- User Guide
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- ES Kernel Enhancement
- Getting Started
- Data Application Guide
- Elasticsearch Guide
- Best Practices
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Instance APIs
- UpdateInstance
- RestartInstance
- DescribeInstances
- DeleteInstance
- CreateInstance
- DescribeInstanceOperations
- DescribeInstanceLogs
- UpgradeLicense
- UpgradeInstance
- UpdatePlugins
- RestartNodes
- RestartKibana
- UpdateRequestTargetNodeTypes
- GetRequestTargetNodeTypes
- DescribeViews
- UpdateDictionaries
- UpdateIndex
- DescribeIndexMeta
- DescribeIndexList
- DeleteIndex
- CreateIndex
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement
- Glossary
- New Version Introduction
- User Guide
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- ES Kernel Enhancement
- Getting Started
- Data Application Guide
- Elasticsearch Guide
- Best Practices
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Instance APIs
- UpdateInstance
- RestartInstance
- DescribeInstances
- DeleteInstance
- CreateInstance
- DescribeInstanceOperations
- DescribeInstanceLogs
- UpgradeLicense
- UpgradeInstance
- UpdatePlugins
- RestartNodes
- RestartKibana
- UpdateRequestTargetNodeTypes
- GetRequestTargetNodeTypes
- DescribeViews
- UpdateDictionaries
- UpdateIndex
- DescribeIndexMeta
- DescribeIndexList
- DeleteIndex
- CreateIndex
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement
- Glossary
- New Version Introduction
Exceptional Cluster Health Status (Red and Yellow)
Last updated: 2021-08-11 11:17:23
Why is the cluster in an exceptional status?
In the following conditions, the cluster will be in the red or yellow status:
- If the cluster has any unassigned primary index shard, the cluster status will become red, which affects index reads/writes and thus requires special attention.
- If all primary index shards in the cluster have been assigned, but there are still unassigned replica index shards, the cluster status will become yellow, which does not affect index reads/writes and generally can be automatically recovered.
Viewing Cluster Status
You can use Kibana Dev Tools to view the cluster status:
GET /_cluster/health
Here, you can see that the current cluster status is red, and there are nine unassigned shards.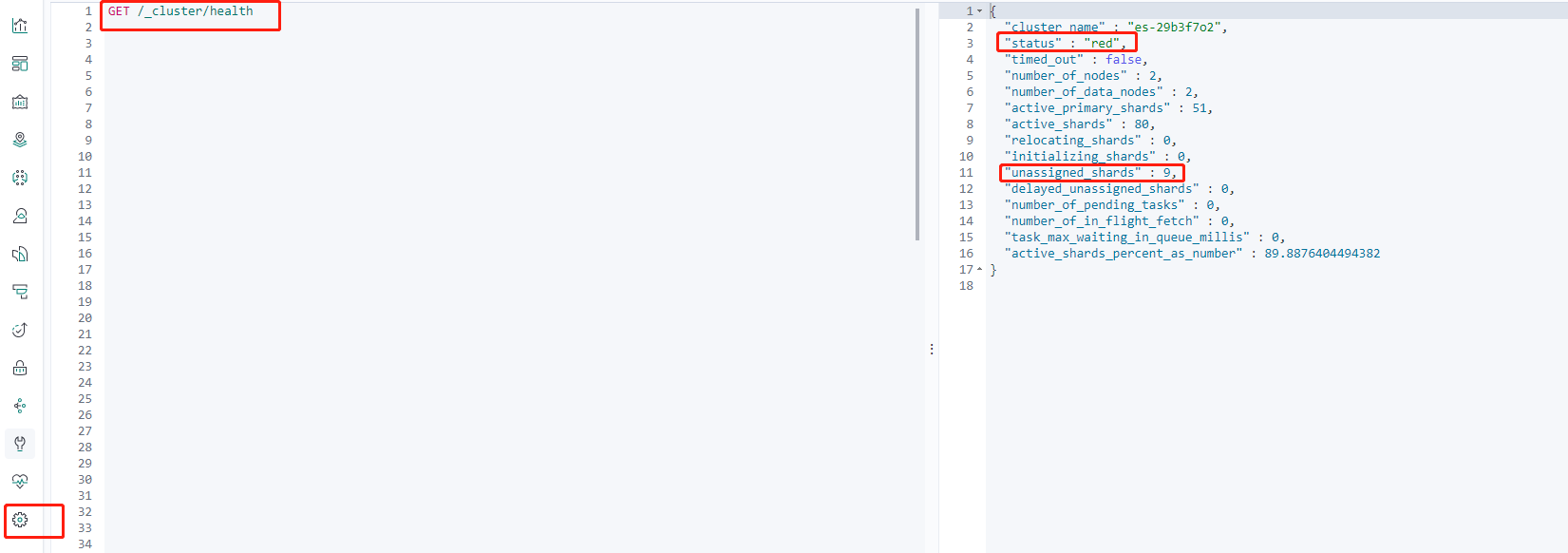
Official descriptions of the Elasticsearch health API responses:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| cluster_name | Cluster name |
| status | Health status of the cluster, based on the state of its primary and replica shards. Statuses are: – green: all shards are assigned – yellow: all primary shards are assigned, but one or more replica shards are unassigned. If a node in the cluster fails, some data may be unavailable until that node is repaired – red: one or more primary shards are unassigned, so some data is unavailable. This can occur briefly during cluster startup as primary shards are assigned |
| timed_out | If false, the response is returned within the period of time that is specified by the timeout parameter (30s by default) |
| number_of_nodes | Number of nodes in the cluster |
| number_of_data_nodes | Number of nodes that are dedicated data nodes |
| active_primary_shards | Number of active primary shards |
| active_shards | Total number of active primary and replica shards |
| relocating_shards | Number of shards that are under relocation |
| initializing_shards | Number of shards that are under initialization |
| unassigned_shards | Number of unassigned shards |
| delayed_unassigned_shards | Number of shards whose assignment has been delayed by the timeout settings |
| number_of_pending_tasks | Number of cluster-level changes that have not yet been executed |
| number_of_in_flight_fetch | Number of unfinished fetches |
| task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis | Time expressed in milliseconds since the earliest initiated task is waiting for being performed |
| active_shards_percent_as_number | Ratio of active shards in the cluster expressed as a percentage |
Troubleshooting
If a cluster is exceptional, you need to pay attention to the shards that are not assigned properly in unassigned_shards. The following is an example:
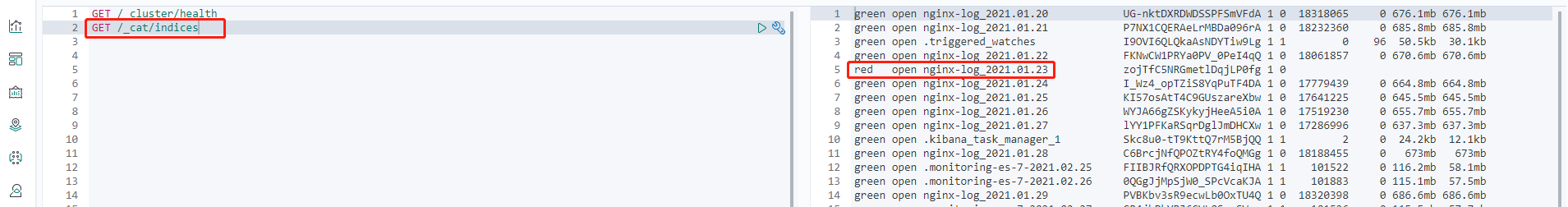
Finding exceptional index
View the index status and find the exceptional index based on the response.
GET /_cat/indices
Viewing exception details
GET /_cluster/allocation/explain
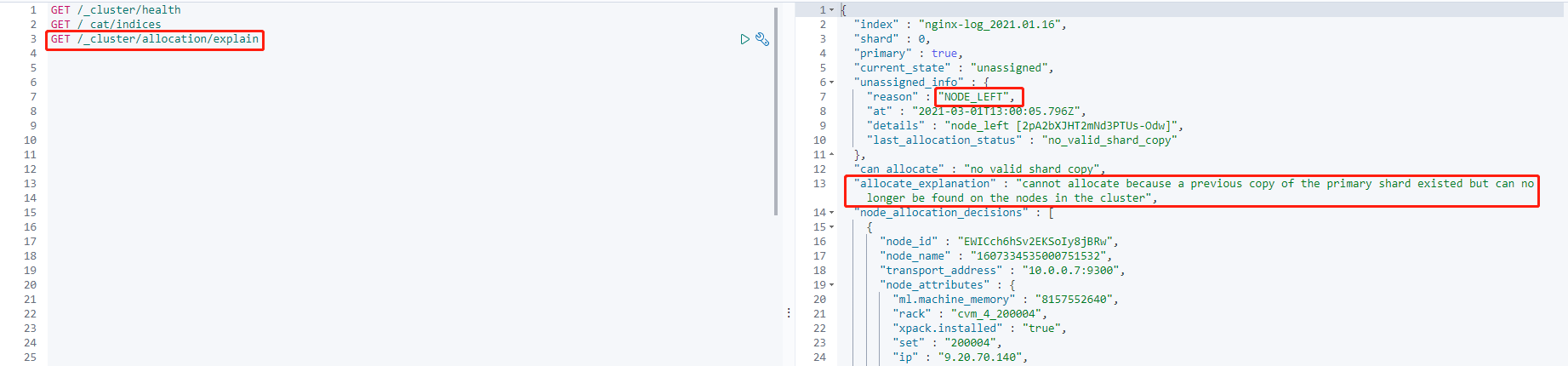
Through the exception information, you can see that:
- The primary shard is currently in the unassigned status (
current_state). This problem occurs because the node to which the shard was assigned left the cluster (unassigned_info.reason). - After the above problem occurs, the shard cannot be automatically assigned because there are no available replicas of the shard in the cluster (
can_allocate). - In addition, more detailed information is provided (
allocate_explanation).
This problem occurs because the cluster has an offline node, so the primary shard has no available shard data. Currently, the only thing you can do is to wait for the node to recover and join the cluster again.
Note:In some extreme cases (for example, a shard in a single-replica cluster is corrupted, or the file system fails, causing the node to be removed permanently), you can only accept the fact of data loss and use the reroute command to assign an empty primary shard again. To avoid such cases as much as possible, we recommend you appropriately design index shards and refrain from setting a single replica for the index (single replica is also called zero replica, which means that an index has a primary shard but no replica shards). With the appropriate design of index shards, you can control the total number of shards in the cluster at a healthy scale, make better use of the distributed cluster characteristics while ensuring high availability, and improve the overall cluster performance.
All possible reasons of unassigned shards (unassigned_info.reason)
You can use the following analysis methods to preliminarily figure out the reason why there is an unassigned shard in the cluster. Generally, you can find the reason through the allocation explain API.
Note:If the cluster status hasn't automatically recovered after a long period of time, or you cannot fix the problem, please submit a ticket for assistance.
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| INDEX_CREATED | Unassigned as a result of an API creation of an index |
| CLUSTER_RECOVERED | Unassigned as a result of a full cluster recovery |
| INDEX_REOPENED | Unassigned as a result of opening a closed index |
| DANGLING_INDEX_IMPORTED | Unassigned as a result of importing a dangling index |
| NEW_INDEX_RESTORED | Unassigned as a result of restoring into a new index |
| EXISTING_INDEX_RESTORED | Unassigned as a result of restoring into a closed index |
| REPLICA_ADDED | Unassigned as a result of explicit addition of a replica |
| ALLOCATION_FAILED | Unassigned as a result of a failed allocation of the shard |
| NODE_LEFT | Unassigned as a result of the node hosting it leaving the cluster |
| REROUTE_CANCELLED | Unassigned as a result of explicit cancel reroute command |
| REINITIALIZED | When a shard moves from started back to initializing |
| REALLOCATED_REPLICA | A better replica location is identified and causes the existing replica allocation to be canceled |

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?