- User Guide
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- ES Kernel Enhancement
- Getting Started
- Data Application Guide
- Elasticsearch Guide
- Best Practices
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Instance APIs
- UpdateInstance
- RestartInstance
- DescribeInstances
- DeleteInstance
- CreateInstance
- DescribeInstanceOperations
- DescribeInstanceLogs
- UpgradeLicense
- UpgradeInstance
- UpdatePlugins
- RestartNodes
- RestartKibana
- UpdateRequestTargetNodeTypes
- GetRequestTargetNodeTypes
- DescribeViews
- UpdateDictionaries
- UpdateIndex
- DescribeIndexMeta
- DescribeIndexList
- DeleteIndex
- CreateIndex
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement
- Glossary
- New Version Introduction
- User Guide
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- ES Kernel Enhancement
- Getting Started
- Data Application Guide
- Elasticsearch Guide
- Best Practices
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Instance APIs
- UpdateInstance
- RestartInstance
- DescribeInstances
- DeleteInstance
- CreateInstance
- DescribeInstanceOperations
- DescribeInstanceLogs
- UpgradeLicense
- UpgradeInstance
- UpdatePlugins
- RestartNodes
- RestartKibana
- UpdateRequestTargetNodeTypes
- GetRequestTargetNodeTypes
- DescribeViews
- UpdateDictionaries
- UpdateIndex
- DescribeIndexMeta
- DescribeIndexList
- DeleteIndex
- CreateIndex
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement
- Glossary
- New Version Introduction
ES offers SDKs for different programming languages through its official website and community.
- Elasticsearch provides clients in a variety of programming languages, such as Java and Python, to meet the needs of different developers. For more information, please see Elasticsearch Clients.
- Starting from Elasticsearch 5.6.0, a new official Java client has been released: the Java High Level REST Client. This client can be used to perform search, index, delete, update, and bulk operations using the same core Java classes as the Transport Client does. It is actually designed to replace the Transport Client. For more information, please see Java High Level REST Client.
In terms of version compatibility, you are recommended to choose the client version that is compatible with the server version. For more information, please see Compatibility. Currently, ES is available in multiple Elasticsearch versions, so be sure to select a compatible client version.
ES provides a VIP for accessing your ES cluster in your VPC, to which all nodes in your ES cluster are mounted through load balancing. This aims to adapt to the auto scaling of your cluster and ensure its high availability. In case of any changes in the nodes, the VIP will automatically update node information. In addition, this simplifies operations and eliminates your need to focus on changes in the information about cluster nodes such as IP and port.
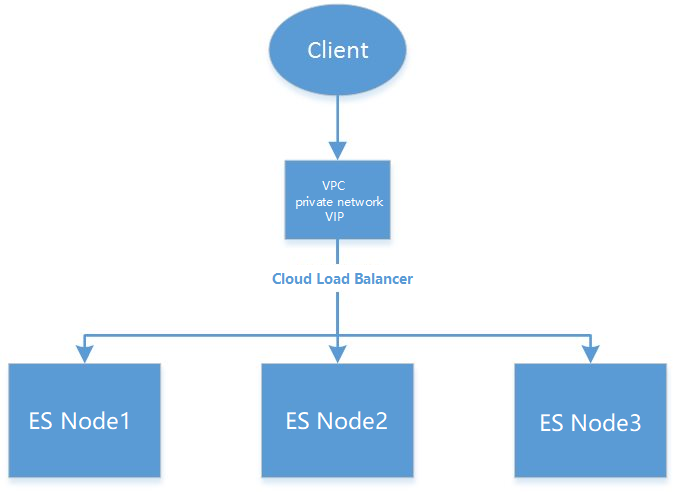
You are not recommended to connect a client to ES nodes directly through Transport Client.
The SDKs of ES allow you configure the address of only one node when creating a connection and use the "node sniffing" feature to sniff out all nodes for connection. However, this goes against our original intention of launching the VIP feature and increases the complexity of using an ES cluster. The following describes how to use the SDKs for different programming languages and how to turn off node sniffing.
Java Client
ES recommends that you connect to your cluster and manipulate data using the Java REST Client, which comes in two types: Low Level and High Level:
- Java Low Level REST Client: when using this client, you need to manually splice the body of an HTTP request into JSON format and encapsulate the returned JSON data in the HTTP response into an object.
- Java High Level REST Client: this client is implemented based on the Low Level Client and provides APIs to eliminate the need to manually convert data format.
The sample steps and code for accessing a cluster using the Java High Level REST Client are as follows:
Adding Maven dependencies
You are recommended to choose the Java REST Client API version that is compatible with the server edition of your ES cluster. Currently, ES is available in multiple versions, so be sure to select a compatible client version. For more information on client APIs, please see Elasticsearch API Version Compatibility.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>6.4.3</version>
</dependency>
- The client version should be compatible with the ES cluster version; otherwise, a compatibility issue may occur. The demo here is applicable to ES 6.4.3. For more information on how to use other versions, please see Java High Level REST Client.
- The Java High REST Client is built on the Java Low REST Client, and both of them connect to an ES cluster using the HTTP protocol. The Java High Level REST provides more APIs with version upgrading. If the APIs currently provided by it cannot meet your needs, you can upgrade your ES cluster version and client version.
- The Transport Client that uses the TCP protocol to connect to an ES cluster is no longer updated, so you are recommended to use the Java High Level or Low Level Client that uses the HTTP protocol. For more information, please see Migrating from Transport Client to Java High REST Client.
Sample code
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.apache.http.auth.AuthScope;
import org.apache.http.auth.UsernamePasswordCredentials;
import org.apache.http.client.CredentialsProvider;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.BasicCredentialsProvider;
import org.apache.http.impl.nio.client.HttpAsyncClientBuilder;
import org.apache.log4j.BasicConfigurator;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchException;
import org.elasticsearch.action.DocWriteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.rest.RestStatus;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class test_es_sdk {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(test_es_sdk.class);
public static void main(String[]args){
BasicConfigurator.configure();
// Set verification information by entering the username and password
final CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
credentialsProvider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY,
new UsernamePasswordCredentials("user", "passwd"));
// Initialize RestClient. For hostName and port, enter the private VIP address and port of the cluster respectively
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("xx.xx.xx.xx", 9200, "http"));
// Set authentication information
builder.setHttpClientConfigCallback(new RestClientBuilder.HttpClientConfigCallback() {
@Override
public HttpAsyncClientBuilder customizeHttpClient(HttpAsyncClientBuilder httpClientBuilder) {
return httpClientBuilder.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider);
}
});
// Set the timeout period
builder.setMaxRetryTimeoutMillis(10000);
// Construct the High Level Client based on the Low Level Client
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
// Index the document
Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
jsonMap.put("user", "bellen");
jsonMap.put("name", new Date());
jsonMap.put("message", "trying out Elasticsearch");
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("posts", "doc", "1")
.source(jsonMap);
try {
// Get the response result
IndexResponse indexResponse = client.index(indexRequest);
String index = indexResponse.getIndex();
String type = indexResponse.getType();
String id = indexResponse.getId();
long version = indexResponse.getVersion();
if (indexResponse.getResult() == DocWriteResponse.Result.CREATED) {
logger.info("doc indexed, index: "+ index +", type:"+ type +",id:"+ id+",version:"+version);
} else if (indexResponse.getResult() == DocWriteResponse.Result.UPDATED) {
logger.info("doc updated, index: "+ index +", type:"+ type +",id:"+ id+",version:"+version);
}
}catch(ElasticsearchException e) {
if (e.status() == RestStatus.CONFLICT) {
logger.error("version conflict");
}
}catch(Exception e){
logger.error("execute index api failed, "+ e.toString());
}
// Query the document
GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest(
"posts",
"doc",
"1");
try {
// Get the response result
GetResponse getResponse = client.get(getRequest);
String index = getResponse.getIndex();
String type = getResponse.getType();
String id = getResponse.getId();
if (getResponse.isExists()) {
long version = getResponse.getVersion();
String sourceAsString = getResponse.getSourceAsString();
logger.info("get doc, index: "+ index +", type:"+ type +",id:"+ id+",version:"+version +", source:"+ sourceAsString);
}
}catch (ElasticsearchException e) {
if (e.status() == RestStatus.NOT_FOUND) {
logger.warn("doc not found");
}
}
catch(Exception e){
logger.error("execute get api failed, "+ e.toString());
}
// Close the client
try {
client.close();
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("close rest client exception:"+ e.toString());
}
}
}
Python Client
Installing through pip
pip install elasticsearchSample code
Set the following three parameters of the Elasticsearch function to turn off node sniffing:
sniff_on_start=Falsesniff_on_connection_fail=Falsesniffer_timeout=None
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
es = Elasticsearch(["http://xx.xx.xx.xx:9200"],
http_auth=('user', 'passwd'),
sniff_on_start=False,
sniff_on_connection_fail=False,
sniffer_timeout=None)
res = es.index(index="my_index", doc_type="my_type", id=1, body={"title": "One", "tags": ["ruby"]})
print(res)
res = es.get(index="my_index", doc_type="my_type", id=1)
print(res['_source'])PHP Client
To avoid sniffing of nodes, you can set the connection pool class as StaticConnectionPool. Do not use the node sniffing connection pool.
Sample code
$client = ClientBuilder::create()
->setConnectionPool('\Elasticsearch\ConnectionPool\StaticConnectionPool', ["http://user:passwd@xx.xx.xx.xx:9200"])
->build();Go Client
gopkg.in/olivere/elastic is a community-contributed SDK that is widely used in the Go language. The demo here is applicable to ES 6.4.3. For information on how to use other versions, please see here.
Installing elastic
go get github.com/olivere/elasticSample code
In the parameters of the NewClient function, set elastic.SetSniff(false) to turn off node sniffing and set elastic.SetHealthcheck(false) to turn off node health check.
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/olivere/elastic"
)
func main() {
client, err := elastic.NewClient(elastic.SetURL("http://user:passwd@xx.xx.xx.xx:9200"),
elastic.SetSniff(false),elastic.SetHealthcheck(false))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
exists, err := client.IndexExists("twitter").Do(context.Background())
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(exists)
}
 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?