | No | 33554432 | [33554432-268435456] | | Replica and shard | mongod | This parameter controls the maximum amount of memory MongoDB can use when performing sort operations. When executing a query that requires sorting, MongoDB may sort the result set in memory. If the size of the result set exceeds the specified value, MongoDB will fall back to disk-based sorting, which may lead to performance degradation. Unit: bytes. |
setParameter.maxTransactionLockRequestTimeoutMillis | No | 5 | [0-60] | | Replica and shard | mongod | This parameter controls the maximum timeout duration before a lock is acquired by a MongoDB transaction. If a transaction attempts to acquire a lock that is currently held by another transaction, it will wait for a certain period. If the waiting time exceeds the value specified by this parameter, the transaction will throw a timeout exception. Unit: milliseconds. |
setParameter.transactionLifetimeLimitSeconds | No | 60 | [5-300] | | Replica and shard | mongod | Sets the maximum lifecycle of a single transaction, in seconds. When a transaction is initiated, MongoDB assigns it a unique transaction ID and records the start time. If the transaction is not completed within the specified duration, MongoDB will automatically roll it back and release the associated resources. |
balance.window | No | NULL | [00:00 | 23:00] | | Shard | mongos | MongoDB cluster balancing operations are used to evenly distribute data across nodes within the cluster to improve performance and availability. This parameter specifies how often MongoDB performs a cluster balancing operation to ensure even data distribution across nodes. |
openBalance.window | No | false | [true | false] | | Shard | mongos | Enables or disables the balance window. |
setParameter.tcmallocAggressiveMemoryDecommit | No | true | [true | false] | | Replica and shard | mongod and mongos | Specifies whether to enable fast memory reclamation. |
cmgo.crossZoneLoadBalancing | No | off | on|off | | Shard | mongos | Specifies whether read-write requests are evenly distributed across multiple availability zones (AZs). |
cmgo.retainVipWhenSwitchover | No | on | on|off | | Replica and shard | mongos | Controls whether the Virtual IP (VIP) remains unchanged during a primary-secondary switchover/failover. |
setParameter.ttlDeleteBatch | No | 2147483647 | [1-2147483647] | | Replica and shard | mongod | Controls the batch size used by Time-To-Live (TTL) indexes when expired documents are deleted. |
setParameter.ttlMonitorSleepSecs | No | 60 | [60-600] | | Replica and shard | mongod | Controls the execution frequency of the MongoDB TTL monitor thread (TTLMonitor), specifically the number of seconds the thread sleeps between each run. |
setParameter.failIndexKeyTooLong | No | true | [true | false] | 3.2, 3.6, and 4.0 | Replica and shard | mongod | Sets whether to impose a limit on the length of index keys. If this parameter is set to true, MongoDB will throw an error and refuse to create the index if the length of the index key exceeds the maximum allowed limit. |
storage.wiredTiger.collectionConfig.blockCompressor | Yes | snappy | [snappy | zlib | zstd] | 4.2, 4.4, 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0 | Replica and shard | mongod | This parameter specifies the block compression algorithm (such as snappy, zlib, or none) used by MongoDB's WiredTiger storage engine for collection data. It is used to compress data blocks during disk storage to save space. snappy (default): Balance compression ratio and CPU overhead, making it suitable for most scenarios. zlib: Provide a higher compression ratio at the cost of significantly increased CPU usage. zstd: Save 20–30% more disk space than snappy (depending on data type); offers decompression speed close to snappy and significantly faster compression than zlib. |
setParameter.migrateCloneInsertionBatchDelayMS | No | 0 | [0-5000] | | Shard | mongod | This parameter controls the wait time (in milliseconds) after each batch of documents is inserted into the destination shard during data migration in a MongoDB sharded cluster. It is used to moderate the I/O pressure on the destination shard. |
setParameter.rangeDeleterBatchDelayMS | No | 20 | [0-5000] | | Shard | mongod | This parameter controls the delay interval (in milliseconds) between each batch deletion of old chunks from the source shard after data migration in a MongoDB sharded cluster. It is used to regulate the I/O pressure caused by the deletion operations on the source shard. |
setParameter.rangeDeleterBatchSize | No | 128 | [0-2147483647] | | Shard | mongod | This parameter controls the upper limit on the number of documents deleted per batch from the source shard after data migration in a MongoDB sharded cluster. It is used to balance deletion efficiency and cluster load. |
setParameter.migrateCloneInsertionBatchSize | No | 0 | [0-5000] | | Shard | mongod | This parameter controls the upper limit on the number of documents inserted per batch into the destination shard during data migration in a MongoDB sharded cluster. It is used to balance migration speed and the load on the destination shard. |
setParameter.internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes | No | 33554432 | [33554432-268435456] | | Replica and shard | mongod and mongos | This parameter controls the maximum size (in bytes) of the in-memory sort buffer that a single MongoDB query can use when performing a blocking sort, which occurs when an index is not available. If this limit is exceeded, MongoDB will sort using temporary files on disk. |
7. Click Confirm in the bottom-right corner to complete the modification. On the Modification Log page, you can view the history of parameter changes, including the values before and after the change, modification status, and modification time.

Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

