- Updates and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- New/Legacy Anti-DDoS Advanced Version Differences
- Comparison of Anti-DDoS Protection Schemes
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Best Practice
- API Documentation
- FAQs
- Troubleshooting
- Anti-DDoS Advanced (Global Enterprise Edition)
- Legacy Anti-DDoS Advanced (Legacy)
- Service Level Agreement
- Contact Us
- Glossary
- Updates and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- New/Legacy Anti-DDoS Advanced Version Differences
- Comparison of Anti-DDoS Protection Schemes
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Best Practice
- API Documentation
- FAQs
- Troubleshooting
- Anti-DDoS Advanced (Global Enterprise Edition)
- Legacy Anti-DDoS Advanced (Legacy)
- Service Level Agreement
- Contact Us
- Glossary
Error Description
A 502 Bad Gateway error occurs when you are using Anti-DDoS Advanced, as shown below:
Common Causes
The following figure shows how the application traffic flows.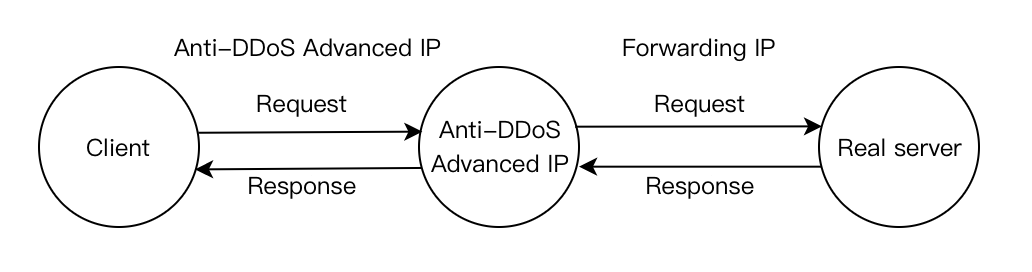
Cause 1: The forwarding IP is blocked by the real server or limited to a specific rate
After you connect to Anti-DDoS Advanced, the instance IP sends received access requests to the real server using the forwarding IP instead of client IP and thus the real server IP becomes invisible to the client. However, the number of forwarding IPs is insufficient to handle volumes of access requests.
If the real server is configured with protection policies, it is possible to trigger corresponding policies to limit the rate of the forwarding IP and even block it.
Cause 2: The real server works exceptionally, causing a response timeout
Possible reasons:
- The real server IP is not connected to Anti-DDoS Advanced and crippled by malicious attacks.
- A failure occurs to the data center of the real server.
- High memory and CPU usage lead to weakening performance.
- Web programs such as Apache and Nginx are abnormal.
- The forwarding linkage between the public network and the real server is faulty.
Cause 3: There is network jitter or a faulty linkage
The poor public network quality affects the stability of application access and a 502 error is returned.
Solutions
Solution to cause 1
Check whether the access of real server and Anti-DDoS Advanced instance is normal.
If only the real server works normally, the access of Anti-DDoS Advanced instance is blocked by the real server or is rate-limited. We recommend adding the instance to your allowlist.
For more details, see Instructions for cause 1.
Solution to cause 2
Modify the local host resolution result to the real server to check whether the real server works normally. Firstly, edit the hosts file and ensure that the hosts binding has taken effect. Then connect to your domain name to check whether the real server can be accessed normally. If the access fails, perform the following steps:
- Protect the real server, as instructed in Measure 1.
- Ask for technical support to check and repair the data center, as instructed in Measure 2.
- Check whether the web service is normal and restore it if it works exceptionally, as instructed in Measure 3.
- Check whether performance metrics including the server process occupancy and memory usage are normal, and restore it if it works exceptionally, as instructed in Measure 4.
- Check the network level for troubleshooting. Alternatively, check the linkage status or change to another linkage. You can refer to Measure 5.
For more details, see Instructions for cause 2.
Solution to cause 3
Check whether there is a linkage failure and contact the network service provider for repair.
For more details, see Instructions for cause 3.
Instructions
Instructions for cause 1
Accept the Anti-DDoS Advanced forwarding IP range to access the firewall and host security software. The following takes the firewall of CentOS 6.5 as an example.
- Run the command to check the Linux firewall status.
service iptables status
- Run the command to check the firewall configuration file.
cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables - Run the command to restart the firewall.
service iptables start
- Run the command to check the firewall status again.
service iptables status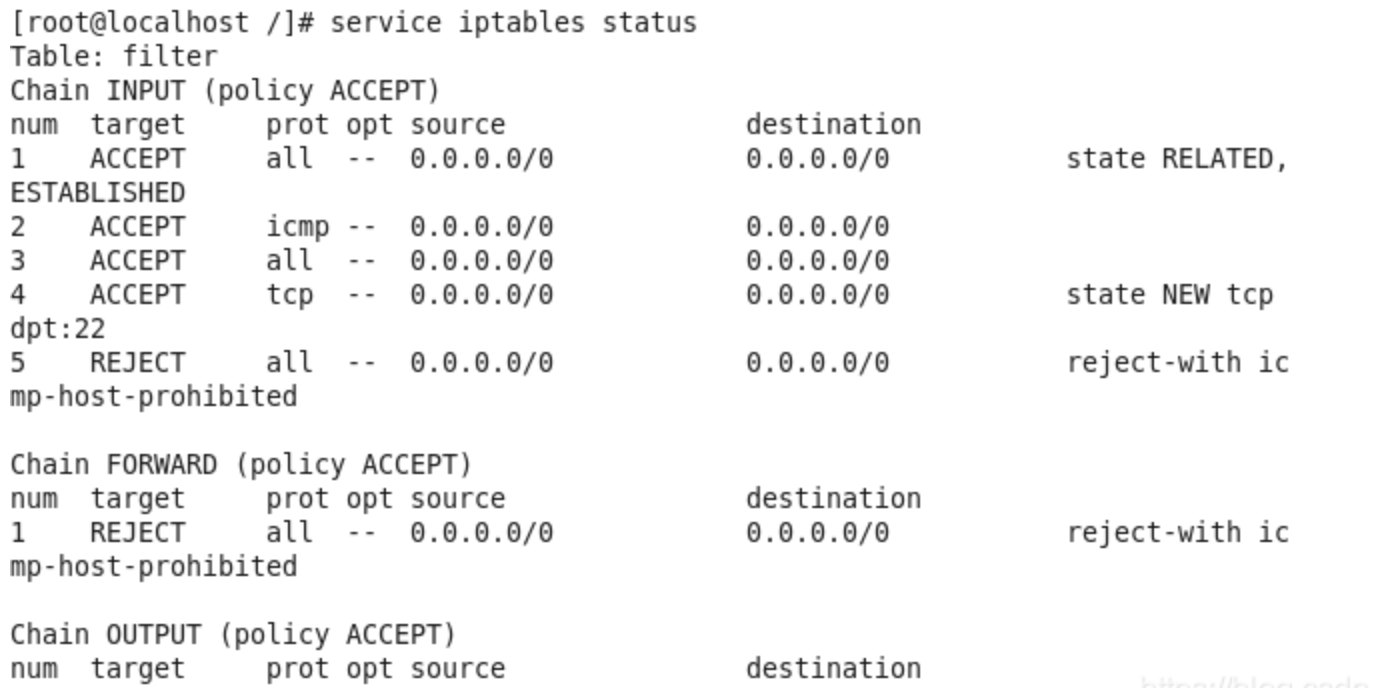
- Run the command to set the IP allowlist and allow the forwarding IP range to access the firewall.
Iptables -A INPUT -s Forwarding IP -j ACCEPT - Run the command to check whether the configured allowlist is added to the firewall setting.
iptables -nL --line-number - Run the command to save the firewall setting.
service iptables save
- Run the command to restart the firewall to have the configuration take effect.
service iptables restart
Instructions for cause 2
Modify the local host resolution result to the real server to check whether the real server is normal. Firstly, modify the local hosts file. The specific operations are as follows:
- Edit the local hosts file to allow the local request to access the real server. The following uses the Windows OS as an example to configure the local hosts file:
Open thehostsfile inC:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
For example, if the real server IP is 10.1.1.1 and the domain name is www.qqq.com, add:

Save the hosts file. Run the ping command on the protected domain name in the local computer.
When the resolved IP address is the real server IP address bound in the hosts file, the local hosts file is valid. If the real server IP is not resolved, run ipconfig /flushdns in the Windows Command Prompt to refresh the local DNS cache.
2. After the binding has taken effect, check whether the access of the real server is normal using the domain name. If it cannot be accessed normally, the following measures can be taken.
Measure 1: Protect the real server
Check whether the real server has a significant increase in the traffic and request volume, and the monitoring data from the Anti-DDoS Advanced console. The following describes how to check the real server traffic volume when the OS is CentOS.
- Check the traffic usage of a Linux server using iftop:
Run the command `iftop [-i interface]`. The parameter "interface" indicates the API name, such as eth0 and eth1.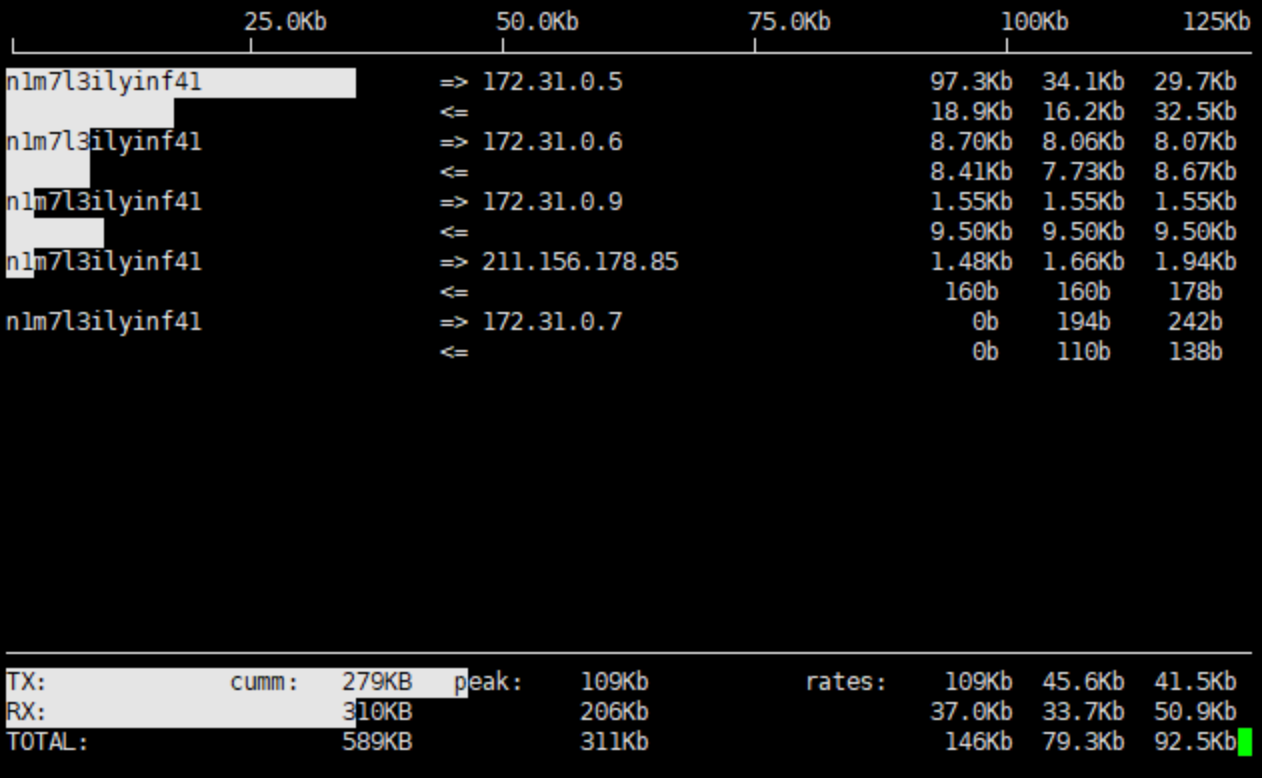
Output description:- The bandwidth usage is displayed at the top.
- The external connection list is at the middle. The list records IPs that are connecting to the local network.
- On the right of the list is real-time traffic information, which are the average traffic of 2 seconds, 10 seconds, and 40 seconds when the real server is accessed.
=>means sending data and<=means receiving data.- The bottom three lines:
- In the first column,
TXstands for sending traffic,RXfor receiving traffic, andTOTALfor total traffic. - In the second column,
cummstands for the total traffic in the first column. - In the third column,
peakstands for peak traffic in the first column. - In the fourth column,
ratesstands for the average traffic for each period of 2 seconds, 10 seconds, and 40 seconds.
- In the first column,
- To know how to view business traffic on the Anti-DDoS Advanced console, refer to Viewing Business Traffic Details.
If the real server is attacked by a large amount of traffic without any exceptions in the Anti-DDoS Advanced console, the attacks have bypassed the instance successfully. You can refer to [In Case of Real Server IP Exposed] (https://www.tencentcloud.com/document/product/297/15568) to deal with this situation.
Measure 2: Ask for technical support on data center
You can check whether the data center has physical hardware failures, such as failures with power, network card, drive, memory, and wiring.
Measure 3: Check the web service
Check the related monitoring of the origin server, CPU usage, memory usage, and bandwidth usage.
Note:
- Normally, if the usage of CPU or memory exceeds 90% for a long time, the web service is in abnormal status.
- Bandwidth usage needs to be compared with the business process occupancy during normal business periods and check if there is a significant increase. For more details, see CVM Bandwidth Utilization Is Too High.
If there is an exception, please contact technical support for further troubleshooting.
Measure 4: Check the server performance parameters
Self-check the web program status. Run the ps -C nginx -o pid command to check whether the server's nginx process is running normally.
If there is an exception, please contact technical support for further troubleshooting.
Measure 5: Check the network level or the linkage
Run a self-check on the linkage quality, linkage connectivity, and forwarding status of intermediate network equipment between the public network and the real server.
Instructions for cause 3
Check and monitor the public network quality of real server and the Anti-DDoS Advanced instance using the Tencent Cloud website monitoring platform.
If the public network is not working well, contact the service provider for assistance.

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?