Webhook Overview
Last updated:2025-08-15 15:16:34
Overview
To give you refined control over app features, Chat provides you with powerful webhooks free of charge. The webhooks use persistent connection mode by default. A webhook means that the Chat backend sends a request to the app backend server before or after an event occurs. This allows the app backend to synchronize data if necessary or intervene in the subsequent event processing. For more information about the webhooks currently supported by Chat, see the Webhook Command List.
A webhook is sent to the app backend server using an HTTP/HTTPS request, and the app backend server must process the Chat webhook request and provide a response as soon as possible. Take the Before Group Message Is Sent webhook event as an example. Before the message is sent, the Chat backend sends a webhook request to the app backend server and determines whether the message should be sent based on the webhook result. Based on the webhook, the app can synchronize the message. The following figure shows the webhook process.
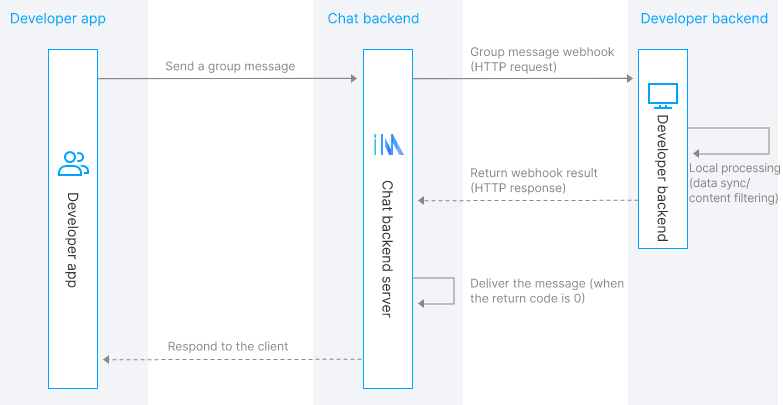
Webhook Classification
Webhooks can be classified into four types according to their functions:
Online status webhooks
Relationship chain webhooks
One-to-one message webhooks
Group webhooks
Webhooks can be classified into two types by process:
Webhook before an action occurs: the purpose of this type of webhook is to allow the app backend to intervene in the processing logic of the event. Chat will determine the subsequent processing flow based on the return code of the webhook. For example, the webhook before a group message is sent is this type of webhook.
Webhook after an action occurs: the purpose of this type of webhook is to allow the app backend to implement essential data synchronization. Chat ignores the return codes of such webhooks. For example, the webhook after a member quits a group is this type of webhook.
Webhook Protocol
Webhooks are based on HTTP/HTTPS protocols. The app backend must provide a webhook URL to Chat, and Chat uses a POST request to initiate a webhook request to the app backend. When initiating a webhook request, Chat adds the following parameters at the end of the URL provided by the app backend:
Parameter | Description |
SdkAppid | App ID assigned by Chat |
CallbackCommand | Webhook command word |
contenttype | Optional. The value is generally a JSON string. |
ClientIP | IP address of the client |
OptPlatform | Client platform. Depending on the platform type, the following values are available: RESTAPI (requests are sent using RESTful APIs) and Web (requests are sent using Web SDKs),Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, iPad, and Unknown (requests are sent using an unknown device). |
Note:
"IOS" (all in uppercase) is used in the
State.StateChange webhook, while "iOS" (the first letter is in lowercase) is used in other webhooks. Please perform compatibility processing during use.The specific webhook content is included in the HTTP request packet. For details, see the following webhook examples.
Webhook Examples
Webhook request example:
POST /?SdkAppid=888888&CallbackCommand=Group.CallbackAfterNewMemberJoin&contenttype=json&ClientIP=$ClientIP&OptPlatform=$OptPlatform HTTP/1.1Host: www.example.comContent-Length: 337{"CallbackCommand": "Group.CallbackAfterNewMemberJoin","GroupId": "@TGS#2J4SZEAEL","Type": "Public","JoinType": "Apply","Operator_Account": "leckie","NewMemberList": [{"Member_Account": "jared"},{"Member_Account": "tommy"}]}
Webhook response example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKServer: nginx/1.7.10Date: Fri, 09 Oct 2015 02:59:55 GMTContent-Length: 75{"ActionStatus": "OK","ErrorInfo": "","ErrorCode":0}
Webhook Timeout Period and Retry
The timeout period for Chat webhooks to the app backend is two seconds.
Before event occurrence, webhooks are not retried. After event occurrence, webhooks are not retried by default, and you can configure whether to retry the webhooks when they time out.
To ensure a high webhook success rate, third-party apps need to process webhooks quickly. For example, the app can send a webhook response and then process the specific business logic.
Handling Policy for Webhook Timeouts Before Event Occurrence
If a webhook times out before event occurrence, the default policy is to deliver the message.
You can also configure the handling policy for webhook timeouts before event occurrence in the console. For example, when a webhook timeout occurs before a group message is sent, you can specify whether to deliver the message.
Security Considerations
Chat supports both HTTP and HTTPS webhooks. For HTTPS webhooks, you need to configure a certificate issued by CA in the WebServer of the app backend.
Related security issues are as follows:
1. HTTP transmits data in plain text, and data confidentiality cannot be guaranteed. Therefore, HTTPS is recommended.
2. It's impossible to determine whether a webhook request really comes from Chat.
For request source security, we provide the Webhook Authentication solution:
1. Configure the webhook URL and enable webhook in the console.
2. During webhook URL configuration, enable authentication and configure the authentication token. Then, the signature (
Sign) and signing timestamp (RequestTime) will be added to the webhook request URL. The signature algorithm is Sign=sha256(TokenRequestTime).3. The app backend authenticates the webhook request. It uses SHA256 to calculate and verify the signature based on the local authentication token and the signing timestamp (
RequestTime) in the webhook URL.Signature algorithm sample:Token=xxxxyyyyRequestTime=1669872112Sign=sha256(xxxxyyyy1669872112)=17773bc39a671d7b9aa835458704d2a6db81360a5940292b587d6d760d484061Webhook URL=URL&Sign=17773bc39a671d7b9aa835458704d2a6db81360a5940292b587d6d760d484061&RequestTime=1669872112
Common Reasons for Webhook Failures
If a webhook failure occurs, check whether the configured webhook service has a problem according to the following checklist:
Webhook Failure Symptom | Possible Reason |
Access to the webhook URL times out | 1. Chat cannot complete DNS resolution. In this case, check whether the domain name is valid on the public network. For example, if the webhook host is http://notexist.com, Chat cannot complete DNS resolution because this domain name does not exist. 2. Chat cannot access the IP address configured in the webhook URL. In this case, check whether this IP address is accessible from the public network. For example, if the webhook host is http://10.0.0.1, Chat cannot access this IP address because the domain name is a private IP address of the app. 3. The failure occurs due to the firewall policy of the app webhook service. In this case, check the firewall configuration. For example, a webhook failure occurs if the app webhook server denies all requests arriving at port 80. |
Access denied by the webhook service | Chat can access the host, but a connection is not established. In this case, check whether the WebServer has started properly. For example, a webhook failure will occur when the WebServer of the app webhook server has not started or when the port configuration is incorrect. |
HTTPS certificate configuration error of the webhook service | This can occur when the webhook type is HTTPS (or HTTPS mutual authentication). Chat can access the app webhook server, but determines that the certificate configured on the app WebServer is invalid. In this case, check that the HTTPS certificate is properly configured. |
HTTPS mutual authentication configuration error of the webhook service | This can occur when the webhook type is HTTPS mutual authentication. Chat verifies that the certificate configured on the app webhook server is valid, but the app webhook server fails to verify the Chat certificate. Note: The HTTPS two-way authentication method has been taken offline, and we recommend you to use the more convenient Webhook Authentication method. |
The HTTP return code of the webhook service is not 200 | The webhook request is successful, but the HTTP return code in the response packet is not 200. |
The webhook response packet could not be parsed | The webhook response packet is not in JSON format. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

