- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- EMR on CVM Operation Guide
- Planning Cluster
- Configuring Cluster
- Managing Cluster
- Instance Information
- Node Specification Management
- Checking and Updating Public IP
- Cluster Scale-Out
- Cluster Scale-in
- Auto Scaling
- Repairing Disks
- Graceful Scale-In
- Disk Update Check
- Scaling up Cloud Disks
- Changing Configurations
- Automatic Replacement
- Exporting Software Configuration
- Cluster Scripts
- Cluster Termination
- Operation Logs
- Task Center
- Managing Service
- Managing Users
- Adding Components
- Restarting Service
- Starting/Stopping Services
- WebUI Access
- Resetting WebUI Password
- Software WebUI Entry
- Operation Guide for Access to WebUI over Private Network
- Role Management
- Client Management
- Configuration Management
- YARN Resource Scheduling
- HBase RIT Fixing
- Component Port Information
- Service Operation
- HBase Table-Level Monitoring
- Component Health Status
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Cluster Overview
- Node Status
- Service Status
- Cluster Event
- Log
- Application Analysis
- Cluster Inspection
- Monitoring Metrics
- Node Monitoring Metrics
- HDFS Monitoring Metrics
- YARN Monitoring Metrics
- ZooKeeper Monitoring Metrics
- HBase Monitoring Metrics
- Hive Monitoring Metrics
- Spark Monitoring Metrics
- Presto Monitoring Metrics
- Trino Monitoring Metrics
- ClickHouse Monitoring Metrics
- Druid Monitoring Metrics
- Kudu Monitoring Metrics
- Alluxio Monitoring Metrics
- PrestoSQL Monitoring Metrics
- Impala Monitoring Metrics
- Ranger Monitoring Metrics
- COSRanger Monitoring Metrics
- Doris Monitoring Metrics
- Kylin Monitoring Metrics
- Zeppelin Monitoring Metrics
- Oozie Monitoring Metrics
- Storm Monitoring Metrics
- Livy Monitoring Metrics
- Kyuubi Monitoring Metrics
- StarRocks Monitoring Metrics
- Kafka Monitoring Metrics
- Alarm Configurations
- Alarm Records
- Container-Based EMR
- EMR Development Guide
- Hadoop Development Guide
- HDFS Common Operations
- HDFS Federation Management Development Guide
- HDFS Federation Management
- Submitting MapReduce Tasks
- Automatically Adding Task Nodes Without Assigning ApplicationMasters
- YARN Task Queue Management
- Practices on YARN Label Scheduling
- Hadoop Best Practices
- Using API to Analyze Data in HDFS and COS
- Dumping YARN Job Logs to COS
- Spark Development Guide
- Hbase Development Guide
- Phoenix on Hbase Development Guide
- Hive Development Guide
- Presto Development Guide
- Sqoop Development Guide
- Hue Development Guide
- Oozie Development Guide
- Flume Development Guide
- Kerberos Development Guide
- Knox Development Guide
- Alluxio Development Guide
- Kylin Development Guide
- Livy Development Guide
- Kyuubi Development Guide
- Zeppelin Development Guide
- Hudi Development Guide
- Superset Development Guide
- Impala Development Guide
- ClickHouse Development Guide
- Druid Development Guide
- TensorFlow Development Guide
- Jupyter Development Guide
- Kudu Development Guide
- Ranger Development Guide
- Doris Development Guide
- Kafka Development Guide
- Iceberg Development Guide
- StarRocks Development Guide
- Flink Development Guide
- RSS Development Guide
- Hadoop Development Guide
- Best Practices
- API Documentation
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement
- Contact Us
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- EMR on CVM Operation Guide
- Planning Cluster
- Configuring Cluster
- Managing Cluster
- Instance Information
- Node Specification Management
- Checking and Updating Public IP
- Cluster Scale-Out
- Cluster Scale-in
- Auto Scaling
- Repairing Disks
- Graceful Scale-In
- Disk Update Check
- Scaling up Cloud Disks
- Changing Configurations
- Automatic Replacement
- Exporting Software Configuration
- Cluster Scripts
- Cluster Termination
- Operation Logs
- Task Center
- Managing Service
- Managing Users
- Adding Components
- Restarting Service
- Starting/Stopping Services
- WebUI Access
- Resetting WebUI Password
- Software WebUI Entry
- Operation Guide for Access to WebUI over Private Network
- Role Management
- Client Management
- Configuration Management
- YARN Resource Scheduling
- HBase RIT Fixing
- Component Port Information
- Service Operation
- HBase Table-Level Monitoring
- Component Health Status
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Cluster Overview
- Node Status
- Service Status
- Cluster Event
- Log
- Application Analysis
- Cluster Inspection
- Monitoring Metrics
- Node Monitoring Metrics
- HDFS Monitoring Metrics
- YARN Monitoring Metrics
- ZooKeeper Monitoring Metrics
- HBase Monitoring Metrics
- Hive Monitoring Metrics
- Spark Monitoring Metrics
- Presto Monitoring Metrics
- Trino Monitoring Metrics
- ClickHouse Monitoring Metrics
- Druid Monitoring Metrics
- Kudu Monitoring Metrics
- Alluxio Monitoring Metrics
- PrestoSQL Monitoring Metrics
- Impala Monitoring Metrics
- Ranger Monitoring Metrics
- COSRanger Monitoring Metrics
- Doris Monitoring Metrics
- Kylin Monitoring Metrics
- Zeppelin Monitoring Metrics
- Oozie Monitoring Metrics
- Storm Monitoring Metrics
- Livy Monitoring Metrics
- Kyuubi Monitoring Metrics
- StarRocks Monitoring Metrics
- Kafka Monitoring Metrics
- Alarm Configurations
- Alarm Records
- Container-Based EMR
- EMR Development Guide
- Hadoop Development Guide
- HDFS Common Operations
- HDFS Federation Management Development Guide
- HDFS Federation Management
- Submitting MapReduce Tasks
- Automatically Adding Task Nodes Without Assigning ApplicationMasters
- YARN Task Queue Management
- Practices on YARN Label Scheduling
- Hadoop Best Practices
- Using API to Analyze Data in HDFS and COS
- Dumping YARN Job Logs to COS
- Spark Development Guide
- Hbase Development Guide
- Phoenix on Hbase Development Guide
- Hive Development Guide
- Presto Development Guide
- Sqoop Development Guide
- Hue Development Guide
- Oozie Development Guide
- Flume Development Guide
- Kerberos Development Guide
- Knox Development Guide
- Alluxio Development Guide
- Kylin Development Guide
- Livy Development Guide
- Kyuubi Development Guide
- Zeppelin Development Guide
- Hudi Development Guide
- Superset Development Guide
- Impala Development Guide
- ClickHouse Development Guide
- Druid Development Guide
- TensorFlow Development Guide
- Jupyter Development Guide
- Kudu Development Guide
- Ranger Development Guide
- Doris Development Guide
- Kafka Development Guide
- Iceberg Development Guide
- StarRocks Development Guide
- Flink Development Guide
- RSS Development Guide
- Hadoop Development Guide
- Best Practices
- API Documentation
- FAQs
- Service Level Agreement
- Contact Us
Apache Hive introduced Live Long and Process (LLAP) on v2.0 and made great optimization on v2.1, which shows that Hive has evolved to memory computing. Currently, as tested by Hortonworks, LLAP working together with Tez is 25 times faster than Hive v1.x. LLAP provides a hybrid execution model consisting of a long-lived daemon which replaces direct interactions with the HDFS DataNode, and a tightly integrated DAG-based framework. For example, features such as caching, pre-fetching, certain query processing, and access control are moved into the daemon. Small/Short queries are largely processed by this daemon directly, while any heavy lifting will be performed in standard YARN containers.
Hive LLAP Structure Diagram
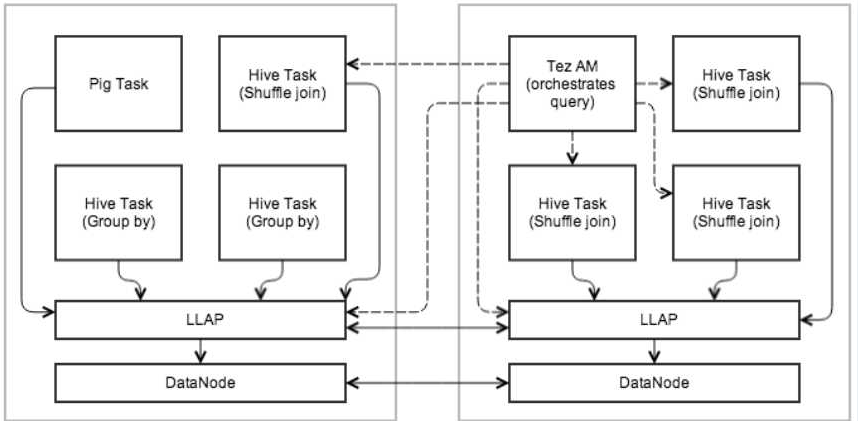
- Persistent daemon
To facilitate caching and JIT optimization, and to eliminate most of the startup costs, a daemon runs on the worker nodes in the cluster. It handles I/O, caching, and query fragment execution. - Execution engine
LLAP works within existing, process-based Hive execution to preserve the scalability and versatility of Hive. It does not replace the existing execution model but rather enhances it. - Query fragment execution
LLAP nodes execute "query fragments" such as filters, projections, data transformations, partial aggregates, sorting, bucketing, and hashjoins/semi-joins. - I/O
The daemon off-loads I/O and transformation from compressed format to separate threads. The data is passed in to the execution as it becomes ready, so the previous batches can be processed while the next ones are being prepared. The data is passed in to the execution in a simple RLE-encoded columnar format that is ready for vectorized processing; this is also the caching format, with the intent to minimize replication between I/O, cache, and execution. - Caching
The daemon caches metadata for input files, as well as the data. The metadata and index information can be cached even for data that is not currently cached.
Installing Hive LLAP
Enter the EMR purchase page.
Select
EMR-V2.3.0as the product version.Select TEZ 0.9.2 in the Optional Component list, and Hive LLAP will be automatically installed in the
/usr/local/service/sliderdirectory.Using Hive LLAP
- Modify
/usr/local/service/slider/conf/slider-client.xmlby adding the following configuration items:<property> <name>hadoop.registry.zk.quorum</name> <value>zk_ip:zk_port</value> </property>
The IP in the value is the master node IP for a non-high-availability cluster. For a high-availability cluster, run the following command to view the ZooKeeper component IP:
cat /usr/local/service/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml |grep 2181
- Modify
hive-site.xml(delivered in the console).<property> <name>hive.execution.engine</name> <value>tez</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.llap.execution.mode</name> <value>all</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.execution.mode</name> <value>llap</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.llap.daemon.service.hosts</name> <value>@llap_service</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>zk_ip:zk_port</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.llap.daemon.memory.per.instance.mb</name> <value>4000</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.llap.daemon.num.executors</name> <value>2</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.tez.default.queues</name> <value>root.default</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.tez.initialize.default.sessions</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hive.server2.tez.sessions.per.default.queue</name> <value>2</value> </property>
Note:Here, you need to enter the actual ZooKeeper address and port in the
hive.zookeeper.quorumconfiguration item.
- Restart all Hive services.
- Generate the LLAP start file and command.
hive --service llap --name llap_service --instances 2 --size 2g --loglevel INFO --cache 1g --executors 2 --iothreads 5 --slider-am-container-mb 1024 --args " -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+ResizeTLAB -XX:+UseNUMA -XX:-ResizePLAB"
Here, LLAP execution and configuration files will be generated in the current directory. Run the run.sh script as prompted as shown below: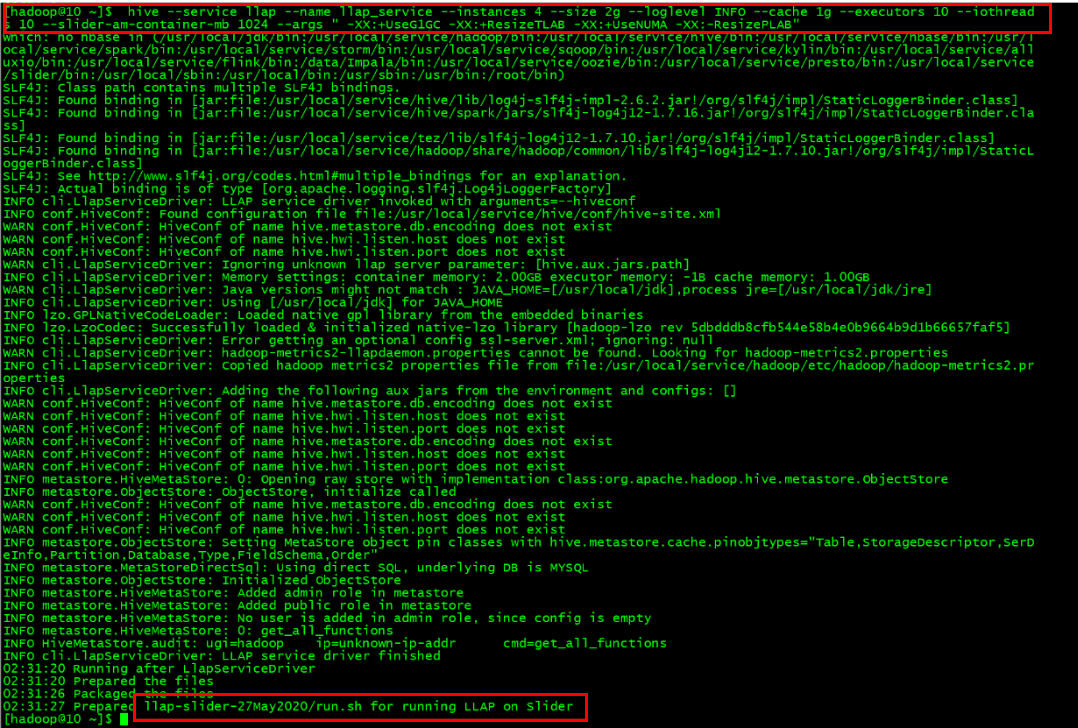
llap-slider-27May2020/run.sh
Run the run.sh file above, and a resident application will be submitted in YARN. Wait for several minutes, and you can see the application in yarn-ui.
Note:LLAP initialization will take several minutes. Wait until it ends before performing data operations.
- Verify LLAP.
Enter Hive CLI:create table t1(id int, name string); insert into t1 values('1','test1'),('2', 'test2'); select id, count(1) from t1 group by id;
Expected result: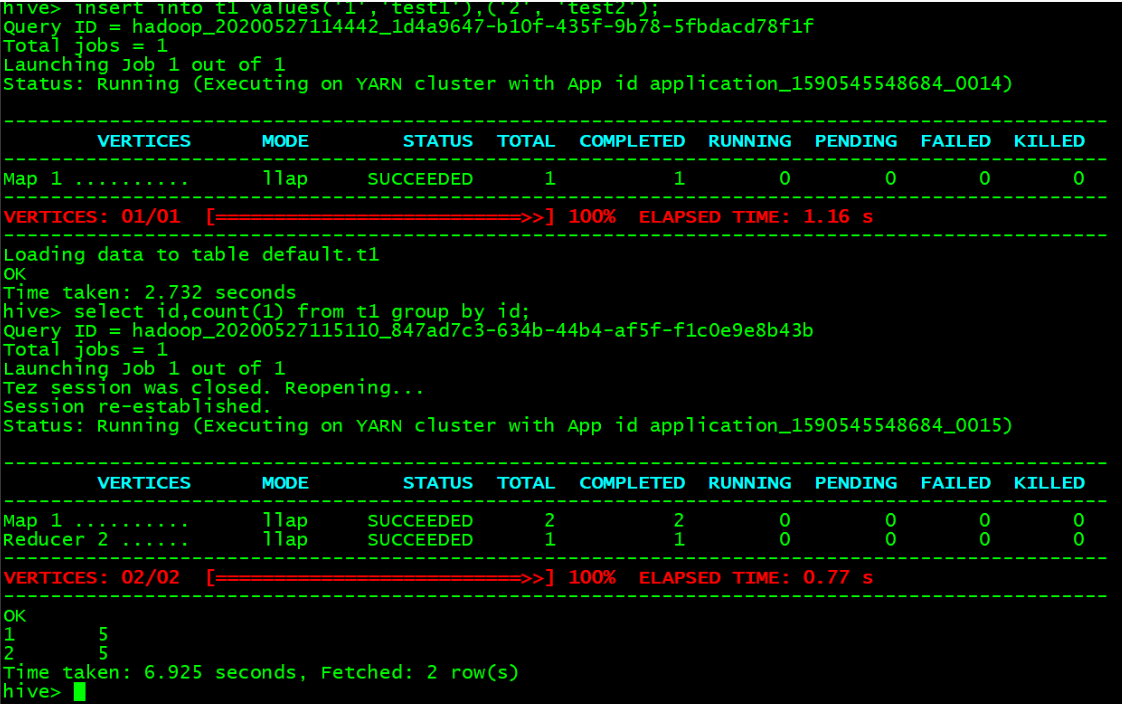

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?