







Support L4 and L7 listeners, including TCP, UDP, TCP-SSL, QUIC, HTTP, HTTPS, and WebSocket (Secure). Layer 7 supports traffic distribution based on forwarding domain name and URL.

Support L4 and L7 listeners, including TCP, UDP, TCP-SSL, QUIC, HTTP, HTTPS, and WebSocket (Secure). Layer 7 supports traffic distribution based on forwarding domain name and URL.

Weight configuration enables faster request processing for backend cloud services. Traffic is distributed to different backend servers via CLB based on weight ratio, or through hash and polling results of the source IP address.

Weight configuration enables faster request processing for backend cloud services. Traffic is distributed to different backend servers via CLB based on weight ratio, or through hash and polling results of the source IP address.

Cloud Load Balancer (CLB) supports Content-based Routing with layer-7 protocol. It allows custom domains/URLs, forwarding rules, and forwarding group Content. Users can distribute requests to different real servers under various forwarding rules. By dividing target groups through CLB, business separation is achieved, significantly improving service efficiency.

Cloud Load Balancer (CLB) supports Content-based Routing with layer-7 protocol. It allows custom domains/URLs, forwarding rules, and forwarding group Content. Users can distribute requests to different real servers under various forwarding rules. By dividing target groups through CLB, business separation is achieved, significantly improving service efficiency.

Application-based CLB supports the custom redirect feature (Rewrite) for L7 protocol, which addresses two major challenges:
-Force HTTPS: When PCs or mobile browsers access web services via HTTP requests, the CLB proxy returns HTTPS responses to the browser, enforcing HTTPS access to the web page.
-Redirect a single path. For example, when a Web business needs to go temporarily offline (such as e-commerce business sold out, page maintenance, or update), redirect the original page to a new page.

Application-based CLB supports the custom redirect feature (Rewrite) for L7 protocol, which addresses two major challenges:
-Force HTTPS: When PCs or mobile browsers access web services via HTTP requests, the CLB proxy returns HTTPS responses to the browser, enforcing HTTPS access to the web page.
-Redirect a single path. For example, when a Web business needs to go temporarily offline (such as e-commerce business sold out, page maintenance, or update), redirect the original page to a new page.

CLB supports weighted round-robin scheduling, IP Hash, and weighted least connections as the three scheduling algorithms, as well as backend server weight settings to ensure more even traffic scheduling and enhance CLB capacity.

CLB supports weighted round-robin scheduling, IP Hash, and weighted least connections as the three scheduling algorithms, as well as backend server weight settings to ensure more even traffic scheduling and enhance CLB capacity.

For L4 services, CLB provides IP-based session persistence. During load balancing, CLB uses the source address of the request as the basis for associating sessions, forwarding all access requests from the same IP (subnet) to the same server. For layer-7 business, CLB offers cookie-based session persistence. CLB is responsible for embedding cookies, and no configuration is required on the real server.

For L4 services, CLB provides IP-based session persistence. During load balancing, CLB uses the source address of the request as the basis for associating sessions, forwarding all access requests from the same IP (subnet) to the same server. For layer-7 business, CLB offers cookie-based session persistence. CLB is responsible for embedding cookies, and no configuration is required on the real server.

CLB performs scheduled detection to check if backend cloud services are running properly. You can customize health check frequency. If server exceptions are detected, CLB stops directing traffic to these affected instances and filters out healthy instances to ensure business continuity.

CLB performs scheduled detection to check if backend cloud services are running properly. You can customize health check frequency. If server exceptions are detected, CLB stops directing traffic to these affected instances and filters out healthy instances to ensure business continuity.

Public network CLB supports primary-secondary AZ mode. When the primary availability zone fails, the load balancer will switch automatically to the secondary AZ and restore service in super short time. Private network CLB implements Closest Access Architecture, where a single CLB instance is deployed to one or more availability zones. When clients access the CLB, traffic is automatically directed to the cluster with minimum latency in the availability zone and forwarded to the backend server. If the CLB cluster in a certain availability zone becomes unavailable, it can switch to the CLB cluster in other availability zones.

Public network CLB supports primary-secondary AZ mode. When the primary availability zone fails, the load balancer will switch automatically to the secondary AZ and restore service in super short time. Private network CLB implements Closest Access Architecture, where a single CLB instance is deployed to one or more availability zones. When clients access the CLB, traffic is automatically directed to the cluster with minimum latency in the availability zone and forwarded to the backend server. If the CLB cluster in a certain availability zone becomes unavailable, it can switch to the CLB cluster in other availability zones.

Support L4 and L7 listeners, including TCP, UDP, TCP-SSL, QUIC, HTTP, HTTPS, and WebSocket (Secure). Layer 7 supports traffic distribution based on forwarding domain name and URL.

Weight configuration enables faster request processing for backend cloud services. Traffic is distributed to different backend servers via CLB based on weight ratio, or through hash and polling results of the source IP address.

Cloud Load Balancer (CLB) supports Content-based Routing with layer-7 protocol. It allows custom domains/URLs, forwarding rules, and forwarding group Content. Users can distribute requests to different real servers under various forwarding rules. By dividing target groups through CLB, business separation is achieved, significantly improving service efficiency.

Application-based CLB supports the custom redirect feature (Rewrite) for L7 protocol, which addresses two major challenges:
-Force HTTPS: When PCs or mobile browsers access web services via HTTP requests, the CLB proxy returns HTTPS responses to the browser, enforcing HTTPS access to the web page.
-Redirect a single path. For example, when a Web business needs to go temporarily offline (such as e-commerce business sold out, page maintenance, or update), redirect the original page to a new page.

CLB supports weighted round-robin scheduling, IP Hash, and weighted least connections as the three scheduling algorithms, as well as backend server weight settings to ensure more even traffic scheduling and enhance CLB capacity.

For L4 services, CLB provides IP-based session persistence. During load balancing, CLB uses the source address of the request as the basis for associating sessions, forwarding all access requests from the same IP (subnet) to the same server. For layer-7 business, CLB offers cookie-based session persistence. CLB is responsible for embedding cookies, and no configuration is required on the real server.

CLB performs scheduled detection to check if backend cloud services are running properly. You can customize health check frequency. If server exceptions are detected, CLB stops directing traffic to these affected instances and filters out healthy instances to ensure business continuity.

Public network CLB supports primary-secondary AZ mode. When the primary availability zone fails, the load balancer will switch automatically to the secondary AZ and restore service in super short time. Private network CLB implements Closest Access Architecture, where a single CLB instance is deployed to one or more availability zones. When clients access the CLB, traffic is automatically directed to the cluster with minimum latency in the availability zone and forwarded to the backend server. If the CLB cluster in a certain availability zone becomes unavailable, it can switch to the CLB cluster in other availability zones.
- The business has obvious peaks and valleys, and business stability and low costs are desired.
Scenario Description
- The business goes through significant peaks and troughs and requires the flexible control of backend resources.
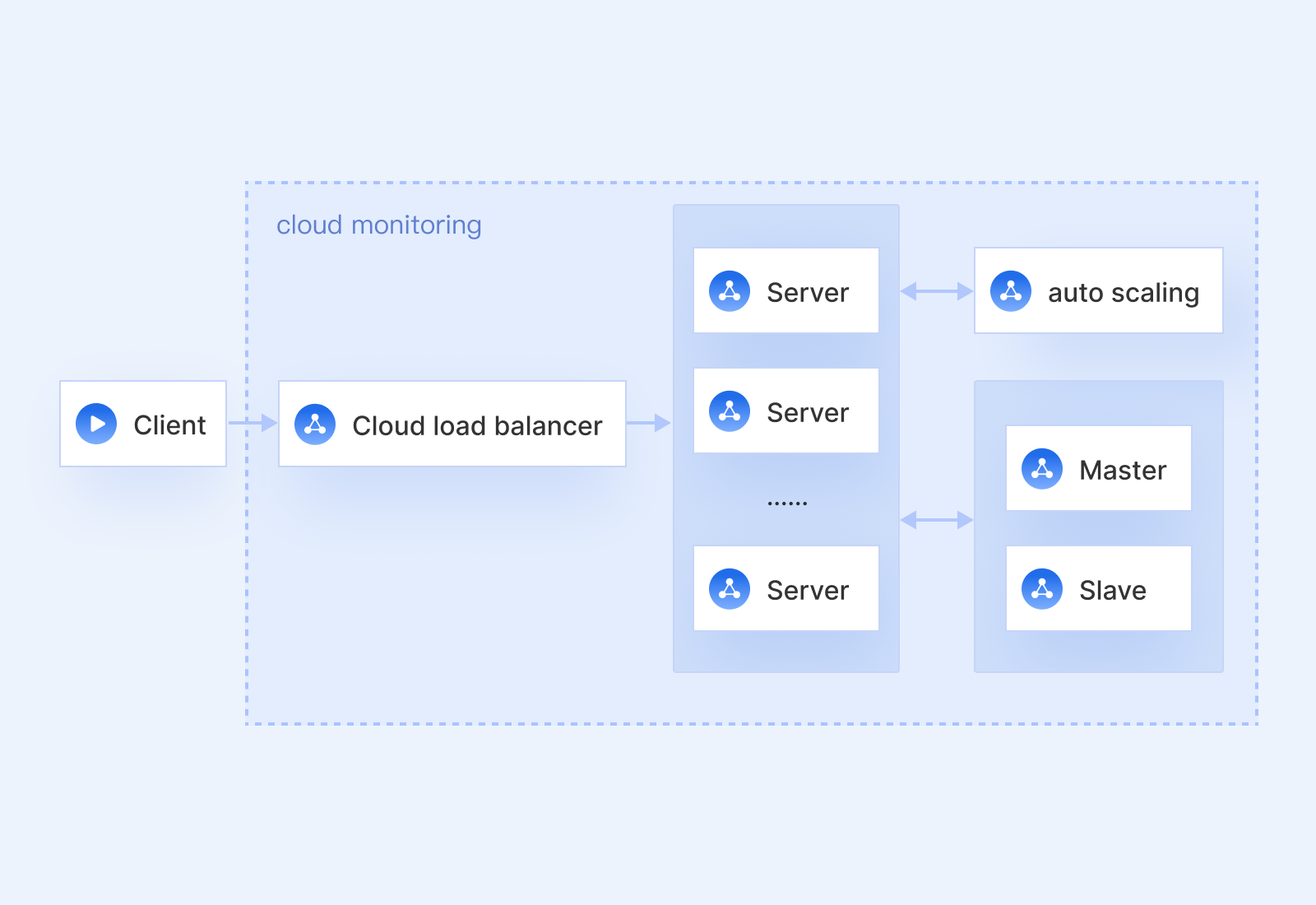
The business has requirements that are highly time-sensitive. For example, during ecommerce promotion campaigns, web page views may increase by over 10 times within a few hours, and a large number of backend CVMs need to be added when the number of visitors surges. When the traffic drops, the unnecessary CVMs needs to be terminated. You can use CLB to distribute traffic to the business systems, which helps flexibly enhance the service capabilities of the application systems and elastically adjust the backend resources in real time.
- The business has high peak traffic and needs to build a low-cost architecture.
When a business has high peak traffic, using traditional hardware to build a cluster is very costly and requires tedious OPS work. CLB can work together with Cloud Monitor to effectively manage high peak traffic and reduce deployment costs, relieving you from hardware OPS duties and allowing you to focus instead on developing product features.
- The business has complex modules and requires the separation of dynamic and static services.
Scenario Description
- The business requires the separation of dynamic and static services and flexible forwarding.
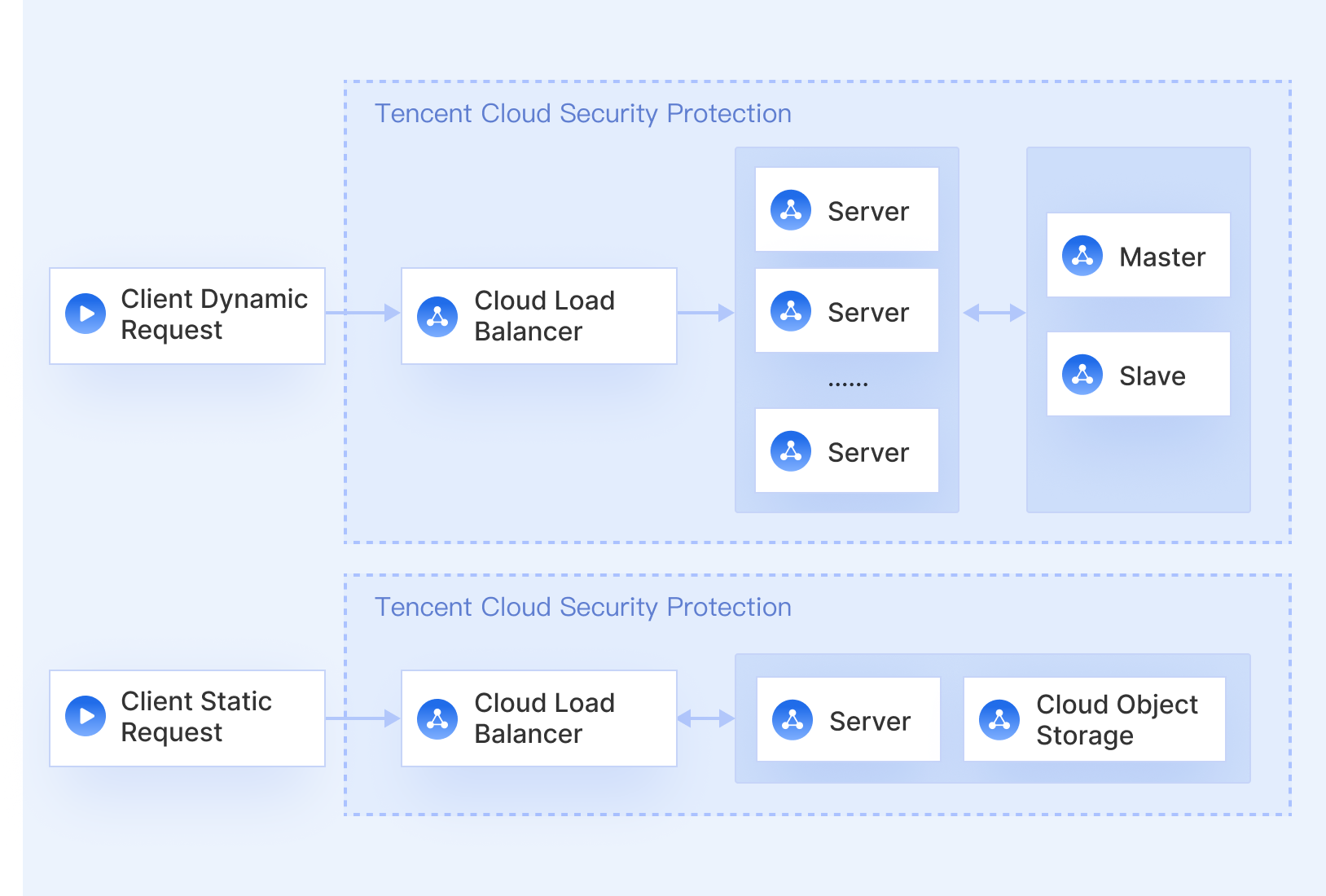
When the number of requests is high, the targeted distribution of requests to the website can be achieved by differentiating the static and dynamic requests, effectively reducing the backend load pressure. The dynamic requests can be processed by the independently deployed CLB and associated backend CVM clusters, while the static content can be connected to CDN and optimized by COS to significantly improve the loading speed.
- The website or business requires data interconnection.
Scenario Description
- The business requires content-based routing and forwarding for IP convergence.
A large website generally has hundreds of business modules. CLB can analyze HTTP headers by setting different forwarding rules or groups to separate the business modules and achieve content-based routing and forwarding. In addition, you can use custom forwarding paths instead of second-level domain names to reduce the number of DNS polls, converge IPs and improve the service accessing speed.
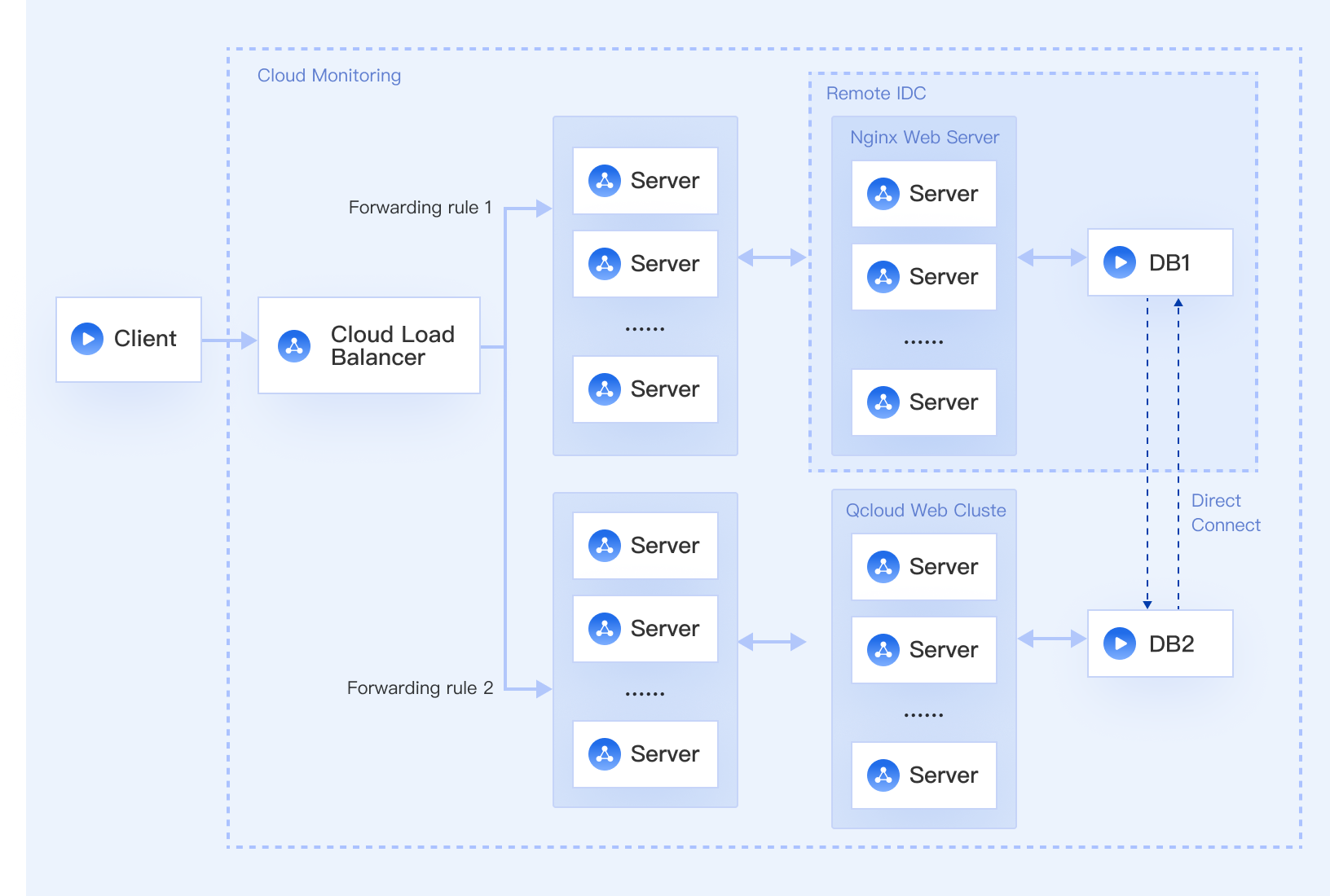
- The Direct Connect-hybrid cloud solution achieves stable data transfer and flexible migration.
With Tencent Cloud's hybrid cloud solution, the core internal systems and data of the business can be stored in the user-built IDC, and the services can be deployed in the cloud to cope with the surge in user traffic. Direct Connect ensures the stability and speed of in/off-cloud data transfer to guarantee data consistency. In addition, the business can be gradually migrated to the cloud through flexible weight configuration, and combined with the data transfer feature of Direct Connect, an elastic, fast, reliable and low-cost business deployment can be easily implemented.
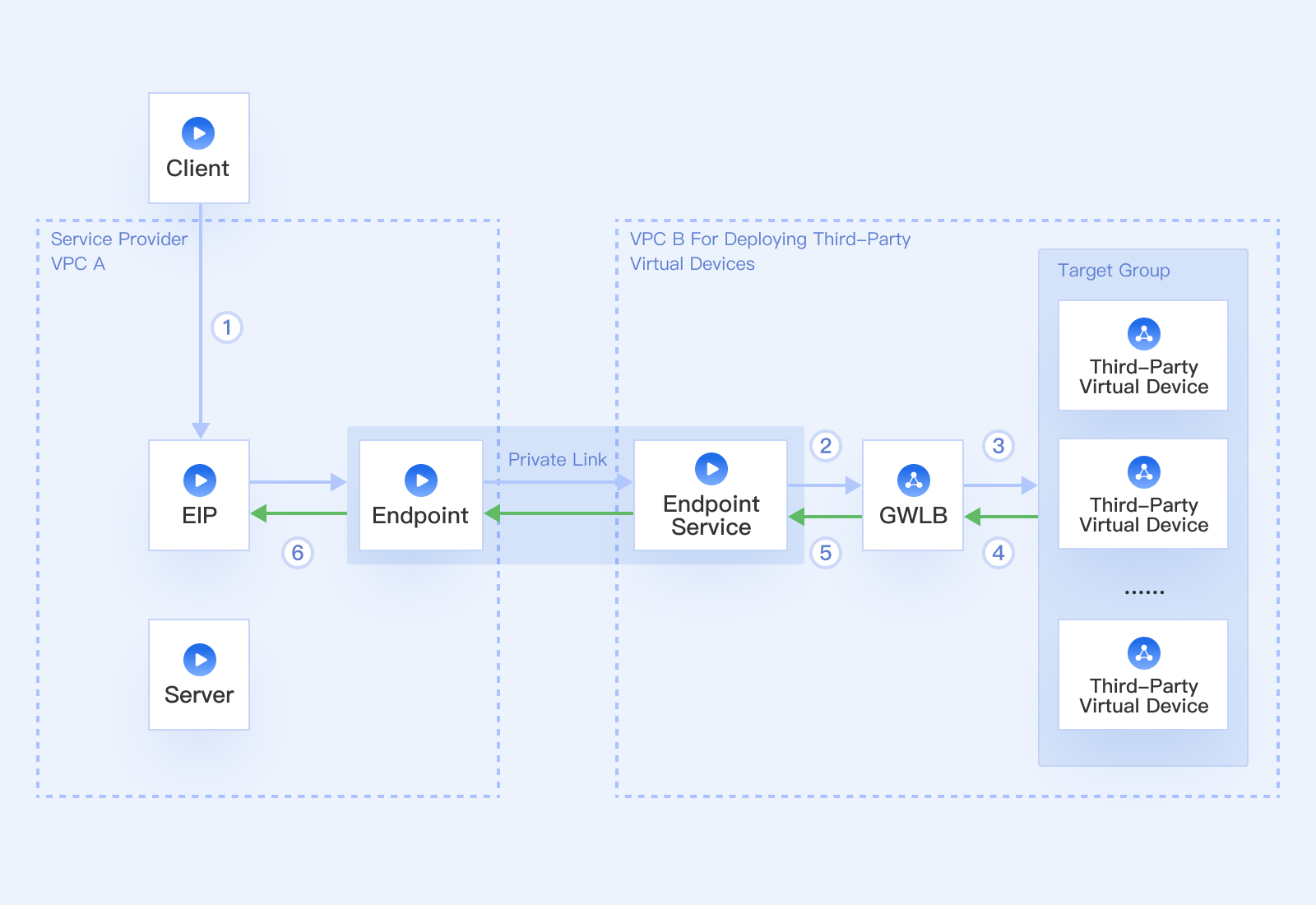
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) is a load balancer running at the network layer. The GWLB instance helps customers deploy, scale, and manage third-party virtual devices such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, analysis, and visibility, making operations simpler and security stronger.
GWLB, in conjunction with third-party virtual devices such as firewalls, can detect inbound and outbound traffic while ensuring high availability zones. GWLB uses the GENEVE protocol to communicate with firewalls, forwards the received traffic to a group of firewalls at the backend, and performs management features such as health checks and load balancing.
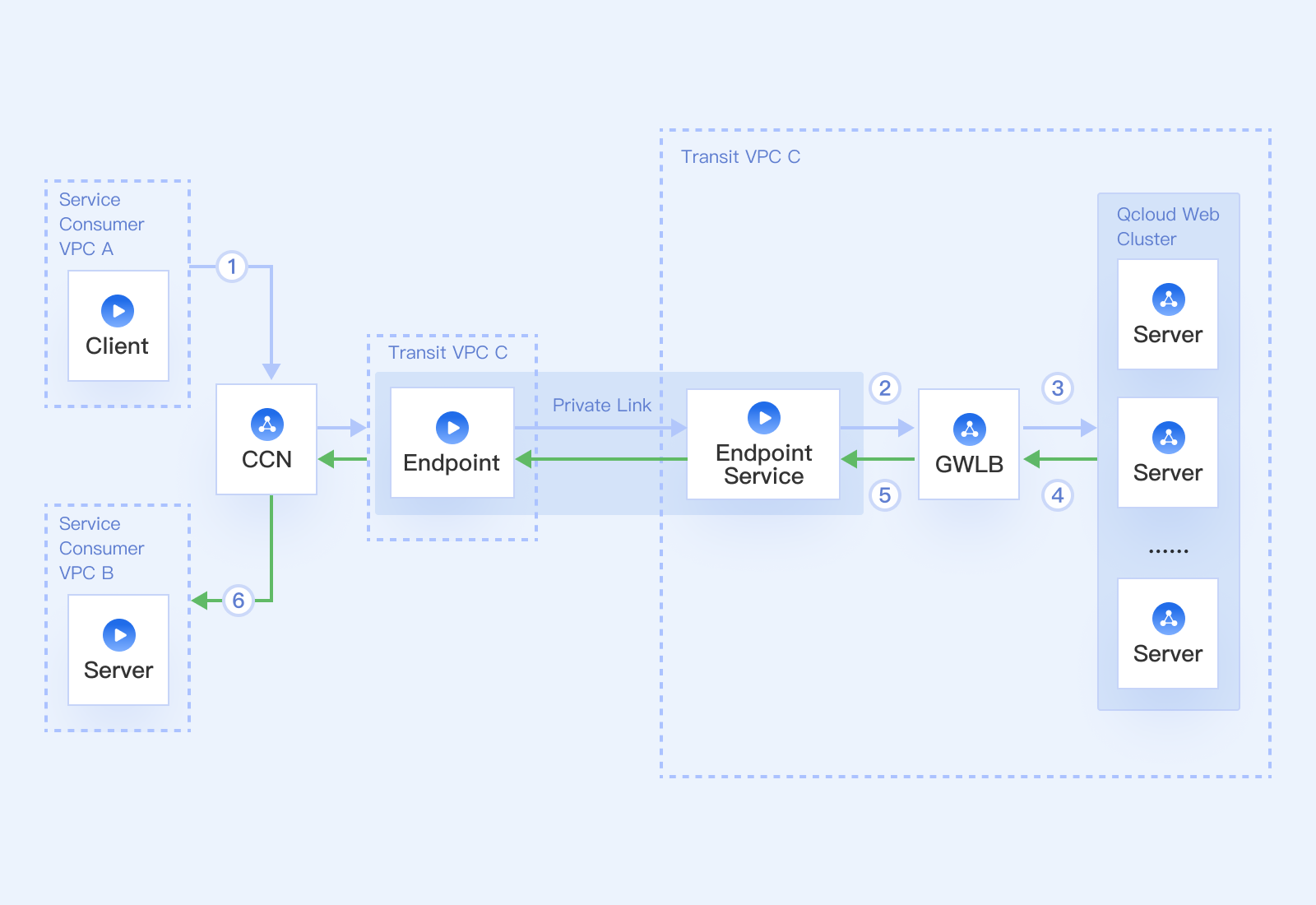
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) is a load balancer running at the network layer. The GWLB instance helps customers deploy, scale, and manage third-party virtual devices such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, analysis, and visibility, making operations simpler and security stronger.
GWLB associates the Elastic IP with the terminal node. Access from the public network to the VPC network where the GWLB instance resides is available through Private Link. Third-party virtual devices, such as firewalls, are deployed directly in the network data path so that all passing data packets will be checked and processed by the firewalls. This stops malicious data from entering the network and protects internal resources from attacks.