Binding an ENI to a CVM
Last updated: 2024-10-23 10:24:13
This document describes how to bind a secondary ENI to a CVM.
Note:
You need to configure the security group for the secondary ENI separately based on your business situation. With no security group bound, the ENI does not have access control on in/outbound traffic by default. To bind the security groups, see binding security groups.
For CVMs using CentOS 8.0, 7.8, 7.6, 7.5 or 7.4 images, install a tool before binding an ENI. The ENI information is automatically configured in the ENI file, and the routing policy is automatically delivered. For more details, see Configuring an ENI on a Linux CVM.
For CVMs using other images, bind an ENI to the CVM as instructed below. Then complete the ENI configuration by referring to Configuring an ENI on a Linux CVM or Configuring an ENI on a Windows CVM.
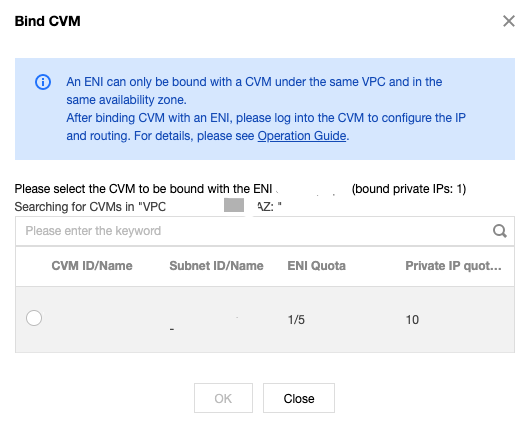
Binding to a CVM
1. Log in to the VPC console.
2. Click IP and ENI > ENI in the left sidebar.
3. Locate the row of the desired ENI, and click More > Bind CVM in the Operation column.

Note:
You can also click the ENI ID to go to the details page, and click Bind CVM.
The ENI can be bound to the CVMs in the same availability zone as the ENI. For more model limits, see Use Limits.
4. In the pop-up window, select the target CVM and click OK.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

