快速搭建 IPv4 私有网络
最后更新时间:2024-01-24 17:22:28
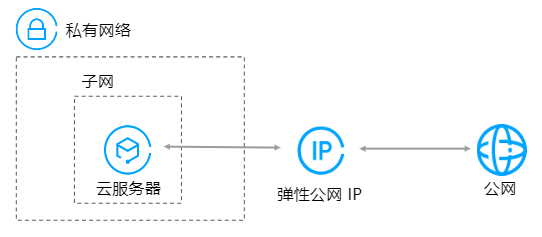
本教程将帮助您快速搭建一个具有 IPv4 CIDR 的私有网络(VPC)。
操作场景
帮助您快速搭建一个具有 IPv4 CIDR 的私有网络(VPC),提供从新建私有网络和子网,到云服务器的购买并绑定一个弹性公网 IP(EIP),并最终实现公网访问的全程指导。

前提条件
操作步骤
步骤一:创建私有网络与子网
说明:
1. 登录 私有网络控制台。
2. 在顶部选择私有网络所属的地域后,单击新建 。
3. 在新建 VPC 弹窗中,根据如下信息配置私有网络信息和初始子网,然后单击确定。
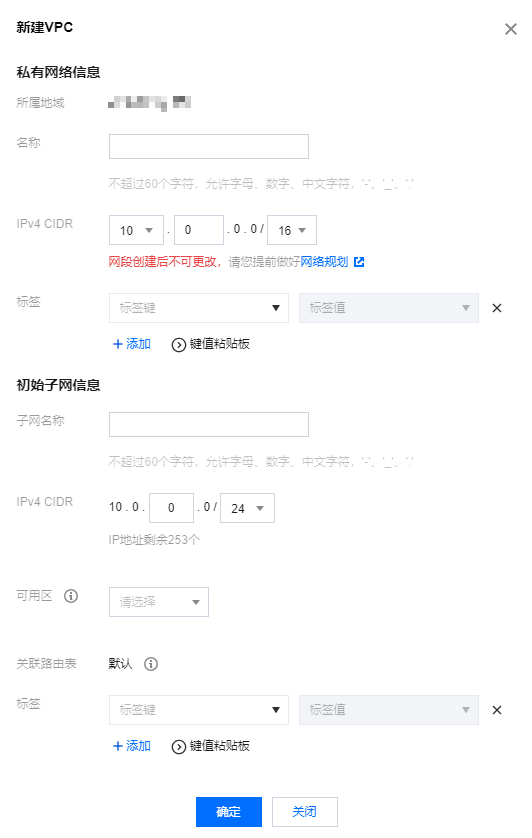
私有网络信息
名称:私有网络名称。
IPv4 CIDR:您可选择如下任意一个网段作为私有网络网段,如10.0.0.0/16。
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255(掩码范围需在12 - 28之间)
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255(掩码范围需在12 - 28之间)
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (掩码范围需在16 - 28之间)
标签:您可按需添加标签,帮助您更好地管理子用户、协作者的资源权限。
初始子网信息
IPv4 CIDR:
您可选择在私有网络网段范围内或与私有网络的网段相同的网段,如私有网络网段为 10.0.0.0/16,则您可选择10.0.0.0/16-10.0.0.248/29之间的网段作为子网网段。
如果子网所属私有网络与其他私有网络或 IDC 有通信需求,请避免子网网段与对端网段重叠,网段重叠则无法内网互通。
可用区:选择子网的可用区。同一私有网络下可有不同可用区的子网,同一私有网络下不同可用区的子网默认内网互通。
标签:您可按需添加标签,帮助您更好地管理子用户、协作者的资源权限。
步骤二:购买云服务器
1. 登录 云服务器控制台,在已创建的私有网络中创建一个云服务器实例。
2. 单击列表页左上方的新建,进入 云服务器购买页。
3. 在自定义配置页面,配置云服务器实例,完成后单击立即购买。本操作中云服务器的网络配置如下:
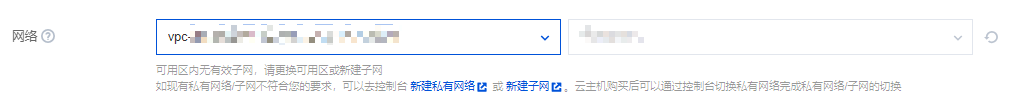
网络:选择已创建的私有网络和子网。
公网 IP:不勾选


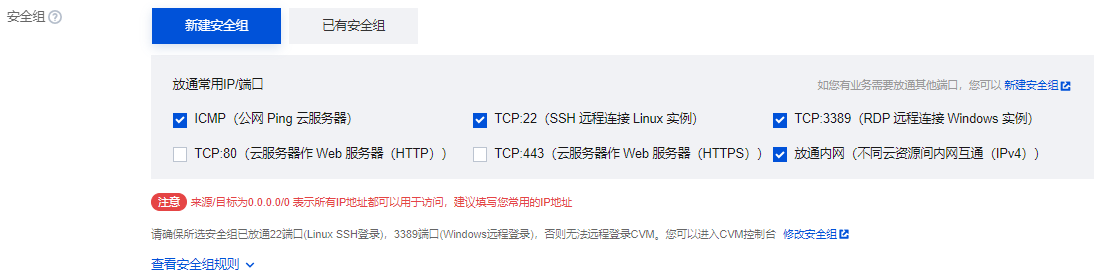
安全组:选择新建安全组,配置建议请参见 配置安全组。
步骤三:申请 EIP 并绑定云服务器
申请弹性公网 IP(即 EIP,可以独立购买和持有的 IP 资源),并将 EIP 绑定到云服务器实例,以实现公网访问。
1. 登录 EIP 控制台。
2. 在 EIP 管理页面,选择已创建的云服务器所在地域,单击申请。
3. 在弹出的 “申请 EIP” 窗口中,配置相关参数,然后单击确定,完成 EIP 的申请。
4. 在 EIP 管理页面,找到已申请的 EIP,单击更多 > 绑定。
5. 在弹出的“绑定资源”窗口中,选择CVM 实例为绑定资源类型,再选择已创建的云服务器,单击确定。
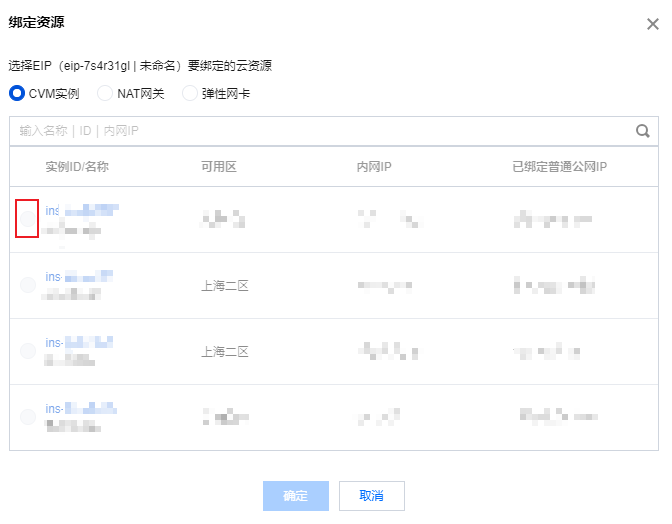
6. 在弹出的提示框中,单击确定,即可完成与云服务器的绑定。
步骤四:测试公网连通性
完成如下操作,测试云服务器实例的公网连通性。
说明:
1. 登录已绑定 EIP 的云服务器实例,具体操作请参见 登录及远程连接。
2. 执行
ping 其它公网地址 ,如 ping www.qq.com 测试公网连通性。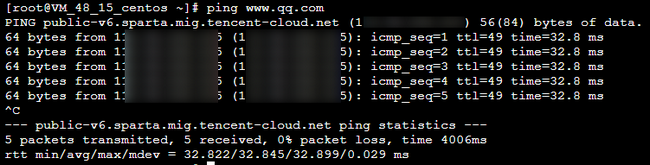
文档反馈

