- Release Notes and Announcements
- Release Notes
- Announcements
- Commercial Billing for Database Proxy
- TencentDB for MySQL Audit Upgrade
- Added Authentication APIs
- API Authentication Upgrade
- TencentDB for MySQL API 2.0 Discontinuation
- Monitoring Module Upgrade in Shanghai Region
- Monitoring Metric Optimization
- Network Architecture Upgrade
- Change of APIs for Querying the Specifications of Purchasable Database Instances
- Replacement of Certain Old Database Proxy APIs
- Added Advanced Monitoring Metrics
- Change of Calculation Formula for Memory Utilization
- Monitoring Module Upgrade and Optimization in Guangzhou and Shanghai Regions
- Monitoring Module Upgrade
- Parameter Template and Instance Purchase Process Optimization
- Binlog Will Take up Disk Space
- User Tutorial
- Product Introduction
- Tencent Kernel TXSQL
- Overview
- Kernel Version Release Notes
- Functionality Features
- Performance Features
- Security Features
- Stability Features
- TXRocks Engine
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Database Audit
- Operation Guide
- Use Limits
- Operation Overview
- Instance Management and Maintenance
- Instance Upgrade
- CPU Elastic Expansion
- Read-Only/Disaster Recovery Instances
- Database Proxy
- Account Management
- Database Management Center (DMC)
- Parameter Configuration
- Network and Security
- Backup and Rollback
- Data Migration
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Operation Logs
- Tag
- Best Practices
- Usage Specifications of TencentDB for MySQL
- Configuring Automatic Application Reconnection
- Impact of Modifying MySQL Source Instance Parameters
- Limits on Automatic Conversion from MyISAM to InnoDB
- Creating VPCs for TencentDB for MySQL
- Enhancing Business Load Capacity with TencentDB for MySQL
- Setting up 2-Region-3-DC Disaster Recovery Architecture
- Improving TencentDB for MySQL Performance with Read/Write Separation
- Migrating Data from InnoDB to RocksDB with DTS
- Building LAMP Stack for Web Application
- Building Drupal Website
- Building All-Scenario High-Availability Architecture
- Calling MySQL APIs in Python
- White Paper
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Instance APIs
- StopCpuExpand
- StartCpuExpand
- DescribeCpuExpandStrategy
- AddTimeWindow
- BalanceRoGroupLoad
- CloseWanService
- CreateDBInstance
- CreateDBInstanceHour
- CreateRoInstanceIp
- DeleteTimeWindow
- DescribeCdbZoneConfig
- DescribeDBFeatures
- DescribeDBInstanceCharset
- DescribeDBInstanceConfig
- DescribeDBInstanceGTID
- DescribeDBInstanceInfo
- DescribeDBInstanceRebootTime
- DescribeDBSwitchRecords
- DescribeRoGroups
- DescribeRoMinScale
- DescribeTagsOfInstanceIds
- DescribeTimeWindow
- InitDBInstances
- IsolateDBInstance
- ModifyAutoRenewFlag
- ModifyDBInstanceName
- ModifyDBInstanceProject
- ModifyDBInstanceVipVport
- ModifyInstanceTag
- ModifyRoGroupInfo
- ModifyTimeWindow
- OfflineIsolatedInstances
- OpenDBInstanceEncryption
- OpenDBInstanceGTID
- OpenWanService
- ReleaseIsolatedDBInstances
- RenewDBInstance
- RestartDBInstances
- StartReplication
- StopReplication
- SwitchDBInstanceMasterSlave
- SwitchDrInstanceToMaster
- SwitchForUpgrade
- UpgradeDBInstance
- UpgradeDBInstanceEngineVersion
- DescribeDBInstances
- DescribeDBZoneConfig
- CreateDeployGroup
- DeleteDeployGroups
- DescribeDeployGroupList
- ModifyNameOrDescByDpId
- Data Import APIs
- Database Proxy APIs
- AdjustCdbProxy
- AdjustCdbProxyAddress
- CloseCdbProxyAddress
- CreateCdbProxy
- CreateCdbProxyAddress
- DescribeCdbProxyInfo
- DescribeProxySupportParam
- ModifyCdbProxyAddressDesc
- ModifyCdbProxyAddressVipAndVPort
- ModifyCdbProxyParam
- CloseCDBProxy
- DescribeProxyCustomConf
- ReloadBalanceProxyNode
- SwitchCDBProxy
- UpgradeCDBProxyVersion
- Database Audit APIs
- Security APIs
- Task APIs
- Account APIs
- Backup APIs
- DescribeBackupDecryptionKey
- CreateBackup
- DeleteBackup
- DescribeBackupDownloadRestriction
- DescribeBackupEncryptionStatus
- DescribeBackupOverview
- DescribeBackupSummaries
- DescribeBinlogBackupOverview
- DescribeDataBackupOverview
- DescribeLocalBinlogConfig
- DescribeRemoteBackupConfig
- DescribeSlowLogs
- ModifyBackupDownloadRestriction
- ModifyBackupEncryptionStatus
- ModifyLocalBinlogConfig
- ModifyRemoteBackupConfig
- DescribeBackups
- DescribeBackupConfig
- ModifyBackupConfig
- DescribeBinlogs
- Rollback APIs
- Parameter APIs
- Database APIs
- Monitoring APIs
- Log-related API
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Service Agreement
- Reference
- Glossary
- Contact Us
- Preset Plugin List
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Release Notes
- Announcements
- Commercial Billing for Database Proxy
- TencentDB for MySQL Audit Upgrade
- Added Authentication APIs
- API Authentication Upgrade
- TencentDB for MySQL API 2.0 Discontinuation
- Monitoring Module Upgrade in Shanghai Region
- Monitoring Metric Optimization
- Network Architecture Upgrade
- Change of APIs for Querying the Specifications of Purchasable Database Instances
- Replacement of Certain Old Database Proxy APIs
- Added Advanced Monitoring Metrics
- Change of Calculation Formula for Memory Utilization
- Monitoring Module Upgrade and Optimization in Guangzhou and Shanghai Regions
- Monitoring Module Upgrade
- Parameter Template and Instance Purchase Process Optimization
- Binlog Will Take up Disk Space
- User Tutorial
- Product Introduction
- Tencent Kernel TXSQL
- Overview
- Kernel Version Release Notes
- Functionality Features
- Performance Features
- Security Features
- Stability Features
- TXRocks Engine
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Database Audit
- Operation Guide
- Use Limits
- Operation Overview
- Instance Management and Maintenance
- Instance Upgrade
- CPU Elastic Expansion
- Read-Only/Disaster Recovery Instances
- Database Proxy
- Account Management
- Database Management Center (DMC)
- Parameter Configuration
- Network and Security
- Backup and Rollback
- Data Migration
- Monitoring and Alarms
- Operation Logs
- Tag
- Best Practices
- Usage Specifications of TencentDB for MySQL
- Configuring Automatic Application Reconnection
- Impact of Modifying MySQL Source Instance Parameters
- Limits on Automatic Conversion from MyISAM to InnoDB
- Creating VPCs for TencentDB for MySQL
- Enhancing Business Load Capacity with TencentDB for MySQL
- Setting up 2-Region-3-DC Disaster Recovery Architecture
- Improving TencentDB for MySQL Performance with Read/Write Separation
- Migrating Data from InnoDB to RocksDB with DTS
- Building LAMP Stack for Web Application
- Building Drupal Website
- Building All-Scenario High-Availability Architecture
- Calling MySQL APIs in Python
- White Paper
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Instance APIs
- StopCpuExpand
- StartCpuExpand
- DescribeCpuExpandStrategy
- AddTimeWindow
- BalanceRoGroupLoad
- CloseWanService
- CreateDBInstance
- CreateDBInstanceHour
- CreateRoInstanceIp
- DeleteTimeWindow
- DescribeCdbZoneConfig
- DescribeDBFeatures
- DescribeDBInstanceCharset
- DescribeDBInstanceConfig
- DescribeDBInstanceGTID
- DescribeDBInstanceInfo
- DescribeDBInstanceRebootTime
- DescribeDBSwitchRecords
- DescribeRoGroups
- DescribeRoMinScale
- DescribeTagsOfInstanceIds
- DescribeTimeWindow
- InitDBInstances
- IsolateDBInstance
- ModifyAutoRenewFlag
- ModifyDBInstanceName
- ModifyDBInstanceProject
- ModifyDBInstanceVipVport
- ModifyInstanceTag
- ModifyRoGroupInfo
- ModifyTimeWindow
- OfflineIsolatedInstances
- OpenDBInstanceEncryption
- OpenDBInstanceGTID
- OpenWanService
- ReleaseIsolatedDBInstances
- RenewDBInstance
- RestartDBInstances
- StartReplication
- StopReplication
- SwitchDBInstanceMasterSlave
- SwitchDrInstanceToMaster
- SwitchForUpgrade
- UpgradeDBInstance
- UpgradeDBInstanceEngineVersion
- DescribeDBInstances
- DescribeDBZoneConfig
- CreateDeployGroup
- DeleteDeployGroups
- DescribeDeployGroupList
- ModifyNameOrDescByDpId
- Data Import APIs
- Database Proxy APIs
- AdjustCdbProxy
- AdjustCdbProxyAddress
- CloseCdbProxyAddress
- CreateCdbProxy
- CreateCdbProxyAddress
- DescribeCdbProxyInfo
- DescribeProxySupportParam
- ModifyCdbProxyAddressDesc
- ModifyCdbProxyAddressVipAndVPort
- ModifyCdbProxyParam
- CloseCDBProxy
- DescribeProxyCustomConf
- ReloadBalanceProxyNode
- SwitchCDBProxy
- UpgradeCDBProxyVersion
- Database Audit APIs
- Security APIs
- Task APIs
- Account APIs
- Backup APIs
- DescribeBackupDecryptionKey
- CreateBackup
- DeleteBackup
- DescribeBackupDownloadRestriction
- DescribeBackupEncryptionStatus
- DescribeBackupOverview
- DescribeBackupSummaries
- DescribeBinlogBackupOverview
- DescribeDataBackupOverview
- DescribeLocalBinlogConfig
- DescribeRemoteBackupConfig
- DescribeSlowLogs
- ModifyBackupDownloadRestriction
- ModifyBackupEncryptionStatus
- ModifyLocalBinlogConfig
- ModifyRemoteBackupConfig
- DescribeBackups
- DescribeBackupConfig
- ModifyBackupConfig
- DescribeBinlogs
- Rollback APIs
- Parameter APIs
- Database APIs
- Monitoring APIs
- Log-related API
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- Service Agreement
- Reference
- Glossary
- Contact Us
- Preset Plugin List
This document provides examples about how to grant a user permissions to view and use specific resources in the TencentDB console by using a CAM policy.
Full access policy for TencentDB
To grant a user permissions to create and manage TencentDB instances, you can implement the QcloudCDBFullAccess policy for the user.
Log in to the CAM console, select Policies on the left sidebar, and search QcloudCDBFullAccess in the upper right corner.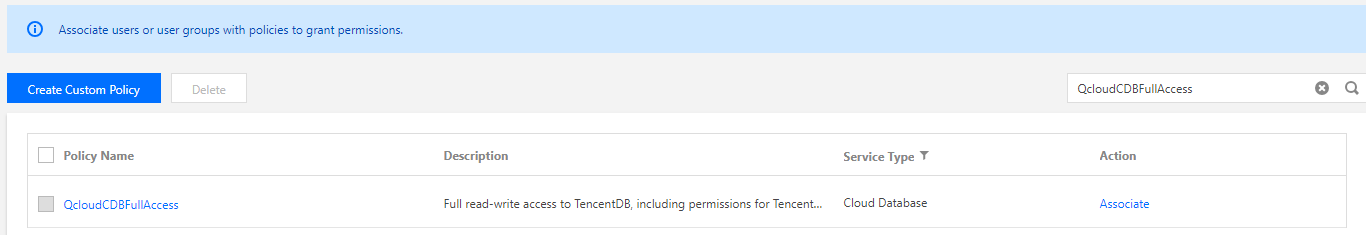
The policy syntax is as follows:
{
"statement": [
{
"action": [
"cdb:*"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
},
{
"action": [
"vpc:*"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
},
{
"action": [
"cvm:*"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "qcs::cvm:::sg/*"
},
{
"action": [
"cos:*"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
},
{
"action": [
"monitor:*",
"cam:ListUsersForGroup",
"cam:ListGroups",
"cam:GetGroup"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
},
{
"action": [
"kms:CreateKey",
"kms:GenerateDataKey",
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:ListKey"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
}
],
"version": "2.0"
}
The above policy achieves its goal by allowing the user to separately authorize the use of TencentDB, VPC, security group, COS, KMS, and all resources available in the monitor with the CAM policy.
Read-only permission policy for TencentDB
To grant a user permission to view TencentDB instances but not create, delete, or modify them, you can implement the policy named QcloudCDBInnerReadOnlyAccess for the user.
Note:We recommend that you configure the read-only policy for TencentDB.
Log in to the CAM console, select Policies on the left sidebar, click Service Type in the policy list and select TencentDB for MySQL in the drop-down list, and then you can see this policy in the results.
The policy syntax is as follows:
{
"statement": [
{
"action": [
"cdb:Describe*"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
}
],
"version": "2.0"
}
Read-only permission policy for TencentDB-related resources
To grant a user permissions to view TencentDB instances and related resources (VPC, security groups, COS, and Cloud Monitor) but not create, delete, or modify them, you can implement the QcloudCDBReadOnlyAccess policy for the user.
Log in to the CAM console, select Policies on the left sidebar, click Service Type in the policy list and select TencentDB for MySQL in the drop-down list, and then you can see this policy in the results.
The policy syntax is as follows:
{
"statement": [
{
"action": [
"cdb:Describe*"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
},
{
"action": [
"monitor:Describe*",
"monitor:Get*",
"cam:ListUsersForGroup",
"cam:ListGroups",
"cam:GetGroup"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
}
],
"version": "2.0"
}
The above policy achieves its goal by allowing the user to separately authorize the use of the following operations with the CAM policy.
- All operations in TencentDB that begin with "Describe".
- All operations in VPC that begin with "Describe", "Inquiry", or "Get".
- All operations in security groups that begin with "DescribeSecurityGroup".
- All operations in COS that begin with "List", "Get", and "Head" as well as the "OptionsObject" operation.
- All operations in the monitor.
Policy for granting a user permissions to use APIs not at the resource level
To grant a user permissions to use only APIs not at the resource level, you can implement the QcloudCDBProjectToUser policy for the user.
Log in to the CAM console, select Policies on the left sidebar, click Service Type in the policy list and select TencentDB for MySQL in the drop-down list, and then you can see this policy in the results.
The policy syntax is as follows:
{
"version": "2.0",
"statement": [
{
"action": [
"cdb:BalanceRoGroupLoad",
"cdb:CancelBatchOperation",
"cdb:CreateBatchJobFiles",
"cdb:CreateDBInstance",
"cdb:CreateDBInstanceHour",
"cdb:CreateMonitorTemplate",
"cdb:CreateParamTemplate",
"cdb:DeleteBatchJobFiles",
"cdb:DeleteMonitorTemplate",
"cdb:DeleteParamTemplate",
"cdb:DescribeBatchJobFileContent",
"cdb:DescribeBatchJobFiles",
"cdb:DescribeBatchJobInfo",
"cdb:DescribeProjectSecurityGroups",
"cdb:DescribeDefaultParams",
"cdb:DescribeMonitorTemplate",
"cdb:DescribeParamTemplateInfo",
"cdb:DescribeParamTemplates",
"cdb:DescribeRequestResult",
"cdb:DescribeRoGroupInfo",
"cdb:DescribeRoMinScale",
"cdb:DescribeTasks",
"cdb:DescribeUploadedFiles",
"cdb:ModifyMonitorTemplate",
"cdb:ModifyParamTemplate",
"cdb:ModifyRoGroupInfo",
"cdb:ModifyRoGroupVipVport",
"cdb:StopDBImportJob",
"cdb:UploadSqlFiles"
],
"effect": "allow",
"resource": "*"
}
]
}
Policy for granting a user permissions to manipulate a specific TencentDB instance
To grant a user the permission to manipulate a specific TencentDB instance, associate the following policy with the user. For example, the policy below allows the user to manipulate the TencentDB instance "dcdb-xxx" in Guangzhou region.
{
"version": "2.0",
"statement": [
{
"action": "cdb:*",
"resource": "qcs::cdb:ap-guangzhou::instanceId/cdb-xxx",
"effect": "allow"
}
]
}
Policy for granting a user permissions to manipulate TencentDB instances in batches
To grant a user permissions to manipulate TencentDB instances in batches, associate the following policy with the user. For example, the policy below allows the user to manipulate the TencentDB instances "cdb-xxx" and "cdb-yyy" in Guangzhou region and "cdb-zzz" in Beijing region.
{
"version": "2.0",
"statement": [
{
"action": "cdb:*",
"resource": ["qcs::cdb:ap-guangzhou::instanceId/cdb-xxx", "qcs::cdb:ap-guangzhou::instanceId/cdb-yyy", "qcs::cdb:ap-beijing::instanceId/cdb-zzz"],
"effect": "allow"
}
]
}
Policy for granting a user permissions to manipulate TencentDB instances in a specific region
To grant a user permissions to manipulate TencentDB instances in a specific region, associate the following policy with the user. This policy authorizes the user to operate TencentDB instances in Guangzhou region.
{
"version": "2.0",
"statement": [
{
"action": "cdb:*",
"resource": "qcs::cdb:ap-guangzhou::*",
"effect": "allow"
}
]
}
Custom policy
If preset policies cannot meet your requirements, you can create custom policies as shown below. If permissions are granted by resources, for a TencentDB API operation that does not support authorization at the resource level, you can still authorize a user to perform it, but you must specify * as the resource element in the policy statement.
The syntax of custom policies is as follows:
{
"version": "2.0",
"statement": [
{
"action": [
"Action"
],
"resource": "Resource",
"effect": "Effect"
}
]
}
- Replace "Action" with the operation to be allowed or denied.
- Replace "Resource" with the resources that you want to authorize the user to manipulate.
- Replace "Effect" with "Allow" or "Deny".

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?