- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Instance Management
- Creating Instance
- Naming with Consecutive Numeric Suffixes or Designated Pattern String
- Viewing Instance
- Upgrading Instance
- Downgrading Instance Configuration
- Terminating/Returning Instances
- Change from Pay-as-You-Go to Monthly Subscription
- Upgrading Instance Version
- Adding Routing Policy
- Public Network Bandwidth Management
- Connecting to Prometheus
- AZ Migration
- Setting Maintenance Time
- Setting Message Size
- Topic Management
- Consumer Group
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Smart Ops
- Permission Management
- Tag Management
- Querying Message
- Event Center
- Migration to Cloud
- Data Compression
- Instance Management
- CKafka Connector
- Best Practices
- Connector Best Practices
- Connecting Flink to CKafka
- Connecting Schema Registry to CKafka
- Connecting Spark Streaming to CKafka
- Connecting Flume to CKafka
- Connecting Kafka Connect to CKafka
- Connecting Storm to CKafka
- Connecting Logstash to CKafka
- Connecting Filebeat to CKafka
- Multi-AZ Deployment
- Production and Consumption
- Log Access
- Replacing Supportive Route (Old)
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- DataHub APIs
- ACL APIs
- Topic APIs
- BatchModifyGroupOffsets
- BatchModifyTopicAttributes
- CreateConsumer
- CreateDatahubTopic
- CreatePartition
- CreateTopic
- CreateTopicIpWhiteList
- DeleteTopic
- DeleteTopicIpWhiteList
- DescribeDatahubTopic
- DescribeTopic
- DescribeTopicAttributes
- DescribeTopicDetail
- DescribeTopicProduceConnection
- DescribeTopicSubscribeGroup
- FetchMessageByOffset
- FetchMessageListByOffset
- ModifyDatahubTopic
- ModifyTopicAttributes
- DescribeTopicSyncReplica
- Instance APIs
- Route APIs
- Other APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- SDK Documentation
- General References
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement (New Version)
- Contact Us
- Glossary
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Instance Management
- Creating Instance
- Naming with Consecutive Numeric Suffixes or Designated Pattern String
- Viewing Instance
- Upgrading Instance
- Downgrading Instance Configuration
- Terminating/Returning Instances
- Change from Pay-as-You-Go to Monthly Subscription
- Upgrading Instance Version
- Adding Routing Policy
- Public Network Bandwidth Management
- Connecting to Prometheus
- AZ Migration
- Setting Maintenance Time
- Setting Message Size
- Topic Management
- Consumer Group
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Smart Ops
- Permission Management
- Tag Management
- Querying Message
- Event Center
- Migration to Cloud
- Data Compression
- Instance Management
- CKafka Connector
- Best Practices
- Connector Best Practices
- Connecting Flink to CKafka
- Connecting Schema Registry to CKafka
- Connecting Spark Streaming to CKafka
- Connecting Flume to CKafka
- Connecting Kafka Connect to CKafka
- Connecting Storm to CKafka
- Connecting Logstash to CKafka
- Connecting Filebeat to CKafka
- Multi-AZ Deployment
- Production and Consumption
- Log Access
- Replacing Supportive Route (Old)
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- DataHub APIs
- ACL APIs
- Topic APIs
- BatchModifyGroupOffsets
- BatchModifyTopicAttributes
- CreateConsumer
- CreateDatahubTopic
- CreatePartition
- CreateTopic
- CreateTopicIpWhiteList
- DeleteTopic
- DeleteTopicIpWhiteList
- DescribeDatahubTopic
- DescribeTopic
- DescribeTopicAttributes
- DescribeTopicDetail
- DescribeTopicProduceConnection
- DescribeTopicSubscribeGroup
- FetchMessageByOffset
- FetchMessageListByOffset
- ModifyDatahubTopic
- ModifyTopicAttributes
- DescribeTopicSyncReplica
- Instance APIs
- Route APIs
- Other APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- SDK Documentation
- General References
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement (New Version)
- Contact Us
- Glossary
As an extension of Spark Core, Spark Streaming is used for high-throughput and fault-tolerant processing of continuous data. Currently supported external input sources include Kafka, Flume, HDFS/S3, Kinesis, Twitter, and TCP socket.


Spark Streaming abstracts continuous data into a Discretized Stream (DStream), which consists of a series of continuous resilient distributed datasets (RDDs). Each RDD contains data generated at a certain time interval. Processing DStream with functions is actually processing these RDDs.
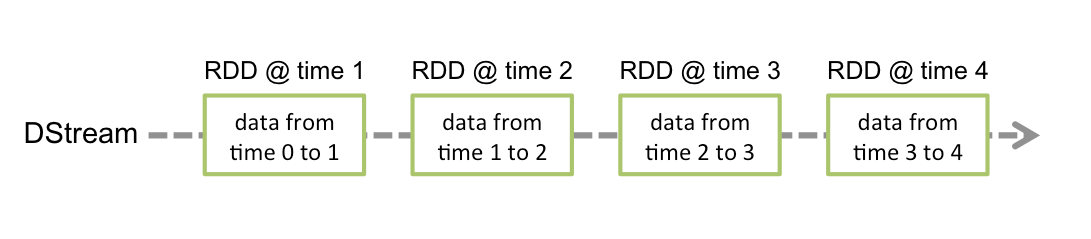

When Spark Streaming is used as data input for Kafka, the following stable and experimental Kafka versions are supported:
Kafka Version | spark-streaming-kafka-0.8 | spark-streaming-kafka-0.10 |
Broker Version | 0.8.2.1 or later | 0.10.0 or later |
API Maturity | Deprecated | Stable |
Language Support | Scala, Java, and Python | Scala and Java |
Receiver DStream | Yes | No |
Direct DStream | Yes | Yes |
SSL / TLS Support | No | Yes |
Offset Commit API | No | Yes |
Dynamic Topic Subscription | No | Yes |
Currently, CKafka is compatible with version above 0.9. The Kafka dependency of v0.10.2.1 is used in this practice scenario.
In addition, Spark Streaming in EMR also supports direct connection to CKafka. For more information, see Connecting Spark Streaming to CKafka.
Directions
Step 1. Get the CKafka instance access address
1. Log in to the CKafka console.
2. Select Instance List on the left sidebar and click the ID of the target instance to enter its basic information page.
3. On the instance's basic information page, get the instance access address in the Access Mode module, which is the
bootstrap-server required by production and consumption.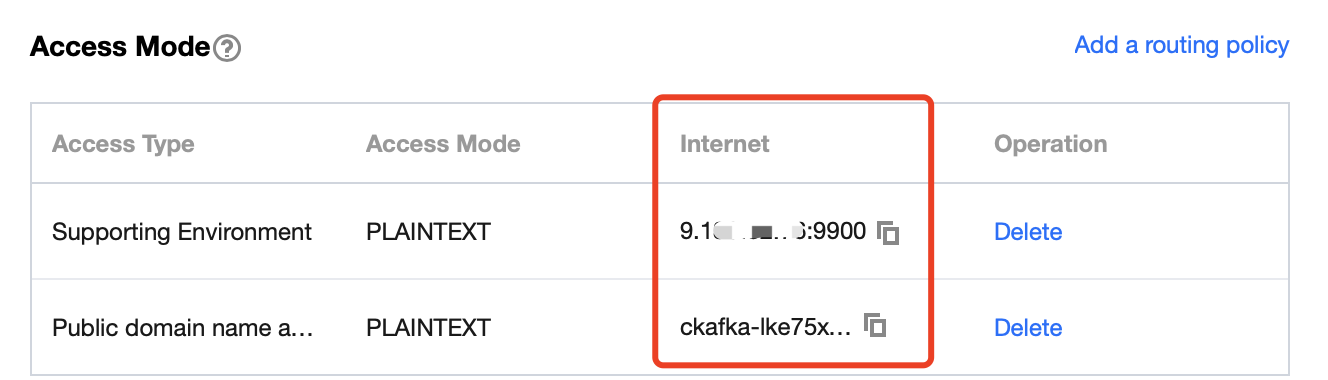

Step 2. Create a topic
1. On the instance's basic information page, select the Topic Management tab at the top.
2. On the topic management page, click Create to create a topic named
test. This topic is used as an example below to describe how to produce and consume messages.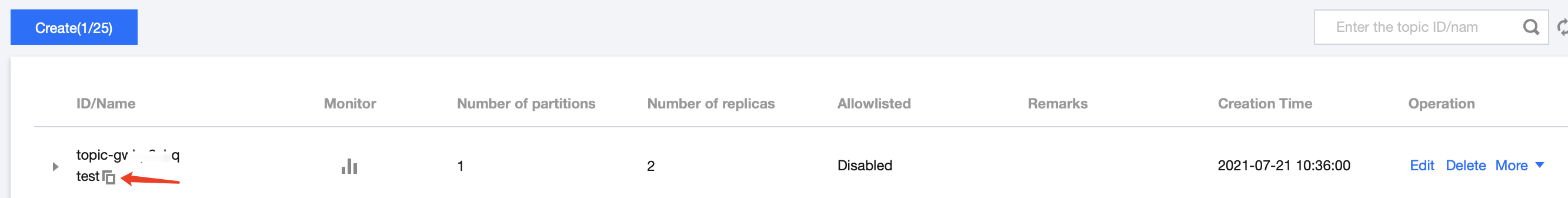

Step 3. Prepare the CVM environment
CentOS 6.8
Package | Version |
sbt | 0.13.16 |
Hadoop | 2.7.3 |
Spark | 2.1.0 |
Protobuf | 2.5.0 |
SSH | Installed on CentOS by default |
Java | 1.8 |
For specific installation steps, see [Configuring environment](#Configuring environment).
Step 4. Connect to CKafka
The Kafka dependency of v0.10.2.1 is used here.
1. Add dependencies to
build.sbt:name := "Producer Example"version := "1.0"scalaVersion := "2.11.8"libraryDependencies += "org.apache.kafka" % "kafka-clients" % "0.10.2.1"
2. Configure
producer_example.scala:import java.util.Propertiesimport org.apache.kafka.clients.producer._object ProducerExample extends App {val props = new Properties()props.put("bootstrap.servers", "172.16.16.12:9092") // Private IP and port in the instance informationprops.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer")props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer")val producer = new KafkaProducer[String, String](props)val TOPIC="test" // Specify the topic to produce tofor(i<- 1 to 50){val record = new ProducerRecord(TOPIC, "key", s"hello $i") // Produce a message whose `key` is "key" and `value` is "hello i"producer.send(record)}val record = new ProducerRecord(TOPIC, "key", "the end "+new java.util.Date)producer.send(record)producer.close() // Disconnect at the end}
DirectStream
1. Add de
pe
ndencies to build.sbt:name := "Consumer Example"version := "1.0"scalaVersion := "2.11.8"libraryDependencies += "org.apache.spark" %% "spark-core" % "2.1.0"libraryDependencies += "org.apache.spark" %% "spark-streaming" % "2.1.0"libraryDependencies += "org.apache.spark" %% "spark-streaming-kafka-0-10" % "2.1.0"
2. Configure
DirectStream_example.scala:import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecordimport org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializerimport org.apache.kafka.common.TopicPartitionimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010._import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.LocationStrategies.PreferConsistentimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.ConsumerStrategies.Subscribeimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.KafkaUtilsimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.OffsetRangeimport org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}import org.apache.spark.SparkConfimport org.apache.spark.SparkContextimport collection.JavaConversions._import Array._object Kafka {def main(args: Array[String]) {val kafkaParams = Map[String, Object]("bootstrap.servers" -> "172.16.16.12:9092","key.deserializer" -> classOf[StringDeserializer],"value.deserializer" -> classOf[StringDeserializer],"group.id" -> "spark_stream_test1","auto.offset.reset" -> "earliest","enable.auto.commit" -> "false")val sparkConf = new SparkConf()sparkConf.setMaster("local")sparkConf.setAppName("Kafka")val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(5))val topics = Array("spark_test")val offsets : Map[TopicPartition, Long] = Map()for (i <- 0 until 3){val tp = new TopicPartition("spark_test", i)offsets.updated(tp , 0L)}val stream = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String](ssc,PreferConsistent,Subscribe[String, String](topics, kafkaParams))println("directStream")stream.foreachRDD{ rdd=>// Output the obtained messagerdd.foreach{iter =>val i = iter.valueprintln(s"${i}")}// Get the offsetval offsetRanges = rdd.asInstanceOf[HasOffsetRanges].offsetRangesrdd.foreachPartition { iter =>val o: OffsetRange = offsetRanges(TaskContext.get.partitionId)println(s"${o.topic} ${o.partition} ${o.fromOffset} ${o.untilOffset}")}}// Start the computationssc.start()ssc.awaitTermination()}}
RDD
1. Configure
build.sbt in the way as detailed here.2. Configure
RDD_example:import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecordimport org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializerimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010._import org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.LocationStrategies.PreferConsistentimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.ConsumerStrategies.Subscribeimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.KafkaUtilsimport org.apache.spark.streaming.kafka010.OffsetRangeimport org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}import org.apache.spark.SparkConfimport org.apache.spark.SparkContextimport collection.JavaConversions._import Array._object Kafka {def main(args: Array[String]) {val kafkaParams = Map[String, Object]("bootstrap.servers" -> "172.16.16.12:9092","key.deserializer" -> classOf[StringDeserializer],"value.deserializer" -> classOf[StringDeserializer],"group.id" -> "spark_stream","auto.offset.reset" -> "earliest","enable.auto.commit" -> (false: java.lang.Boolean))val sc = new SparkContext("local", "Kafka", new SparkConf())val java_kafkaParams : java.util.Map[String, Object] = kafkaParams// Pull messages in the corresponding offset range from the partition in order. The request will be blocked if no messages can be pulled, until the specified waiting time elapses or the number of produced new messages reaches the number for messages to be pulledval offsetRanges = Array[OffsetRange](OffsetRange("spark_test", 0, 0, 5),OffsetRange("spark_test", 1, 0, 5),OffsetRange("spark_test", 2, 0, 5))val range = KafkaUtils.createRDD[String, String](sc,java_kafkaParams,offsetRanges,PreferConsistent)range.foreach(rdd=>println(rdd.value))sc.stop()}}
Configuring environment[](id:Configuring environment)
Installing sbt
1. Download the sbt package from sbt's official website.
2. After decompression, create an
sbt_run.sh script with the following content in the sbt directory and add executable permissions:#!/bin/bashSBT_OPTS="-Xms512M -Xmx1536M -Xss1M -XX:+CMSClassUnloadingEnabled -XX:MaxPermSize=256M"java $SBT_OPTS -jar `dirname $0`/bin/sbt-launch.jar "$@"
chmod u+x ./sbt_run.sh
3. Run the following command:
./sbt-run.sh sbt-version
The display of sbt version indicates a successful installation.
Installing Protobuf
1. Download an appropriate version of Protobuf.
2. Decompress and enter the directory.
./configuremake && make install
You should install gcc-g++ in advance, and the root permission may be required during installation.
3. Log in again and enter the following on the command line:
protoc --version
4. The display of Protobuf version indicates a successful installation.
Installing Hadoop
1. Download the required version at Hadoop's official website.
2. Add a Hadoop user.
useradd -m hadoop -s /bin/bash
3. Grant admin permissions.
visudo
4. Add the following in a new line under
root ALL=(ALL) ALL:hadoop ALL=(ALL) ALLSave and exit.
5. Use Hadoop for operations.
su hadoop
6. Configure SSH password-free login.
cd ~/.ssh/ # If there is no such directory, run `ssh localhost` firstssh-keygen -t rsa # There will be prompts. Simply press Entercat id_rsa.pub >> authorized_keys # Add authorizationchmod 600 ./authorized_keys # Modify file permission
7. Install Java.
sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel
8. Configure
${JAVA_HOME}.vim /etc/profile
Add the following at the end:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.121-0.b13.el6_8.x86_64/jreexport PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME
Modify the corresponding path based on the installation information.
9. Decompress Hadoop and enter the directory.
./bin/hadoop version
The display of version information indicates a successful installation.
10. Configure the pseudo-distributed mode (so that you can build different forms of clusters as needed).
vim /etc/profile
Add the following at the end:
export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoopexport PATH=$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$PATH
Modify the corresponding path based on the installation information.
11. Modify
/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml.<configuration><property><name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name><value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp</value><description>Abase for other temporary directories.</description></property><property><name>fs.defaultFS</name><value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value></property></configuration>
12. Modify
/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml.<configuration><property><name>dfs.replication</name><value>1</value></property><property><name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name><value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp/dfs/name</value></property><property><name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name><value>file:/usr/local/hadoop/tmp/dfs/data</value></property></configuration>
13. Change
JAVA_HOME in /etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh to the Java path.export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.121-0.b13.el6_8.x86_64/jre
14. Format the NameNode.
./bin/hdfs namenode -format
The display of
Exitting with status 0 indicates a success.15. Start Hadoop.
./sbin/start-dfs.sh
NameNode, DataNode, and SecondaryNameNode processes will exist upon successful startup.Installing Spark
As Hadoop has already been installed, select
Pre-build with user-provided Apache Hadoop here.Note:
This example also uses the
hadoop user for operations.1. Decompress and enter the directory.
2. Modify the configuration file.
cp ./conf/spark-env.sh.template ./conf/spark-env.shvim ./conf/spark-env.sh
Add the following in the first line:
export SPARK_DIST_CLASSPATH=$(/usr/local/hadoop/bin/hadoop classpath)
Modify the path based on the Hadoop installation information.
3. Run the example.
bin/run-example SparkPi
The display of an approximate value of
π output by the program indicates a successful installation.
 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?