- Release Notes and Announcements
- Release Notes
- Announcements
- qGPU Service Adjustment
- Version Upgrade of Master Add-On of TKE Managed Cluster
- Upgrading tke-monitor-agent
- Discontinuing TKE API 2.0
- Instructions on Cluster Resource Quota Adjustment
- Discontinuing Kubernetes v1.14 and Earlier Versions
- Deactivation of Scaling Group Feature
- Notice on TPS Discontinuation on May 16, 2022 at 10:00 (UTC +8)
- Basic Monitoring Architecture Upgrade
- Starting Charging on Managed Clusters
- Instructions on Stopping Delivering the Kubeconfig File to Nodes
- Security Vulnerability Fix Description
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Quick Start
- TKE General Cluster Guide
- TKE General Cluster Overview
- Purchase a TKE General Cluster
- High-risk Operations of Container Service
- Deploying Containerized Applications in the Cloud
- Kubernetes API Operation Guide
- Open Source Components
- Permission Management
- Cluster Management
- Cluster Overview
- Cluster Hosting Modes Introduction
- Cluster Lifecycle
- Creating a Cluster
- Deleting a Cluster
- Cluster Scaling
- Changing the Cluster Operating System
- Connecting to a Cluster
- Upgrading a Cluster
- Enabling IPVS for a Cluster
- Enabling GPU Scheduling for a Cluster
- Custom Kubernetes Component Launch Parameters
- Using KMS for Kubernetes Data Source Encryption
- Images
- Worker node introduction
- Normal Node Management
- Native Node Management
- Overview
- Purchasing Native Nodes
- Lifecycle of a Native Node
- Native Node Parameters
- Creating Native Nodes
- Deleting Native Nodes
- Self-Heal Rules
- Declarative Operation Practice
- Native Node Scaling
- In-place Pod Configuration Adjustment
- Enabling SSH Key Login for a Native Node
- Management Parameters
- Enabling Public Network Access for a Native Node
- Supernode management
- Registered Node Management
- GPU Share
- Kubernetes Object Management
- Overview
- Namespace
- Workload
- Deployment Management
- StatefulSet Management
- DaemonSet Management
- Job Management
- CronJob Management
- Setting the Resource Limit of Workload
- Setting the Scheduling Rule for a Workload
- Setting the Health Check for a Workload
- Setting the Run Command and Parameter for a Workload
- Using a Container Image in a TCR Enterprise Instance to Create a Workload
- Auto Scaling
- Configuration
- Register node management
- Service Management
- Ingress Management
- Storage Management
- Application and Add-On Feature Management Description
- Add-On Management
- Add-on Overview
- Add-On Lifecycle Management
- CBS-CSI Description
- UserGroupAccessControl
- COS-CSI
- CFS-CSI
- P2P
- OOMGuard
- TCR Introduction
- TCR Hosts Updater
- DNSAutoscaler
- NodeProblemDetectorPlus Add-on
- NodeLocalDNSCache
- Network Policy
- DynamicScheduler
- DeScheduler
- Nginx-ingress
- HPC
- Description of tke-monitor-agent
- GPU-Manager Add-on
- CFSTURBO-CSI
- tke-log-agent
- Helm Application
- Application Market
- Network Management
- Container Network Overview
- GlobalRouter Mode
- VPC-CNI Mode
- VPC-CNI Mode
- Multiple Pods with Shared ENI Mode
- Pods with Exclusive ENI Mode
- Static IP Address Mode Instructions
- Non-static IP Address Mode Instructions
- Interconnection Between VPC-CNI and Other Cloud Resources/IDC Resources
- Security Group of VPC-CNI Mode
- Instructions on Binding an EIP to a Pod
- VPC-CNI Component Description
- Limits on the Number of Pods in VPC-CNI Mode
- Cilium-Overlay Mode
- OPS Center
- Log Management
- Backup Center
- Cloud Native Monitoring
- Remote Terminals
- TKE Serverless Cluster Guide
- TKE Edge Cluster Guide
- TKE Registered Cluster Guide
- TKE Container Instance Guide
- Cloud Native Service Guide
- Best Practices
- Cluster
- Cluster Migration
- Serverless Cluster
- Edge Cluster
- Security
- Service Deployment
- Hybrid Cloud
- Network
- DNS
- Using Network Policy for Network Access Control
- Deploying NGINX Ingress on TKE
- Nginx Ingress High-Concurrency Practices
- Nginx Ingress Best Practices
- Limiting the bandwidth on pods in TKE
- Directly connecting TKE to the CLB of pods based on the ENI
- Use CLB-Pod Direct Connection on TKE
- Obtaining the Real Client Source IP in TKE
- Using Traefik Ingress in TKE
- Release
- Logs
- Monitoring
- OPS
- Removing and Re-adding Nodes from and to Cluster
- Using Ansible to Batch Operate TKE Nodes
- Using Cluster Audit for Troubleshooting
- Renewing a TKE Ingress Certificate
- Using cert-manager to Issue Free Certificates
- Using cert-manager to Issue Free Certificate for DNSPod Domain Name
- Using the TKE NPDPlus Plug-In to Enhance the Self-Healing Capability of Nodes
- Using kubecm to Manage Multiple Clusters kubeconfig
- Quick Troubleshooting Using TKE Audit and Event Services
- Customizing RBAC Authorization in TKE
- Clearing De-registered Tencent Cloud Account Resources
- Terraform
- DevOps
- Auto Scaling
- Cluster Auto Scaling Practices
- Using tke-autoscaling-placeholder to Implement Auto Scaling in Seconds
- Installing metrics-server on TKE
- Using Custom Metrics for Auto Scaling in TKE
- Utilizing HPA to Auto Scale Businesses on TKE
- Using VPA to Realize Pod Scaling up and Scaling down in TKE
- Adjusting HPA Scaling Sensitivity Based on Different Business Scenarios
- Storage
- Containerization
- Microservice
- Cost Management
- Fault Handling
- Disk Full
- High Workload
- Memory Fragmentation
- Cluster DNS Troubleshooting
- Cluster kube-proxy Troubleshooting
- Cluster API Server Inaccessibility Troubleshooting
- Service and Ingress Inaccessibility Troubleshooting
- Troubleshooting for Pod Network Inaccessibility
- Pod Status Exception and Handling
- Authorizing Tencent Cloud OPS Team for Troubleshooting
- Engel Ingres appears in Connechtin Reverside
- CLB Loopback
- CLB Ingress Creation Error
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Cluster APIs
- DescribeEncryptionStatus
- DisableEncryptionProtection
- EnableEncryptionProtection
- AcquireClusterAdminRole
- CreateClusterEndpoint
- CreateClusterEndpointVip
- DeleteCluster
- DeleteClusterEndpoint
- DeleteClusterEndpointVip
- DescribeAvailableClusterVersion
- DescribeClusterAuthenticationOptions
- DescribeClusterCommonNames
- DescribeClusterEndpointStatus
- DescribeClusterEndpointVipStatus
- DescribeClusterEndpoints
- DescribeClusterKubeconfig
- DescribeClusterLevelAttribute
- DescribeClusterLevelChangeRecords
- DescribeClusterSecurity
- DescribeClusterStatus
- DescribeClusters
- DescribeEdgeAvailableExtraArgs
- DescribeEdgeClusterExtraArgs
- DescribeResourceUsage
- DisableClusterDeletionProtection
- EnableClusterDeletionProtection
- GetClusterLevelPrice
- GetUpgradeInstanceProgress
- ModifyClusterAttribute
- ModifyClusterAuthenticationOptions
- ModifyClusterEndpointSP
- UpgradeClusterInstances
- CreateCluster
- UpdateClusterVersion
- UpdateClusterKubeconfig
- DescribeBackupStorageLocations
- DeleteBackupStorageLocation
- CreateBackupStorageLocation
- Add-on APIs
- Network APIs
- Node APIs
- Node Pool APIs
- TKE Edge Cluster APIs
- DescribeTKEEdgeScript
- DescribeTKEEdgeExternalKubeconfig
- DescribeTKEEdgeClusters
- DescribeTKEEdgeClusterStatus
- DescribeTKEEdgeClusterCredential
- DescribeEdgeClusterInstances
- DescribeEdgeCVMInstances
- DescribeECMInstances
- DescribeAvailableTKEEdgeVersion
- DeleteTKEEdgeCluster
- DeleteEdgeClusterInstances
- DeleteEdgeCVMInstances
- DeleteECMInstances
- CreateTKEEdgeCluster
- CreateECMInstances
- CheckEdgeClusterCIDR
- ForwardTKEEdgeApplicationRequestV3
- UninstallEdgeLogAgent
- InstallEdgeLogAgent
- DescribeEdgeLogSwitches
- CreateEdgeLogConfig
- CreateEdgeCVMInstances
- UpdateEdgeClusterVersion
- DescribeEdgeClusterUpgradeInfo
- Cloud Native Monitoring APIs
- Virtual node APIs
- Other APIs
- Scaling group APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- API Mapping Guide
- TKE Insight
- TKE Scheduling
- FAQs
- Service Agreement
- Contact Us
- Purchase Channels
- Glossary
- User Guide(Old)
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Release Notes
- Announcements
- qGPU Service Adjustment
- Version Upgrade of Master Add-On of TKE Managed Cluster
- Upgrading tke-monitor-agent
- Discontinuing TKE API 2.0
- Instructions on Cluster Resource Quota Adjustment
- Discontinuing Kubernetes v1.14 and Earlier Versions
- Deactivation of Scaling Group Feature
- Notice on TPS Discontinuation on May 16, 2022 at 10:00 (UTC +8)
- Basic Monitoring Architecture Upgrade
- Starting Charging on Managed Clusters
- Instructions on Stopping Delivering the Kubeconfig File to Nodes
- Security Vulnerability Fix Description
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Quick Start
- TKE General Cluster Guide
- TKE General Cluster Overview
- Purchase a TKE General Cluster
- High-risk Operations of Container Service
- Deploying Containerized Applications in the Cloud
- Kubernetes API Operation Guide
- Open Source Components
- Permission Management
- Cluster Management
- Cluster Overview
- Cluster Hosting Modes Introduction
- Cluster Lifecycle
- Creating a Cluster
- Deleting a Cluster
- Cluster Scaling
- Changing the Cluster Operating System
- Connecting to a Cluster
- Upgrading a Cluster
- Enabling IPVS for a Cluster
- Enabling GPU Scheduling for a Cluster
- Custom Kubernetes Component Launch Parameters
- Using KMS for Kubernetes Data Source Encryption
- Images
- Worker node introduction
- Normal Node Management
- Native Node Management
- Overview
- Purchasing Native Nodes
- Lifecycle of a Native Node
- Native Node Parameters
- Creating Native Nodes
- Deleting Native Nodes
- Self-Heal Rules
- Declarative Operation Practice
- Native Node Scaling
- In-place Pod Configuration Adjustment
- Enabling SSH Key Login for a Native Node
- Management Parameters
- Enabling Public Network Access for a Native Node
- Supernode management
- Registered Node Management
- GPU Share
- Kubernetes Object Management
- Overview
- Namespace
- Workload
- Deployment Management
- StatefulSet Management
- DaemonSet Management
- Job Management
- CronJob Management
- Setting the Resource Limit of Workload
- Setting the Scheduling Rule for a Workload
- Setting the Health Check for a Workload
- Setting the Run Command and Parameter for a Workload
- Using a Container Image in a TCR Enterprise Instance to Create a Workload
- Auto Scaling
- Configuration
- Register node management
- Service Management
- Ingress Management
- Storage Management
- Application and Add-On Feature Management Description
- Add-On Management
- Add-on Overview
- Add-On Lifecycle Management
- CBS-CSI Description
- UserGroupAccessControl
- COS-CSI
- CFS-CSI
- P2P
- OOMGuard
- TCR Introduction
- TCR Hosts Updater
- DNSAutoscaler
- NodeProblemDetectorPlus Add-on
- NodeLocalDNSCache
- Network Policy
- DynamicScheduler
- DeScheduler
- Nginx-ingress
- HPC
- Description of tke-monitor-agent
- GPU-Manager Add-on
- CFSTURBO-CSI
- tke-log-agent
- Helm Application
- Application Market
- Network Management
- Container Network Overview
- GlobalRouter Mode
- VPC-CNI Mode
- VPC-CNI Mode
- Multiple Pods with Shared ENI Mode
- Pods with Exclusive ENI Mode
- Static IP Address Mode Instructions
- Non-static IP Address Mode Instructions
- Interconnection Between VPC-CNI and Other Cloud Resources/IDC Resources
- Security Group of VPC-CNI Mode
- Instructions on Binding an EIP to a Pod
- VPC-CNI Component Description
- Limits on the Number of Pods in VPC-CNI Mode
- Cilium-Overlay Mode
- OPS Center
- Log Management
- Backup Center
- Cloud Native Monitoring
- Remote Terminals
- TKE Serverless Cluster Guide
- TKE Edge Cluster Guide
- TKE Registered Cluster Guide
- TKE Container Instance Guide
- Cloud Native Service Guide
- Best Practices
- Cluster
- Cluster Migration
- Serverless Cluster
- Edge Cluster
- Security
- Service Deployment
- Hybrid Cloud
- Network
- DNS
- Using Network Policy for Network Access Control
- Deploying NGINX Ingress on TKE
- Nginx Ingress High-Concurrency Practices
- Nginx Ingress Best Practices
- Limiting the bandwidth on pods in TKE
- Directly connecting TKE to the CLB of pods based on the ENI
- Use CLB-Pod Direct Connection on TKE
- Obtaining the Real Client Source IP in TKE
- Using Traefik Ingress in TKE
- Release
- Logs
- Monitoring
- OPS
- Removing and Re-adding Nodes from and to Cluster
- Using Ansible to Batch Operate TKE Nodes
- Using Cluster Audit for Troubleshooting
- Renewing a TKE Ingress Certificate
- Using cert-manager to Issue Free Certificates
- Using cert-manager to Issue Free Certificate for DNSPod Domain Name
- Using the TKE NPDPlus Plug-In to Enhance the Self-Healing Capability of Nodes
- Using kubecm to Manage Multiple Clusters kubeconfig
- Quick Troubleshooting Using TKE Audit and Event Services
- Customizing RBAC Authorization in TKE
- Clearing De-registered Tencent Cloud Account Resources
- Terraform
- DevOps
- Auto Scaling
- Cluster Auto Scaling Practices
- Using tke-autoscaling-placeholder to Implement Auto Scaling in Seconds
- Installing metrics-server on TKE
- Using Custom Metrics for Auto Scaling in TKE
- Utilizing HPA to Auto Scale Businesses on TKE
- Using VPA to Realize Pod Scaling up and Scaling down in TKE
- Adjusting HPA Scaling Sensitivity Based on Different Business Scenarios
- Storage
- Containerization
- Microservice
- Cost Management
- Fault Handling
- Disk Full
- High Workload
- Memory Fragmentation
- Cluster DNS Troubleshooting
- Cluster kube-proxy Troubleshooting
- Cluster API Server Inaccessibility Troubleshooting
- Service and Ingress Inaccessibility Troubleshooting
- Troubleshooting for Pod Network Inaccessibility
- Pod Status Exception and Handling
- Authorizing Tencent Cloud OPS Team for Troubleshooting
- Engel Ingres appears in Connechtin Reverside
- CLB Loopback
- CLB Ingress Creation Error
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Cluster APIs
- DescribeEncryptionStatus
- DisableEncryptionProtection
- EnableEncryptionProtection
- AcquireClusterAdminRole
- CreateClusterEndpoint
- CreateClusterEndpointVip
- DeleteCluster
- DeleteClusterEndpoint
- DeleteClusterEndpointVip
- DescribeAvailableClusterVersion
- DescribeClusterAuthenticationOptions
- DescribeClusterCommonNames
- DescribeClusterEndpointStatus
- DescribeClusterEndpointVipStatus
- DescribeClusterEndpoints
- DescribeClusterKubeconfig
- DescribeClusterLevelAttribute
- DescribeClusterLevelChangeRecords
- DescribeClusterSecurity
- DescribeClusterStatus
- DescribeClusters
- DescribeEdgeAvailableExtraArgs
- DescribeEdgeClusterExtraArgs
- DescribeResourceUsage
- DisableClusterDeletionProtection
- EnableClusterDeletionProtection
- GetClusterLevelPrice
- GetUpgradeInstanceProgress
- ModifyClusterAttribute
- ModifyClusterAuthenticationOptions
- ModifyClusterEndpointSP
- UpgradeClusterInstances
- CreateCluster
- UpdateClusterVersion
- UpdateClusterKubeconfig
- DescribeBackupStorageLocations
- DeleteBackupStorageLocation
- CreateBackupStorageLocation
- Add-on APIs
- Network APIs
- Node APIs
- Node Pool APIs
- TKE Edge Cluster APIs
- DescribeTKEEdgeScript
- DescribeTKEEdgeExternalKubeconfig
- DescribeTKEEdgeClusters
- DescribeTKEEdgeClusterStatus
- DescribeTKEEdgeClusterCredential
- DescribeEdgeClusterInstances
- DescribeEdgeCVMInstances
- DescribeECMInstances
- DescribeAvailableTKEEdgeVersion
- DeleteTKEEdgeCluster
- DeleteEdgeClusterInstances
- DeleteEdgeCVMInstances
- DeleteECMInstances
- CreateTKEEdgeCluster
- CreateECMInstances
- CheckEdgeClusterCIDR
- ForwardTKEEdgeApplicationRequestV3
- UninstallEdgeLogAgent
- InstallEdgeLogAgent
- DescribeEdgeLogSwitches
- CreateEdgeLogConfig
- CreateEdgeCVMInstances
- UpdateEdgeClusterVersion
- DescribeEdgeClusterUpgradeInfo
- Cloud Native Monitoring APIs
- Virtual node APIs
- Other APIs
- Scaling group APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- API Mapping Guide
- TKE Insight
- TKE Scheduling
- FAQs
- Service Agreement
- Contact Us
- Purchase Channels
- Glossary
- User Guide(Old)
FAQs About Service Creation
Why must a service name be unique?
A service name is a unique identifier of a service in the current cluster. Services access each other through the service name and access port.
Can I use a third-party image instead of a Tencent Cloud or Docker Hub image when creating services?
Yes. You can log in to your CVM instance and run the docker login command to log in to the third-party image repository and pull the image.
What are the prerequisites for using public network services?
Make sure that the CVM instances in the cluster have public bandwidth; otherwise, public network services may fail to be created.
How do I configure memory and CPU limits?
For more information, see Setting the Resource Limit of Workload.
What does the "Privileged" option mean when I am creating a service?
If this option is enabled, applications in the container will have true root permission. We recommend you enable it when you need to perform higher-level system operations on applications in the container, such as building an NFS server.
Can I specify the security group for a CLB instance when creating it?
Yes. Currently, you can use the following two options to specify the security group for a CLB instance when a service uses it:
- Use an existing CLB instance. You can create a CLB instance, configure the security group, and then mount it to the service. For more information, see Using Existing CLBs.
- You can configure the security group through
TkeServiceConfigin the service. A CLB instance will use a security group according to the configuration at the time of creation. If you need to use this feature, submit a ticket for application.
Note:To avoid access failure, we recommend you not access a service in the cluster over the CLB IP.
In general, a layer-4 CLB instance will bind multiple nodes as real servers (RS). In this case, make sure that the client and RS are not on the same CVM instance; otherwise, there will be a certain probability that the packet will fail to loop back.
When a Pod accesses a CLB instance, the Pod is the source IP. When it is transferred to the private network, the CLB instance will not translate the source IP to the Node IP via SNAT. Therefore, the CLB instance cannot identify the source node of the packet. The CLB instance's loopback avoidance policy will not take effect, and the packet may be forwarded to any RS. When the packet is forwarded to the Node where the client is located, the CLB instance will be unable to receive the response, leading to access failure.
FAQs About Updating the Number of Service Containers
What should I pay attention to when I update the number of containers?
Confirm whether CPU and memory resources are sufficient. If the resources are insufficient, a container may fail to be created.
Can I set the number of containers to 0?
Yes. You can set the number of containers to 0 to release the resources while retaining service configurations.
FAQs About Service Configuration Update
Is rolling update supported?
Both rolling update and quick update are supported.
Can I switch from a public network CLB instance to a private network CLB instance?
Yes. You can switch from the public network to a VPC, from a VPC to the public network, or between different subnets of a VPC. For more information, see Overview.
Note:
- If the service is responsible for lifecycle management of the CLB instance, the CLB instance and its public network IP will be released.
- The process of switching from the public network to the private network is not instantaneous. It takes a certain amount of time to deactivate the public network CLB instance and activate the private network CLB instance. We recommend you configure a private network service resource in the cluster, conduct a test, and delete the original public network service resource after the traffic switch is completed.
FAQs About Service Deletion
Will the CLB instance auto-created by a service be terminated after I delete the service?
When a service is deleted, the CLB instance auto-created at the time of the service creation will be deleted simultaneously. If an existing CLB instance is selected at the time of service creation, the CLB instance will not be affected at all.
Is business data affected by deleting a service?
The business container will not be deleted and business data will not be affected if the service is deleted. No need to back up data in this regard.
FAQs About Service Running
How do I set the container system time to UTC+8 time?
The container uses UTC time by default. Users often encounter the problem of eight hours difference between the container system time and UTC+8 time. You can create a time zone file in dockerfile to solve this problem. For more information, see Solve the inconsistent time zone problem in the container.
What should I do when some Docker Hub images, such as Ubuntu, PHP, and BusyBox, encounter exceptions in TKE?
If no start command is set or the default start command is bash, the container will exit after start. To keep the container running, make sure that the process whose PID is 1 in the container is a resident process; otherwise, the container will exit when this process ends. For some images such as CentOS, you can create services by using /bin/bash as the running command and -c sleep 800000 as the running parameter. -c and sleep 800000 must be entered in different rows in the console.
Currently, images that cannot be started when default parameters are used include Clear Linux, ROS, Mageia, Amazon Linux, Ubuntu, Clojure, CRUX, GCC, Photon, Java, Debian, Oracle Linux, Mono, Bash, buildpack-deps, Go, Source Mage, Swift, OpenJDK, CentOS, BusyBox, Docker, Alpine, IBM Java, PHP, and Python.
What should I do if an error message "Operation not permitted" appears when a container is executing perf top -p to check the process CPU status?
When a container is executing perf top -p to check the process CPU status, an error message "Operation not permitted" appears as shown below: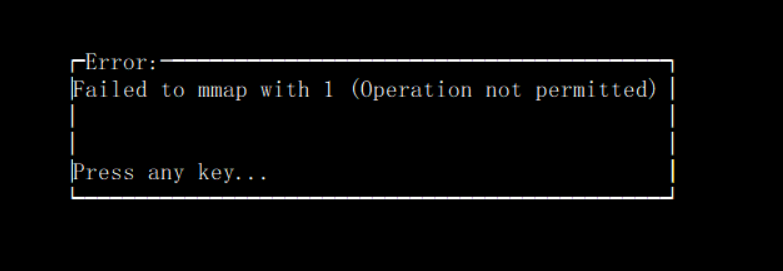
The default configuration file of Docker prevents important system calls. perf_event_open is disabled because it may leak a large amount of information on the host. If you need to call it, configure a privileged container or change the value of the Pod YAML field privileged to true. You need to assess the security risks yourself.

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?